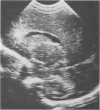
Abstract
During an 18 month period, 120 preterm infants of 34 weeks' gestation or less were prospectively examined for periventricular leucomalacia (PVL) by cerebral ultrasound. Neurological and developmental assessment was carried out at 18 months of age corrected for prematurity in 82 surviving neonates. The developmental outcome (Griffiths development quotient) was above 80 and similar in infants with normal scans (n = 41), isolated periventricular-intraventricular haemorrhage (n = 13), and post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus (n = 4), and no major handicap was diagnosed in these groups. By contrast, the prognosis was variable and poorer in infants with PVL (n = 24) and depended on the extent and site of the lesion. Infants with frontal PVL (n = 13) developed normally. Major sequelae (n = 8) were closely related to frontal-parietal PVL and frontal-parietal-occipital PVL and could be ascribed to the presence of cysts as well as to a persistent hyperechogenic ultrasonographic PVL appearance. A relation between size and site of the lesion and type and severity of the handicap was established.
Full text
PDF
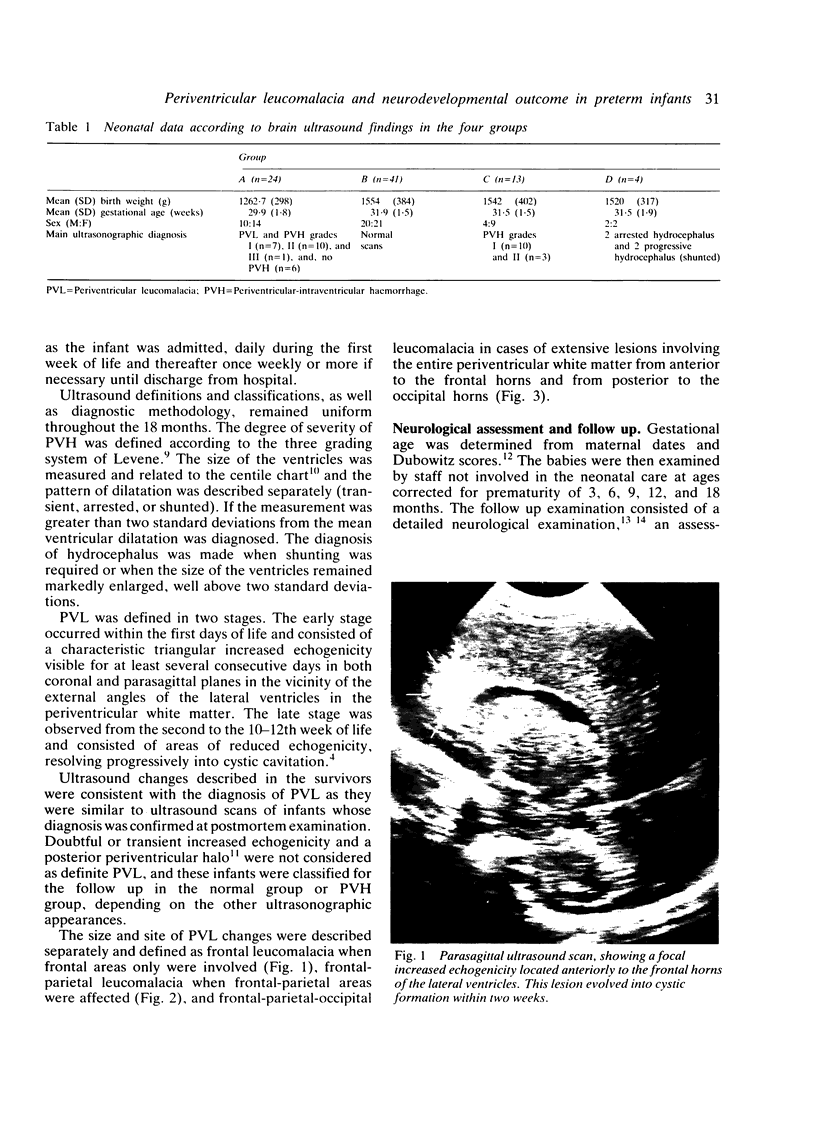
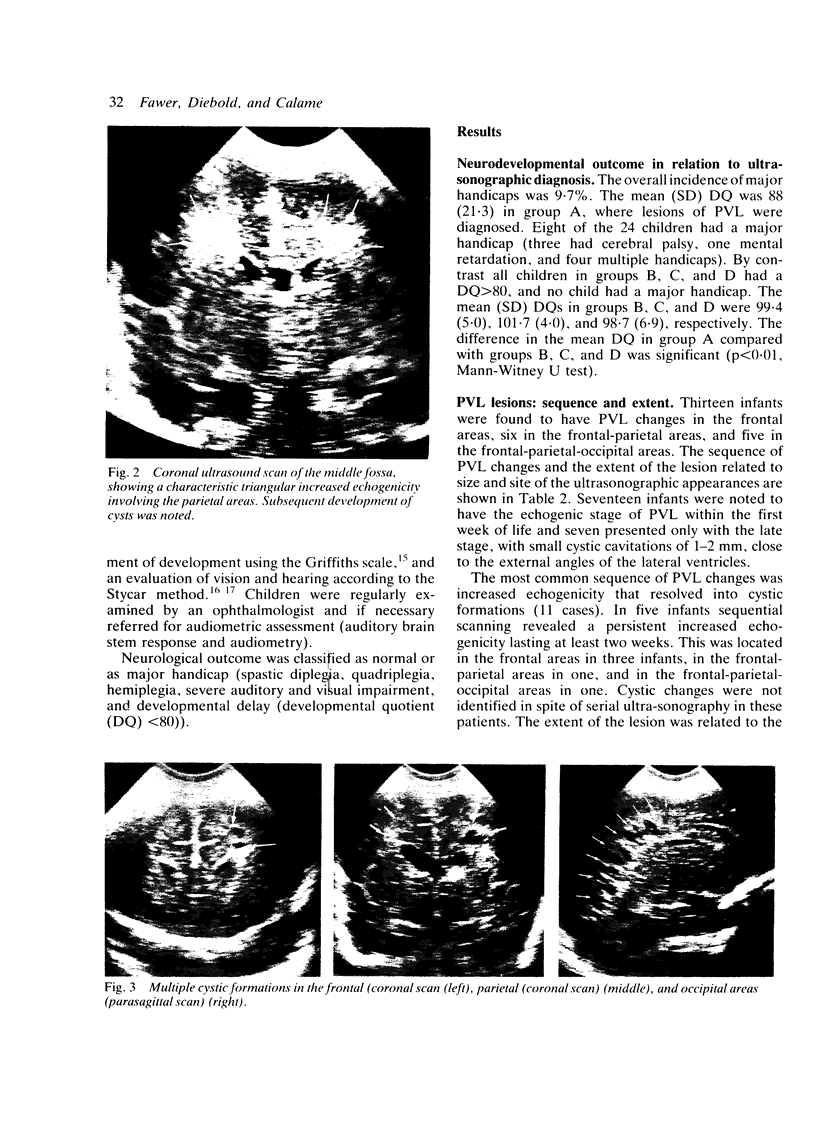
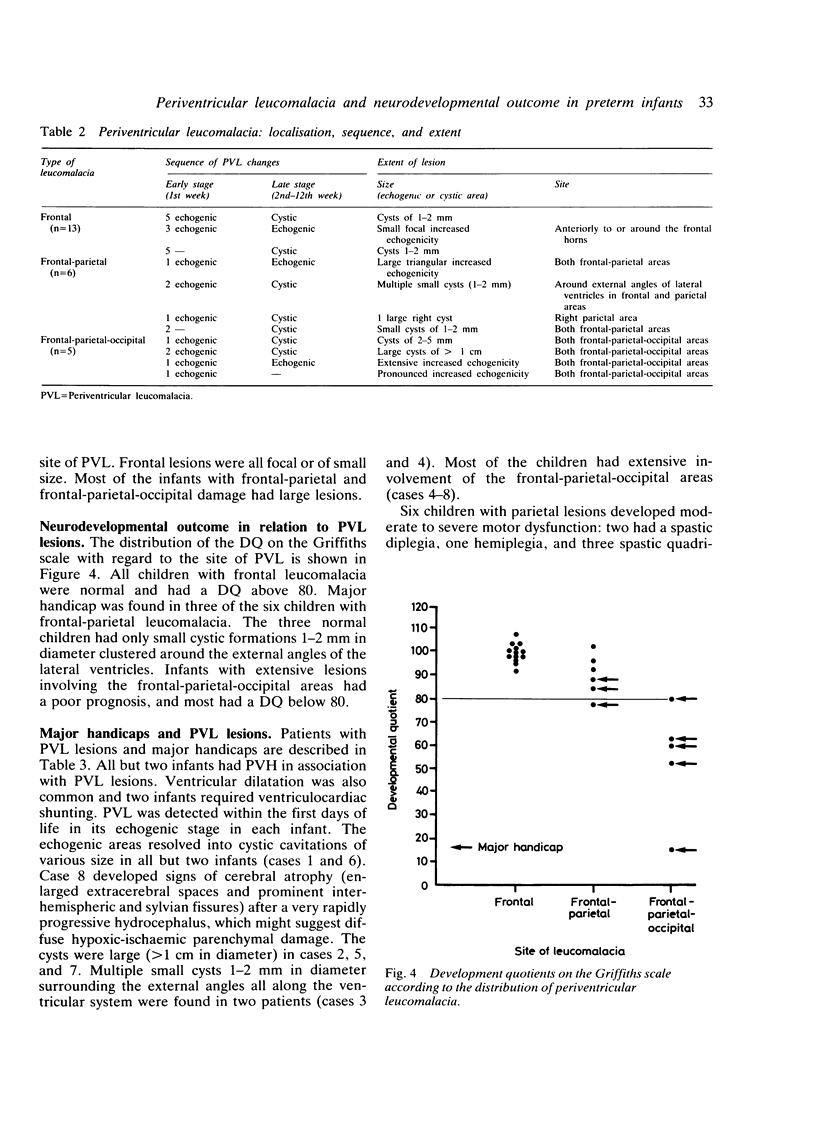



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amiel-Tison C. A method for neurologic evaluation within the first year of life. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1976 Nov;7(1):1–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANKER B. Q., LARROCHE J. C. Periventricular leukomalacia of infancy. A form of neonatal anoxic encephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 1962 Nov;7:386–410. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.04210050022004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calame A., Fawer C. L., Anderegg A., Perentes E. Interaction between perinatal brain damage and processes of normal brain development. Ultrasonographic and neurodevelopmental study in the first year of life. Dev Neurosci. 1985;7(1):1–11. doi: 10.1159/000112272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catto-Smith A. G., Yu V. Y., Bajuk B., Orgill A. A., Astbury J. Effect of neonatal periventricular haemorrhage on neurodevelopmental outcome. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Jan;60(1):8–11. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeReuck J., Chattha A. S., Richardson E. P., Jr Pathogenesis and evolution of periventricular leukomalacia in infancy. Arch Neurol. 