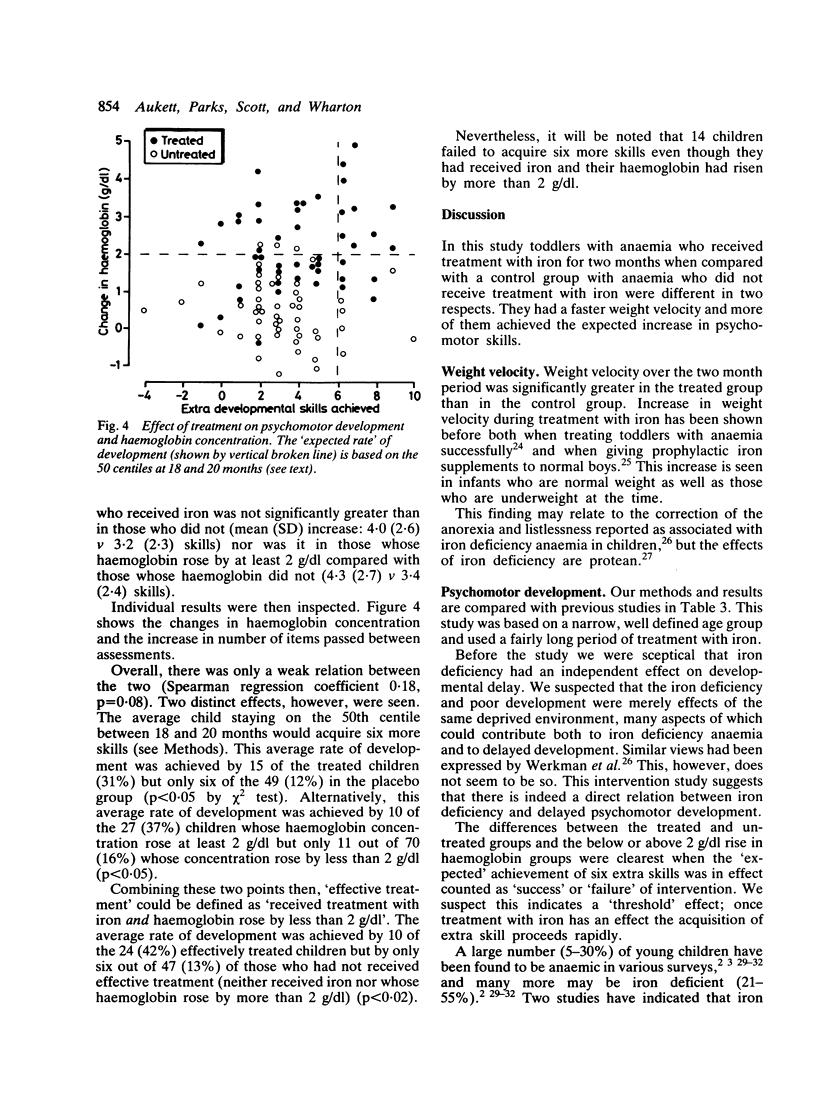
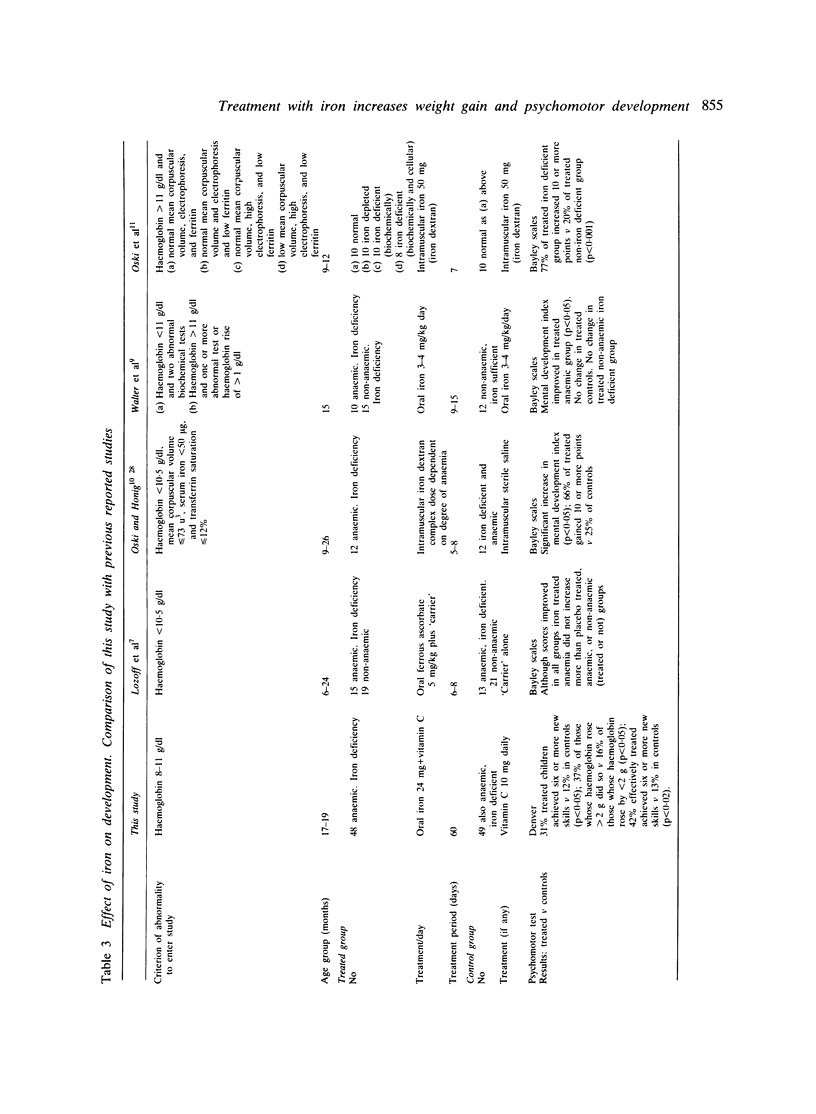
Abstract
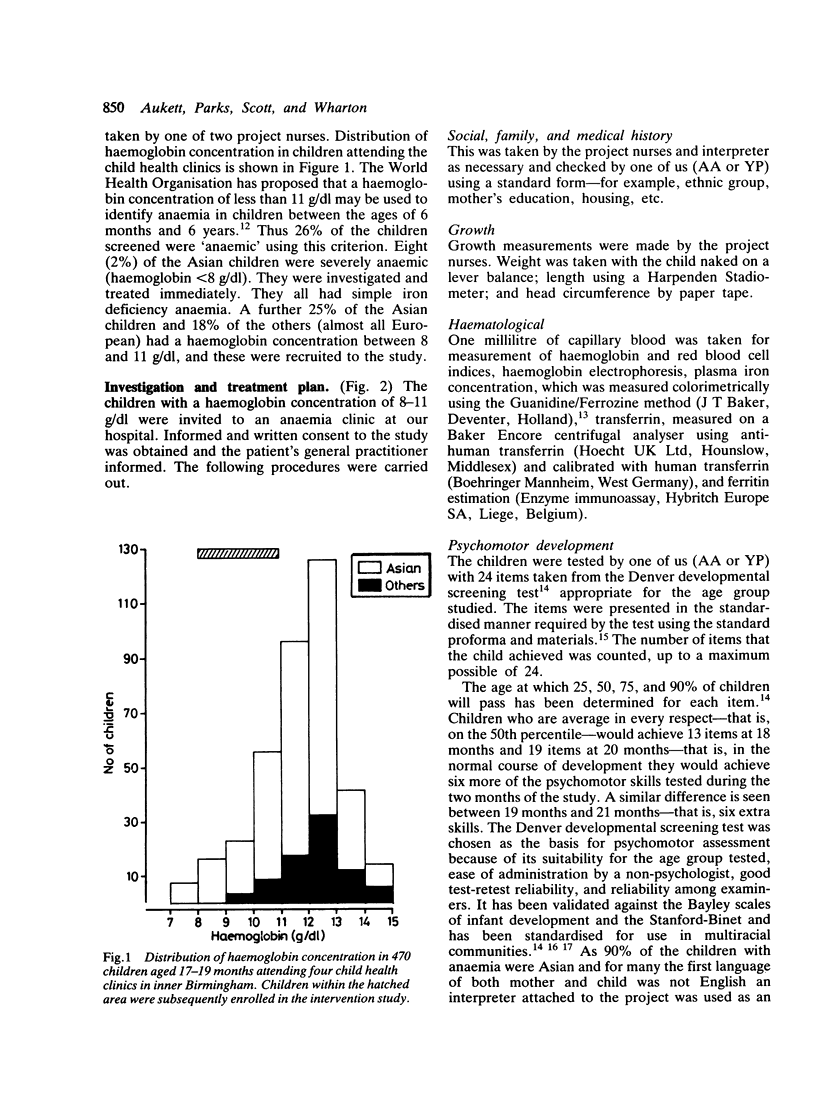
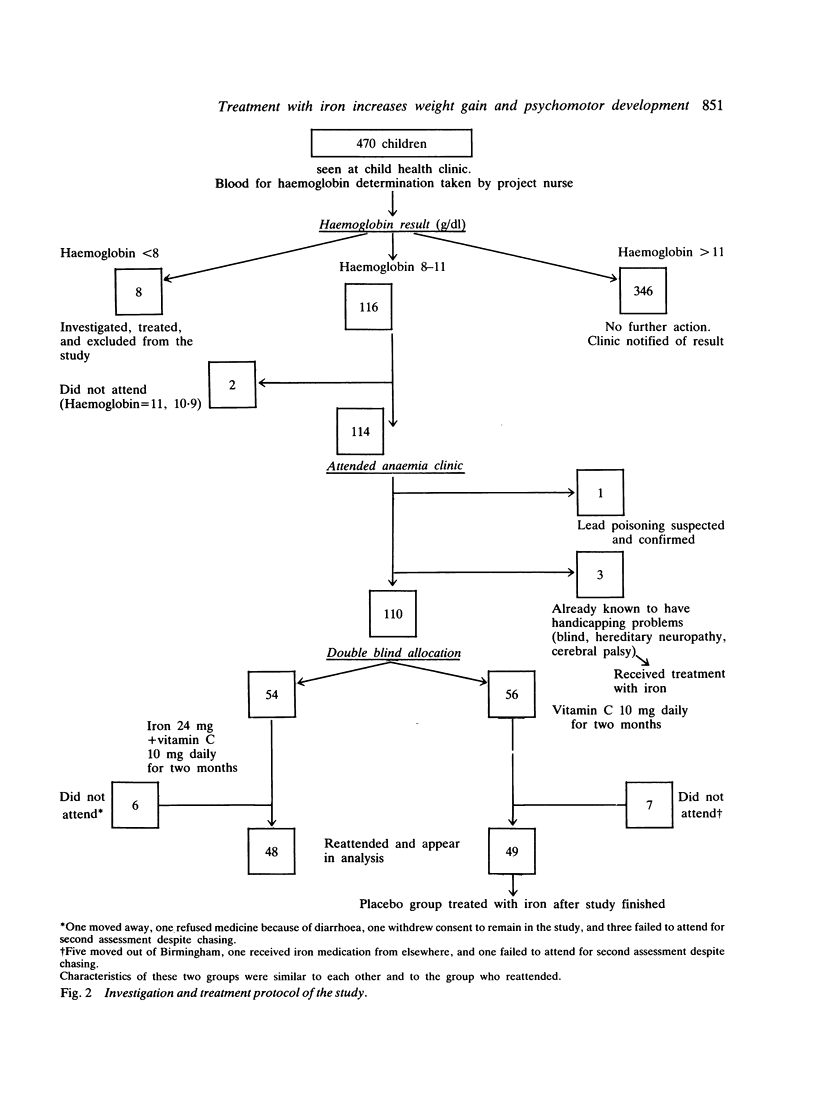
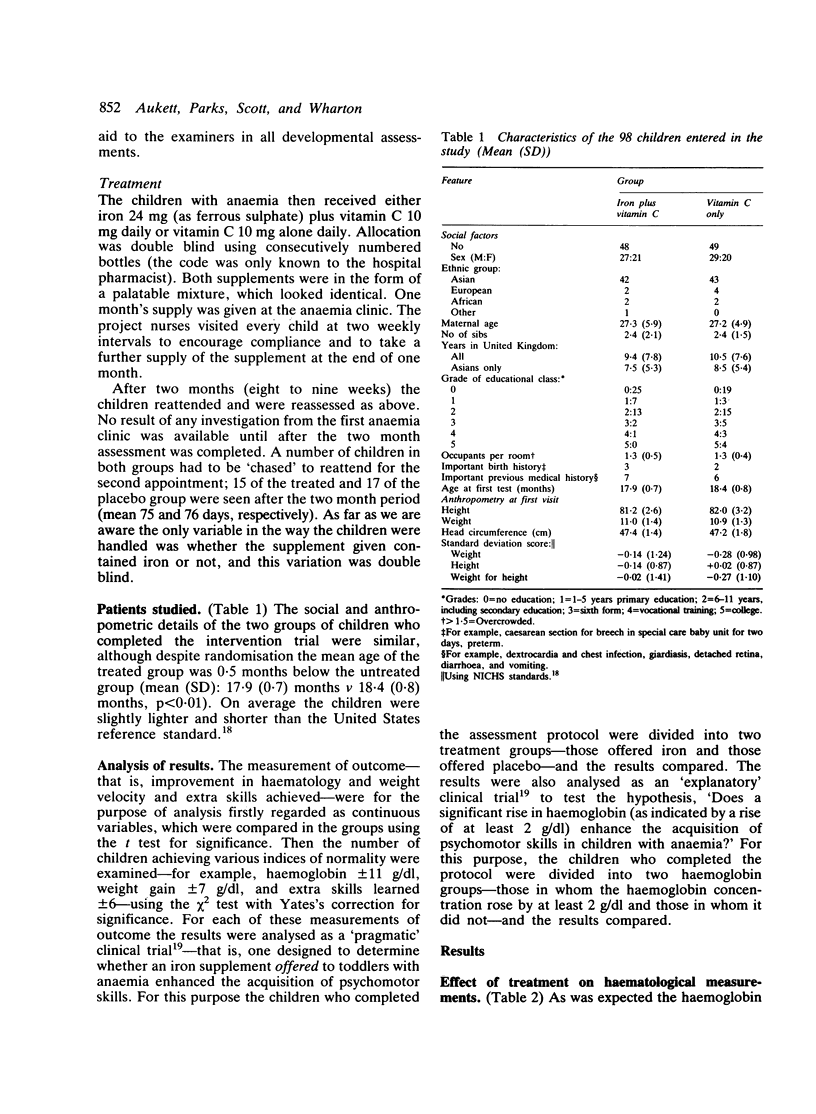
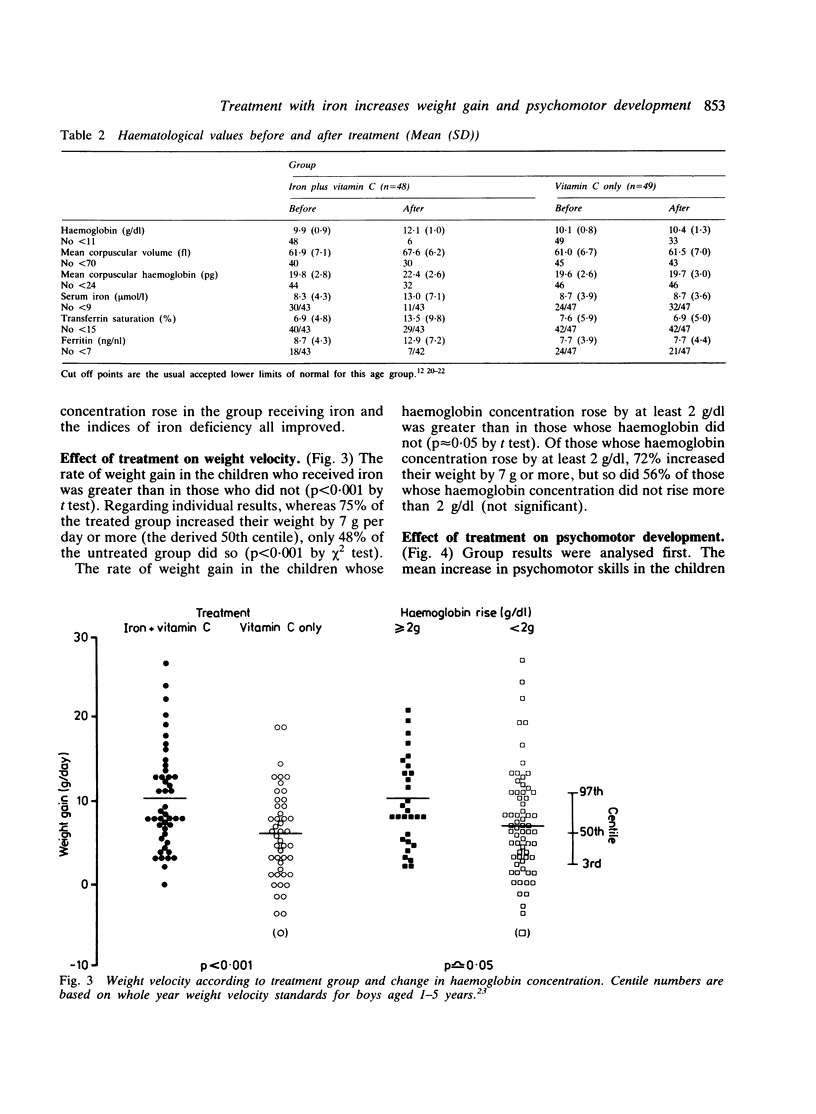
Previous work at this hospital and elsewhere has shown that anaemia in toddlers is common and is associated with psychomotor delay. It seemed unclear, however, whether this association was cause and effect or merely due to the same underprivileged environment. A double blind randomised intervention study was, therefore, performed. After an initial assessment 97 children with anaemia (haemoglobin 8-11 g/dl) aged 17-19 months received either iron and vitamin C or vitamin C only (control group) for two months and were then reassessed. The children who received the iron had an increased rate of weight gain and more of them achieved the expected rate of development. While iron deficiency anaemia is unlikely to be the only factor in the slower development of children living in underprivileged circumstances, it can at least be easily identified and treated. Routine child health surveillance in such areas should include a haemoglobin determination.