Abstract
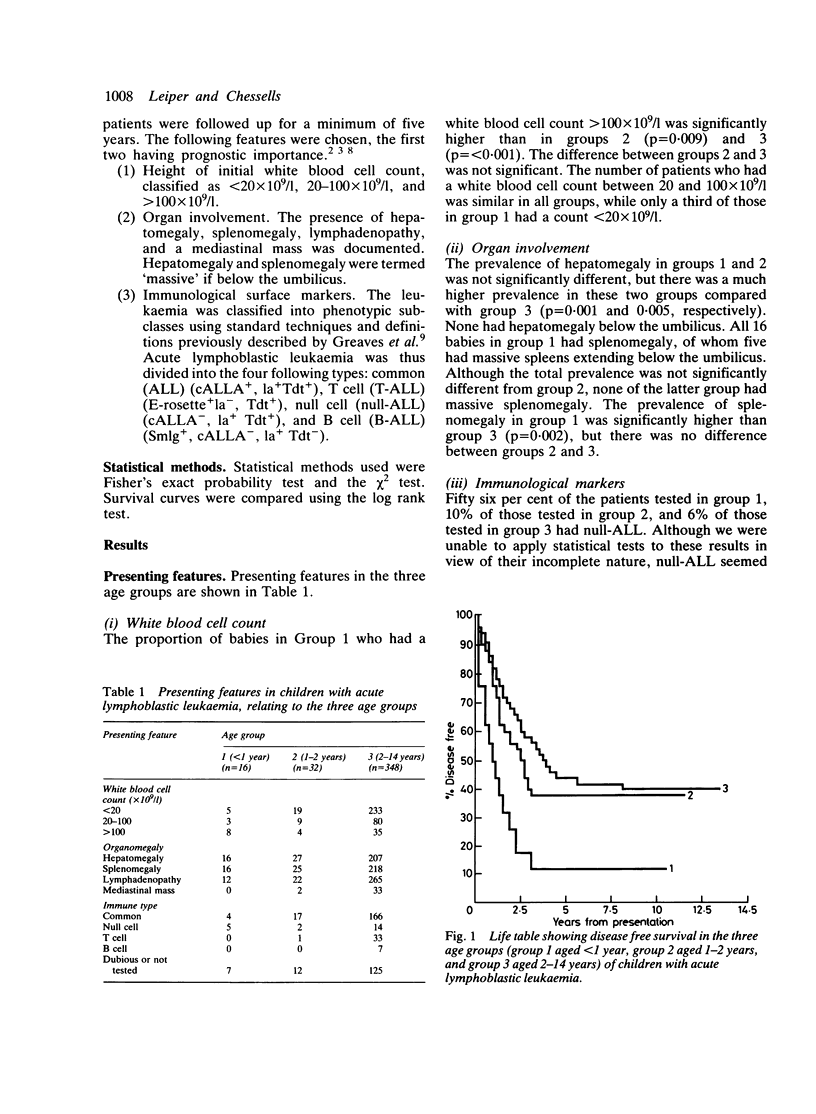
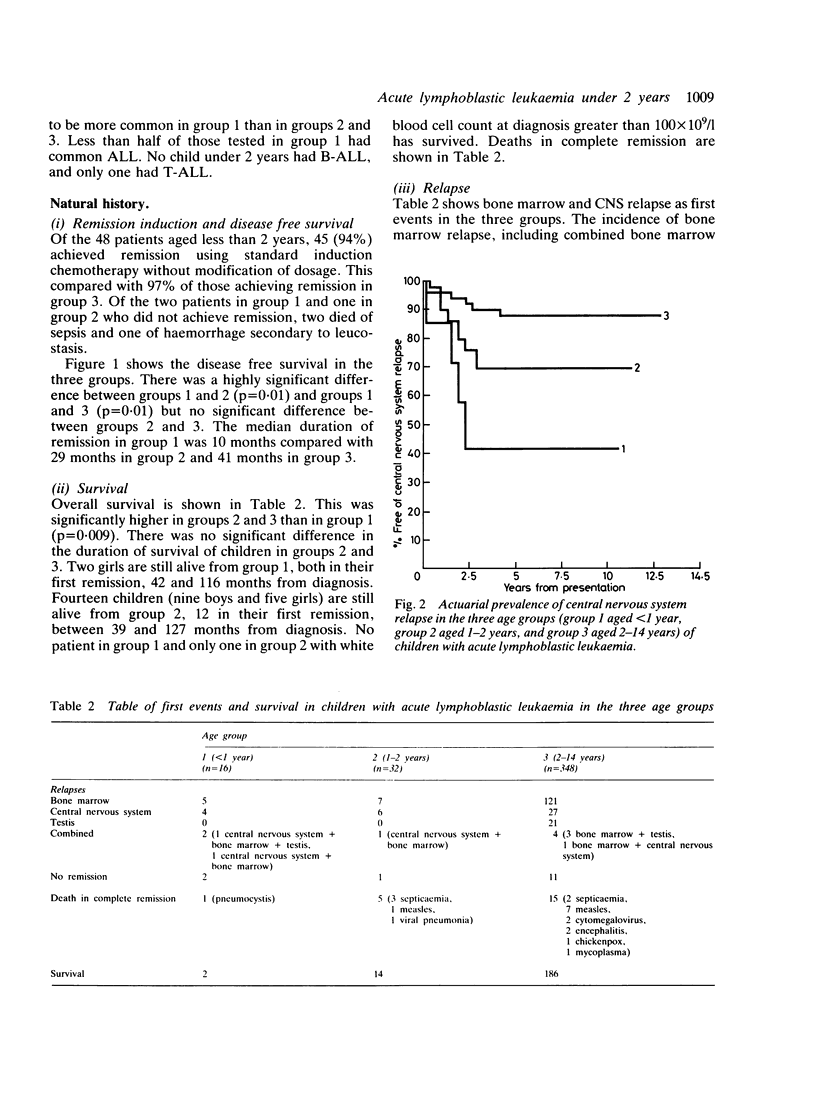
Presenting features and natural history were assessed in 48 children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia less than 2 years of age at diagnosis. Of these, 16 were less than 1 year (group 1) and 32 were between 1 and 2 years (group 2). Results were compared with a group of 348 children between the ages of 2 and 14 years (group 3) diagnosed over the same period. The children in group 1 presented with a higher prevalence of null cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, leucocyte counts greater than 100 X 10(9)/l, and hepatosplenomegaly and had a higher central nervous system (CNS) relapse rate and shorter duration of remission than those in the other two groups. Disease free survival and overall survival in group 2 paralleled that of group 3, although children in group 2 had a significantly higher CNS relapse rate. Neurological toxicity resulting from treatment with methotrexate and radiation was common in those under 2 years as a whole. In conclusion, children under 1 year have a particularly poor prognosis, while those between 1 and 2 years have a prognosis similar to that in the older age group. Alternative approaches to CNS prophylaxis are needed to reduce the high prevalence of CNS disease and toxicity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur D. C., Bloomfield C. D., Lindquist L. L., Nesbit M. E., Jr Translocation 4; 11 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: clinical characteristics and prognostic significance. Blood. 1982 Jan;59(1):96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. H., Marshall W. C., Chessells J. M. Neurological complications of childhood leukaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Nov;52(11):850–858. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.11.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangir A., George S., Sullivan M. Unfavorable prognosis of acute leukemia in infancy. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):1973–1978. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessells J. M., Ninane J., Tiedemann K. Present problems in management of childhood lymphoblastic leukaemia: experience from the Hospital for Sick Children, London. Haematol Blood Transfus. 1981;26:108–114. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67984-1_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiser C. Effects of chronic illness on intellectual development. A comparison of normal children with those treated for childhood leukaemia and solid tumours. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Oct;55(10):766–770. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.10.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiser C. Intellectual abilities among survivors of childhood leukaemia as a function of CNS irradiation. Arch Dis Child. 1978 May;53(5):391–395. doi: 10.1136/adc.53.5.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. L., Fernbach D. J., Vietti T. J., Sullivan M. P., Lane D. M., Haggard M. E., Berry D. H., Lonsdale D., Komp D. Factors influencing survival in pediatric acute leukemia. The SWCCSG experience, 1958-1970. Cancer. 