1972 Sep;27(3):229–236. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490150037007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz L. M., Bydder G. M., Mushin J. Developmental sequence of periventricular leukomalacia. Correlation of ultrasound, clinical, and nuclear magnetic resonance functions. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Apr;60(4):349–355. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.4.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz L. M., Dubowitz V., Goldberg C. Clinical assessment of gestational age in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1970 Jul;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawer C. L., Calame A., Furrer M. T. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 12 months of age related to cerebral ultrasound appearances of high risk preterm infants. Early Hum Dev. 1985 Jul;11(2):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(85)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawer C. L., Calame A., Perentes E., Anderegg A. Periventricular leukomalacia: a correlation study between real-time ultrasound and autopsy findings. Periventricular leukomalacia in the neonate. Neuroradiology. 1985;27(4):292–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00339560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Melson G. L., Clark H. B., Volpe J. J. Hemorrhagic periventricular leukomalacia: diagnosis by real time ultrasound and correlation with autopsy findings. Pediatrics. 1982 Mar;69(3):282–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laub M. C., Ingrisch H. Increased periventricular echogenicity (periventricular halos) in neonatal brain: a sonographic study. Neuropediatrics. 1986 Feb;17(1):39–43. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech R. W., Alvord E. C., Jr Morphologic variations in periventricular leukomalacia. Am J Pathol. 1974 Mar;74(3):591–602. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I., Fawer C. L., Lamont R. F. Risk factors in the development of intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm neonate. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Jun;57(6):410–417. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.6.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I., Starte D. R. A longitudinal study of post-haemorrhagic ventricular dilatation in the newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Dec;56(12):905–910. