Abstract
A cheap telemetric device, the 'Sport-tester', has been shown to be useful in monitoring the free running test for bronchoconstriction.
Full text
PDF
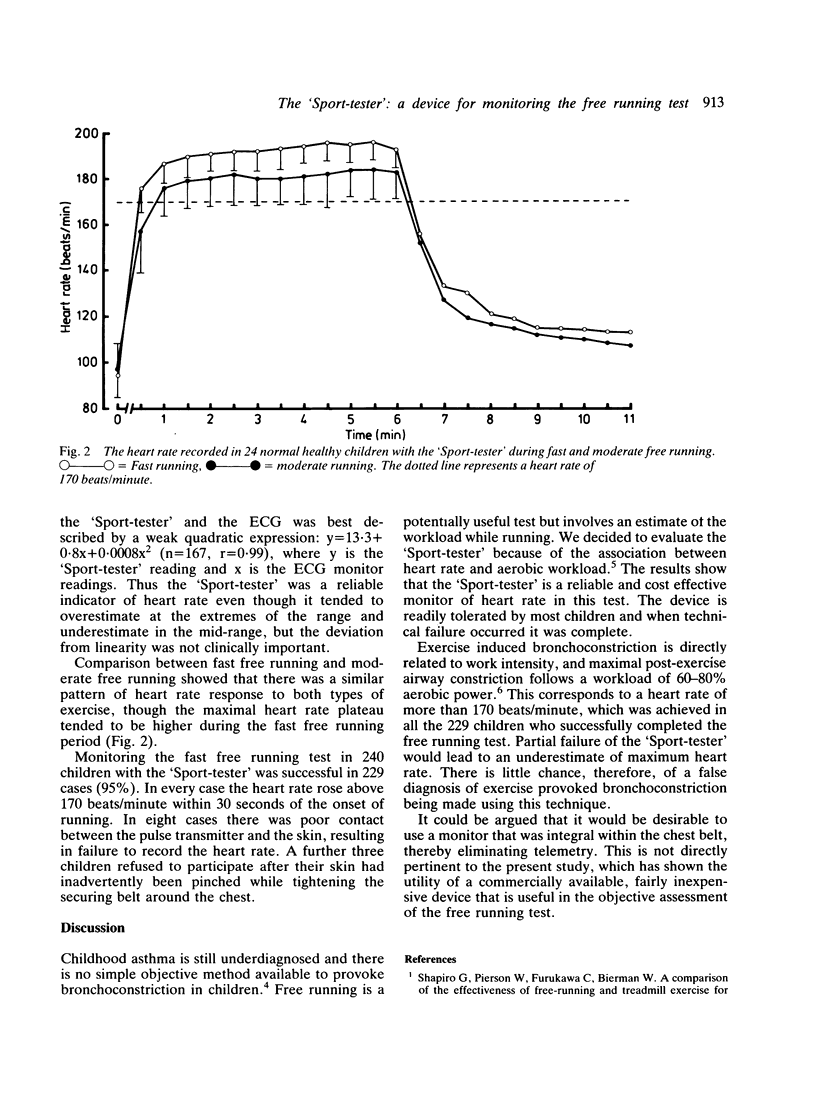

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson H. R., Bailey P. A., Cooper J. S., Palmer J. C., West S. Medical care of asthma and wheezing illness in children: a community survey. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1983 Sep;37(3):180–186. doi: 10.1136/jech.37.3.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggleston P. A., Guerrant J. L. A standardized method of evaluating exercise-induced asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1976 Sep;58(3):414–425. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(76)90122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey S., Silverman M., Anderson S. D. The use of the treadmill for assessing exercise-induced asthma and the effect of varying the severity and duration of exercise. Pediatrics. 1975 Nov;56(5 PT-2):893–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro G. G., Pierson W. E., Furukawa C. T., Bierman C. W. A comparison of the effectiveness of free-running and treadmill exercise for assessing exercise-induced bronchospasm in clinical practice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Dec;64(6 Pt 2):609–611. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. A., Evans J. N. Standardization of work intensity for evaluation of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1981;47(3):289–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00422474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



