Abstract
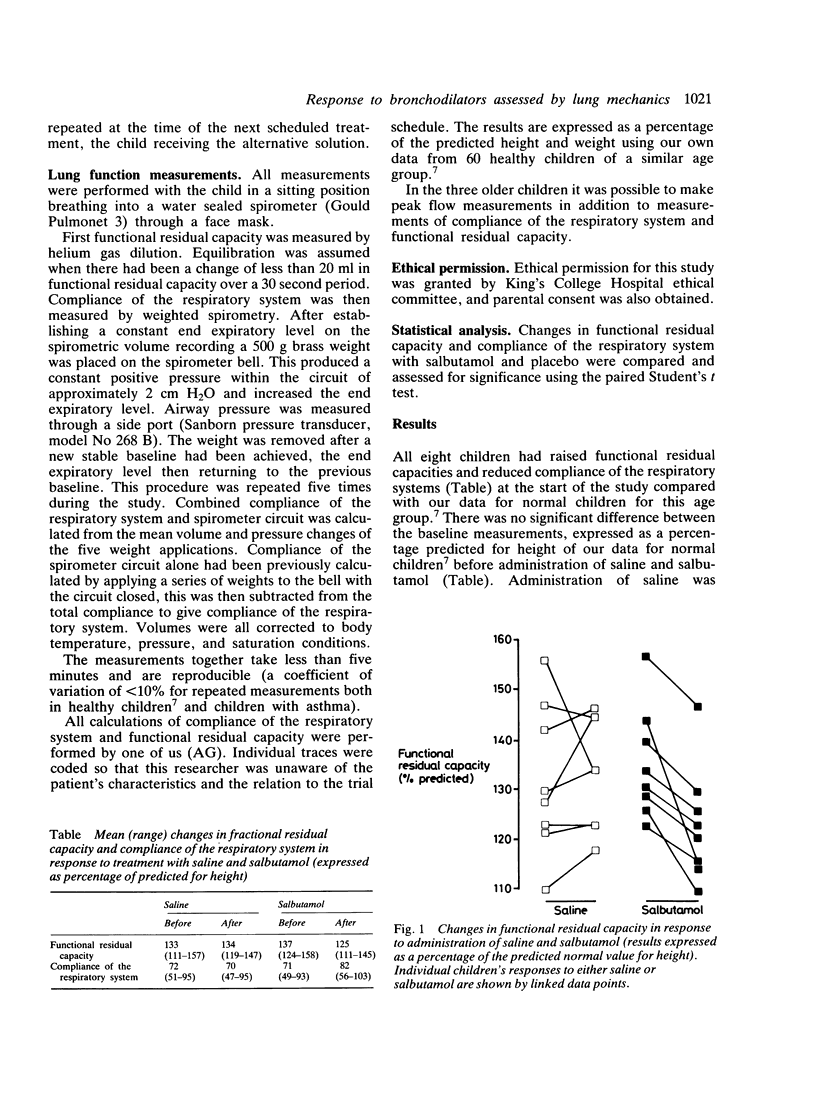
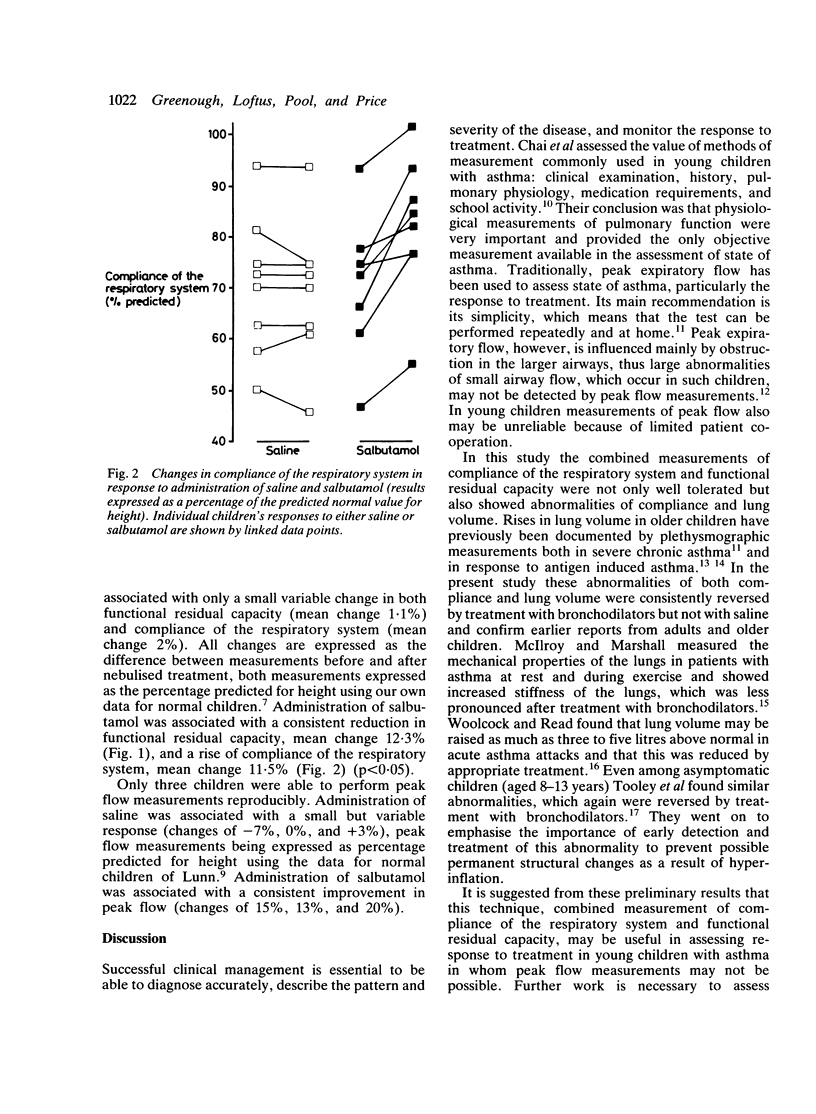
Abnormalities of compliance and functional residual capacity were shown in eight young children aged 2-8 years with asthma during an acute attack. In a randomised, placebo controlled study treatment with bronchodilator (salbutamol) was associated with a significant improvement in compliance and lessening of hyperinflation as shown by a reduction in functional residual capacity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chai H., Purcell K., Brady K., Falliers C. J. Therapeutic and investiational evaluation of asthmatic children. J Allergy. 1968 Jan;41(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(68)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogswell J. J. Forced oscillation technique for determination of resistance to breathing in children. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Apr;48(4):259–266. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.4.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groggins R. C., Lenney W., Milner A. D., Stokes G. M. Efficacy of orally administered salbutamol and theophylline in pre-schoolchildren with asthma. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Mar;55(3):204–206. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.3.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groggins R. C., Milner A. D., Stokes G. M. Bronchodilator effects of clemastine, ipratropium, bromide, and salbutamol in preschool children with asthma. Arch Dis Child. 1981 May;56(5):342–344. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.5.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenney W., Milner A. D. At what age do bronchodilator drugs work? Arch Dis Child. 1978 Jul;53(7):532–535. doi: 10.1136/adc.53.7.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL R., MCILROY M. B. The mechanical properties of the lungs in asthma. Clin Sci. 1956 May;15(2):345–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansell A., Dubrawsky C., Levison H., Bryan A. C., Langer H., Collins-Williams C., Orange R. P. Lung mechanics in antigen-induced asthma. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Sep;37(3):297–301. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.37.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J., Turner J. M., Macklem P. T., Little J. B. Significance of the relationship between lung recoil and maximum expiratory flow. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Jan;22(1):95–108. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J. L., Wesley H. M. Children with asthma: will nebulised salbutamol reduce hospital admissions? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Feb 23;290(6468):595–597. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6468.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner N., Phelan P. D. Physiological assessment of severe chronic asthma in children. Respiration. 1978;35(1):30–36. doi: 10.1159/000193856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan D. P. The prevalence and natural history of wheezing in early childhood. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1985 Apr;35(273):182–184. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOOLEY W. H., DEMUTH G., NADEL J. A. THE REVERSIBILITY OF OBSTRUCTIVE CHANGES IN SEVERE CHILDHOOD ASTHMA. J Pediatr. 1965 Mar;66:517–524. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(65)80116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. O. Significance of late reactions after bronchial challenge with house dust mite. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Dec;51(12):905–911. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.12.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock A. J., Read J. Improvement in bronchial asthma not reflected in forced expiratory volume. Lancet. 1965 Dec 25;2(7426):1323–1325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock A. J., Read J. Lung volumes in exacerbations of asthma. Am J Med. 1966 Aug;41(2):259–273. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