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryant G. M., Davies K. J., Newcombe R. G. Standardisation of the Denver Developmental Screening Test for Cardiff children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1979 Jun;21(3):353–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1979.tb01627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman D. Haemoglobin levels in normal infants aged 3 to 24 months, and the effect of iron. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Apr;47(252):261–271. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.252.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman P. R., Siimes M. A. Percentile curves for hemoglobin and red cell volume in infancy and childhood. J Pediatr. 1979 Jan;94(1):26–31. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80344-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhardt P. Iron deficiency in young Bradford children from different ethnic groups. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Jan 11;292(6513):90–93. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6513.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwood P. C., Hughes D. Clinical trial of iron therapy of psychomotor function in anaemic women. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 1;3(5717):254–255. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5717.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenburg W. K., Dodds J. B. The Denver developmental screening test. J Pediatr. 1967 Aug;71(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goel K. M., Logan R. W., House F., Connell M. D., Strevens E., Watson W. H., Bulloch C. B. The prevalence of haemoglobinopathies, nutritional iron and folate deficiencies in native and immigrant children in Glasgow. Health Bull (Edinb) 1978 Jul;36(4):176–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gore S. M. Assessing clinical trials--trial discipline. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jul 18;283(6285):211–213. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6285.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindulis H., Scott P. H., Belton N. R., Wharton B. A. Combined deficiency of iron and vitamin D in Asian toddlers. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Sep;61(9):843–848. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.9.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddy T. B., Jurkowski C., Brody H., Kallen D. J., Czajka-Narins D. M. Iron deficiency with and without anemia in infants and children. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Dec;128(6):787–793. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110310035006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAM T. T., RUSSELL E. M. The reproductive histories of mothers of patients suffering from congenital diplegia. Arch Dis Child. 1961 Feb;36:34–41. doi: 10.1136/adc.36.185.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judisch J. M., Naiman J. L., Oski F. A. The fallacy of the fat iron-deficient child. Pediatrics. 1966 Jun;37(6):987–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozoff B., Brittenham G. M., Viteri F. E., Wolf A. W., Urrutia J. J. The effects of short-term oral iron therapy on developmental deficits in iron-deficient anemic infants. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):351–357. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80428-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V., Onotera R. T., Deinard A. S. Denver Developmental Screening Test: cultural variations in Southeast Asian children. J Pediatr. 1984 Mar;104(3):481–482. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)81122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oski F. A., Honig A. S., Helu B., Howanitz P. Effect of iron therapy on behavior performance in nonanemic, iron-deficient infants. Pediatrics. 1983 Jun;71(6):877–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oski F. A., Honig A. S. The effects of therapy on the developmental scores of iron-deficient infants. J Pediatr. 1978 Jan;92(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oski F. A. Iron deficiency--facts and fallacies. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1985 Apr;32(2):493–497. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34799-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oski F. A. The nonhematologic manifestations of iron deficiency. Am J Dis Child. 1979 Mar;133(3):315–322. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1979.02130030091017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt E., Leibel R. L. Iron deficiency and behavior. J Pediatr. 1976 Mar;88(3):372–381. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt E., Soemantri A. G., Yunis F., Scrimshaw N. S. Cognitive effects of iron-deficiency anaemia. Lancet. 1985 Jan 19;1(8421):158–158. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91921-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siimes M. A., Addiego J. E., Jr, Dallman P. R. Ferritin in serum: diagnosis of iron deficiency and iron overload in infants and children. Blood. 1974 Apr;43(4):581–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Whitehouse R. H., Takaishi M. Standards from birth to maturity for height, weight, height velocity, and weight velocity: British children, 1965. I. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Oct;41(219):454–471. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.219.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERKMAN S. L., SHIFMAN L., SKELLY T. PSYCHOSOCIAL CORRELATES OF IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA IN EARLY CHILDHOOD. Psychosom Med. 1964 Mar-Apr;26:125–134. doi: 10.1097/00006842-196403000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter T., Kovalskys J., Stekel A. Effect of mild iron deficiency on infant mental development scores. J Pediatr. 1983 Apr;102(4):519–522. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. E., Oski F. A. Iron deficiency anemia and scholastic achievement in young adolescents. J Pediatr. 1973 May;82(5):827–830. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams H. L., Johnson D. J., Haut M. J. Simultaneous spectrophotometry of Fe2+ and Cu2+ in serum denatured with guanidine hydrochloride. Clin Chem. 1977 Feb;23(2 Pt 1):237–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