1973 Dec;32(6):1542–1553. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197312)32:6<1542::aid-cncr2820320634>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Janossy G., Peto J., Kay H. Immunologically defined subclasses of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children: their relationship to presentation features and prognosis. Br J Haematol. 1981 Jun;48(2):179–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardisty R. M., Till M. M. Acute leukaemia 1959-64: factors affecting prognosis. Arch Dis Child. 1968 Feb;43(227):107–115. doi: 10.1136/adc.43.227.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannoun L. Are cognitive and educational development affected by age at which prophylactic therapy is given in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia? Arch Dis Child. 1983 Dec;58(12):953–958. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.12.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. R., Leikin S., Albo V., Sather H., Karon M., Hammond D. Prognostic factors and therapy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia of childhood: CCG-141. A report from childrens cancer study group. Cancer. 1983 Mar 15;51(6):1041–1049. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830315)51:6<1041::aid-cncr2820510612>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss H. A., Nannis E. D., Poplack D. G. The effects of prophylactic treatment of the central nervous system on the intellectual functioning of children with acute lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Med. 1981 Jul;71(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaman G., Zeltzer P., Bleyer W. A., Amendola B., Level C., Sather H., Hammond D. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in infants less than one year of age: a cumulative experience of the Children's Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 1985 Nov;3(11):1513–1521. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1985.3.11.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secker-Walker L. M., Stewart E. L., Chan L., O'Callaghan U., Chessells J. M. The (4;11) translocation in acute leukaemia of childhood: the importance of additional chromosomal aberrations. Br J Haematol. 1985 Sep;61(1):101–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb04065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simone J. V., Verzosa M. S., Rudy J. A. Initial features and prognosis in 363 children with acute lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):2099–2108. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. P., Chen T., Dyment P. G., Hvizdala E., Steuber C. P. Equivalence of intrathecal chemotherapy and radiotherapy as central nervous system prophylaxis in children with acute lymphatic leukemia: a pediatric oncology group study. Blood. 1982 Oct;60(4):948–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zippin C., Cutler S. J., Reeves W. J., Jr, Lum D. Variation in survival among patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1971 Jan;37(1):59–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


