Abstract
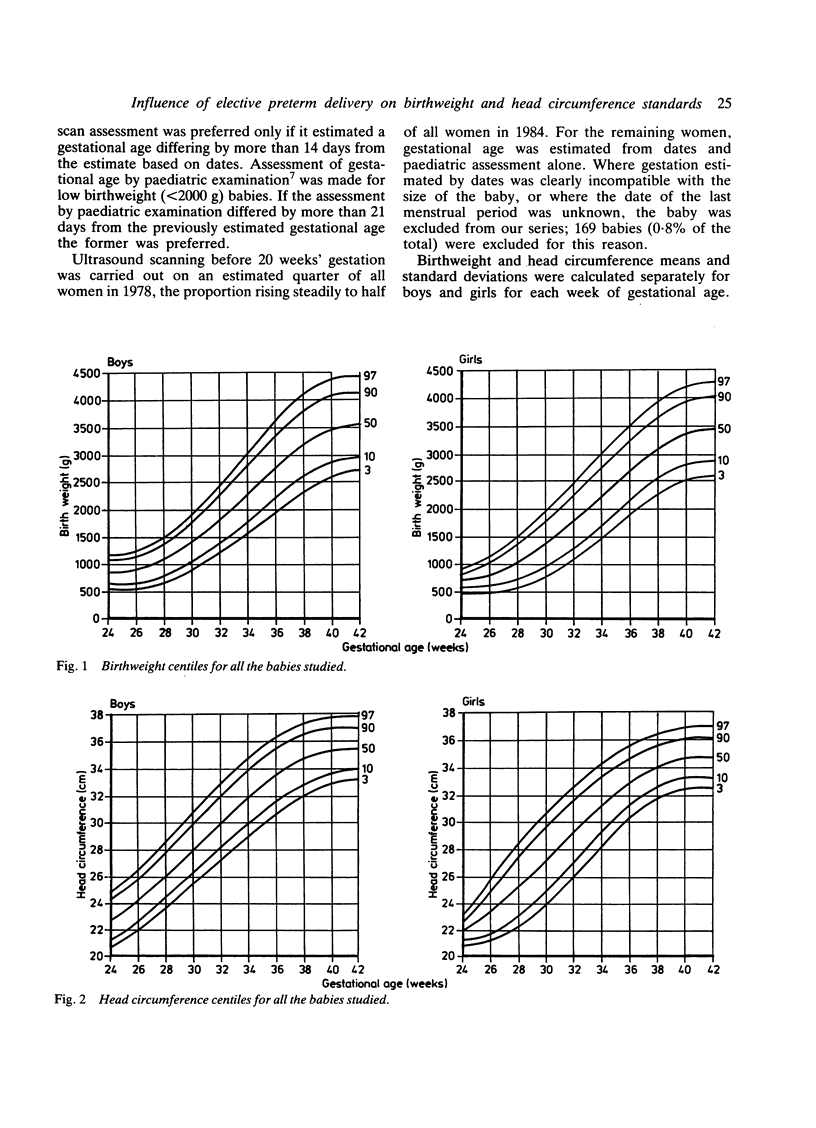
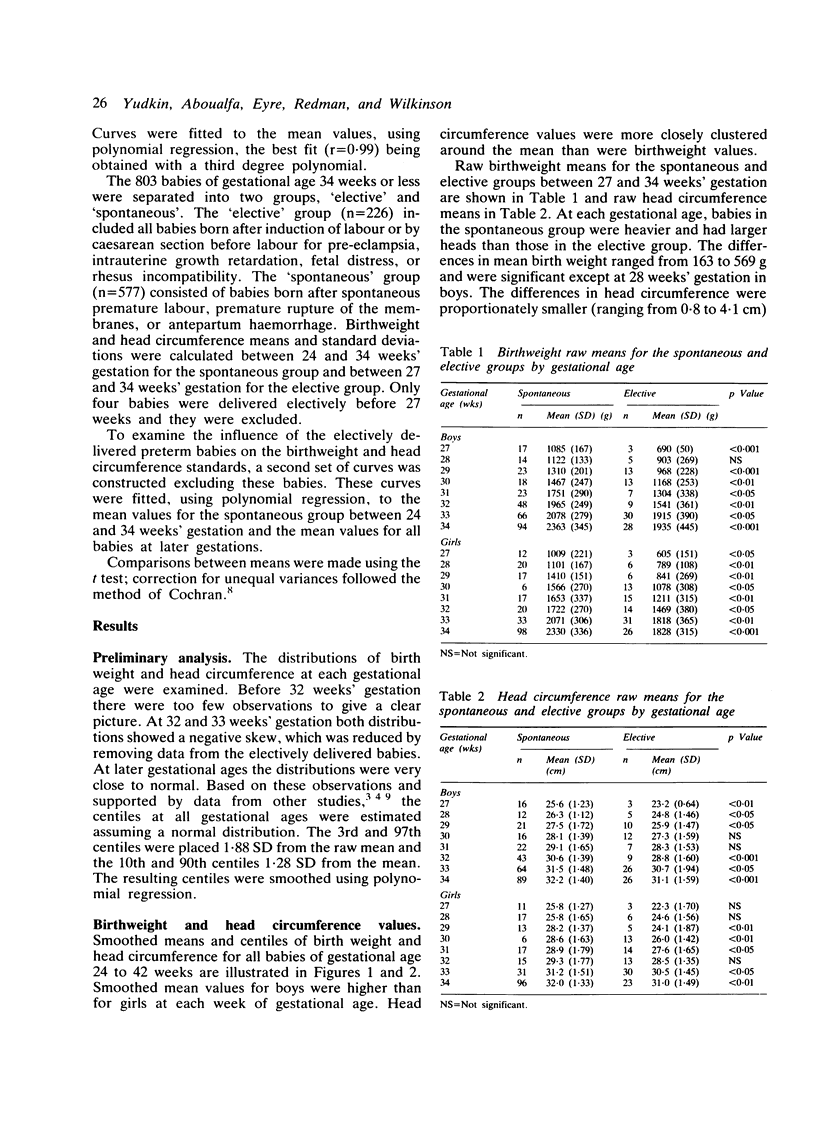
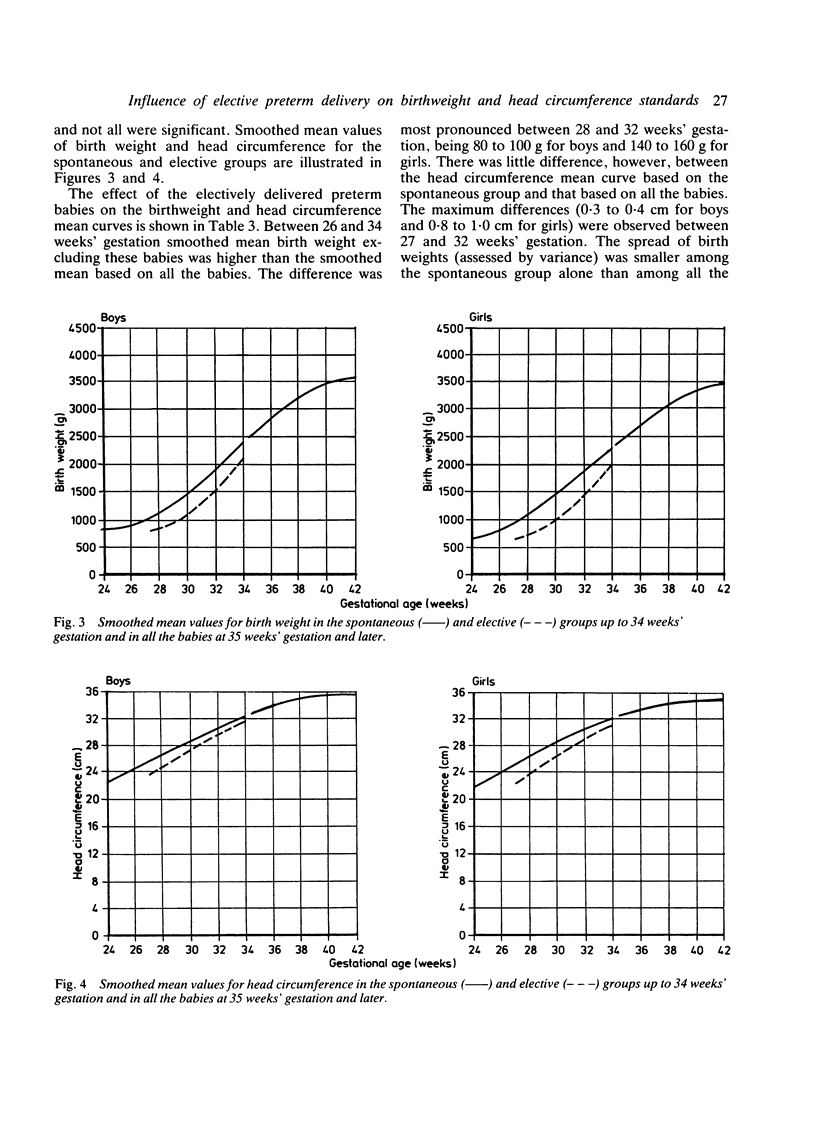
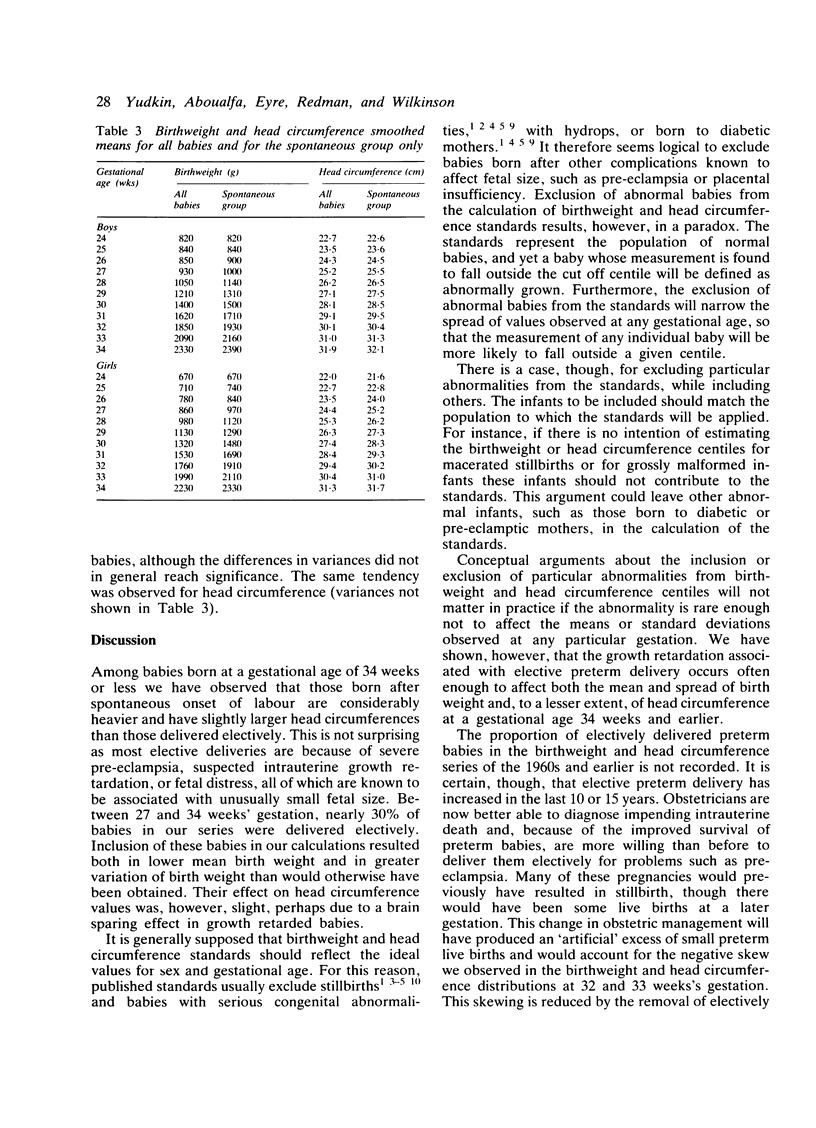
We calculated new birthweight and head circumference centiles for boys and girls between 24 and 42 weeks' gestation from 20,713 singleton live births at our hospital between 1978 and 1984. Among the 803 babies born at or before 34 weeks' gestation, 28% were delivered electively for fetal problems; they were considerably lighter than babies born after spontaneous preterm labour. In contrast, they showed only a small deficit in head circumference, possibly due to a brain sparing effect in growth retarded infants. Electively delivered preterm infants cause a bias in birthweight and head circumference centiles and we recommend that these babies should be excluded when these centiles are calculated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babson S. G., Behrman R. E., Lessel R. Fetal growth. Liveborn birth weights for gestational age of white middle class infants. Pediatrics. 