Abstract
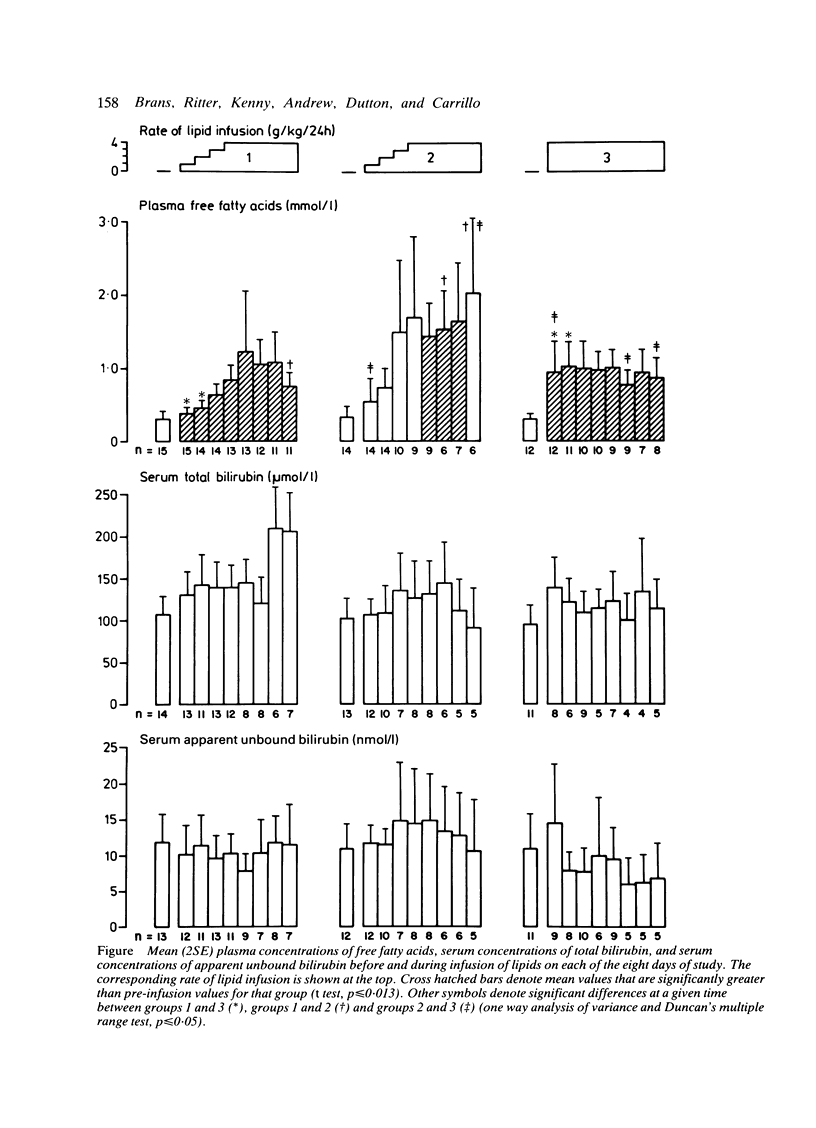
Thirty nine very low birthweight neonates (with a birth weight of 820 to 1500 g and gestation of 27 to 34 weeks) who required total parenteral nutrition were randomly assigned to one of three regimens of administration of fat emulsion for a period of eight days. Groups 1 and 2 received the emulsion at a constant rate over 24 and 16 hours, respectively, beginning with a daily dosage of 1 g/kg and increasing daily by 1 g/kg to a maximum of 4 g/kg. Group 3 received the emulsion at a constant rate of 4 g/kg a day over 24 hours. Plasma concentrations of free fatty acids and serum concentrations of total bilirubin, apparent unbound bilirubin, and albumin were measured at regular intervals. Effects of the three regimens on serum bilirubin measurements were determined. The regimen of fat infusion and rate of infusion seemed to have no effect on serum concentrations of total and apparent unbound bilirubin, although there was a trend towards greater variability in apparent unbound concentrations with the intermittent regimen.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew G., Chan G., Schiff D. Lipid metabolism in the neonate. II. The effect of Intralipid on bilirubin binding in vitro and in vivo. J Pediatr. 1976 Feb;88(2):279–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brans Y. W., Dutton E. B., Andrew D. S., Menchaca E. M., West D. L. Fat emulsion tolerance in very low birth weight neonates: effect on diffusion of oxygen in the lungs and on blood pH. Pediatrics. 1986 Jul;78(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brans Y. W. Erratum: values for plasma glycerol, FFA, and triglycerides. J Pediatr. 1984 Nov;105(5):855–855. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brans Y. W. Parenteral nutrition of the very low birth weight neonate: a critical view. Clin Perinatol. 1977 Sep;4(2):367–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodersen R. Prevention of kernicterus, based on recent progress in bilirubin chemistry. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1977 Sep;66(5):625–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1977.tb07959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashore W. J., Oh W. Unbound bilirubin and kernicterus in low-birth-weight infants. Pediatrics. 1982 Apr;69(4):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doumas B. T., Watson W. A., Biggs H. G. Albumin standards and the measurement of serum albumin with bromcresol green. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Jan;31(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90365-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz L. M., Dubowitz V., Goldberg C. Clinical assessment of gestational age in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1970 Jul;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freman M. G., Graves W. L., Thompson R. L. Indigent Negro and Caucasian birth weight-gestational age tables. Pediatrics. 1970 Jul;46(1):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliard J. L., Shannon D. L., Hunter M. A., Brans Y. W. Plasma lipid levels in preterm neonates receiving parenteral fat emulsions. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Jan;58(1):29–33. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J., Wennberg R. P. Determination of unbound bilirubin in the serum of newborns. Clin Chem. 1974 Jul;20(7):783–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao L. C., Cheng M. H., Warburton D. Triglycerides, free fatty acids, free fatty acids/albumin molar ratio, and cholesterol levels in serum of neonates receiving long-term lipid infusions: controlled trial of continuous and intermittent regimens. J Pediatr. 1984 Mar;104(3):429–435. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)81111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter D. A., Kenny J. D., Norton H. J., Rudolph A. J. A prospective study of free bilirubin and other risk factors in the development of kernicterus in premature infants. Pediatrics. 1982 Mar;69(3):260–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shennan A. T., Cherian A. G., Angel A., Bryan M. H. The effect of Intralipid on the estimation of serum bilirubin in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1976 Feb;88(2):285–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starinsky R., Shafrir E. Displacement of albumin-bound bilirubin by free fatty acids. Implications for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Aug;29(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaler M. M., Wennberg R. P. Influence of intravenous nutrients on bilirubin transport. II. Emulsified lipid solutions. Pediatr Res. 1977 Mar;11(3 Pt 1):167–171. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197703000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiessen H., Jacobsen J., Brodersen R. Displacement of albumin-bound bilirubin by fatty acids. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1972 May;61(3):285–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1972.tb16100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