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.12.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I., Wigglesworth J. S., Dubowitz V. Hemorrhagic periventricular leukomalacia in the neonate: a real-time ultrasound study. Pediatrics. 1983 May;71(5):794–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwaesei C. G., Pape K. E., Martin D. J., Becker L. E., Fitz C. R. Periventricular infarction diagnosed by ultrasound: a postmortem correlation. J Pediatr. 1984 Jul;105(1):106–110. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80372-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer P., Dubowitz L. M., Levene M. I., Dubowitz V. Developmental and neurological progress of preterm infants with intraventricular haemorrhage and ventricular dilatation. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Oct;57(10):748–753. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.10.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papile L. A., Munsick-Bruno G., Schaefer A. Relationship of cerebral intraventricular hemorrhage and early childhood neurologic handicaps. J Pediatr. 1983 Aug;103(2):273–277. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80366-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton D. I., Preston P. R., Durbin G. M. Structure and evolution of echo dense lesions in the neonatal brain. A combined ultrasound and necropsy study. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Sep;60(9):798–808. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.9.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman R. M., Selednik L. J. Periventricular leukomalacia. A one-year autopsy study. Arch Neurol. 1980 Apr;37(4):231–235. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500530069011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. L., Thorburn R. J., Hope P. L., Goldsmith M., Lipscomb A. P., Reynolds E. O. Ultrasound appearance of the brain in very preterm infants and neurodevelopmental outcome at 18 months of age. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Aug;58(8):598–604. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.8.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weindling A. M., Rochefort M. J., Calvert S. A., Fok T. F., Wilkinson A. Development of cerebral palsy after ultrasonographic detection of periventricular cysts in the newborn. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1985 Dec;27(6):800–806. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]