1970 Jun;45(6):937–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr V., Kerridge D. F., Mitchell R. G. The value of some external characteristics in the assessment of gestational age at birth. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1966 Dec;8(6):657–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1966.tb01823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen D. V., Pearse R. G. Birthweight between 14 and 42 weeks' gestation. Arch Dis Child. 1985 May;60(5):440–446. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.5.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBCHENCO L. O., HANSMAN C., DRESSLER M., BOYD E. INTRAUTERINE GROWTH AS ESTIMATED FROM LIVEBORN BIRTH-WEIGHT DATA AT 24 TO 42 WEEKS OF GESTATION. Pediatrics. 1963 Nov;32:793–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. D., Richards B. An analysis of birth weight by gestational age of infants born in England and Wales, 1967 to 1971. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1974 Dec;81(12):956–967. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1974.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M., Billewicz W. Z., Hytten F. E. The assessment of fetal growth. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1968 Sep;75(9):903–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1968.tb01615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usher R., McLean F. Intrauterine growth of live-born Caucasian infants at sea level: standards obtained from measurements in 7 dimensions of infants born between 25 and 44 weeks of gestation. J Pediatr. 1969 Jun;74(6):901–910. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warsof S. L., Pearce J. M., Campbell S. The present place of routine ultrasound screening. Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 1983 Dec;10(3):445–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


