Abstract
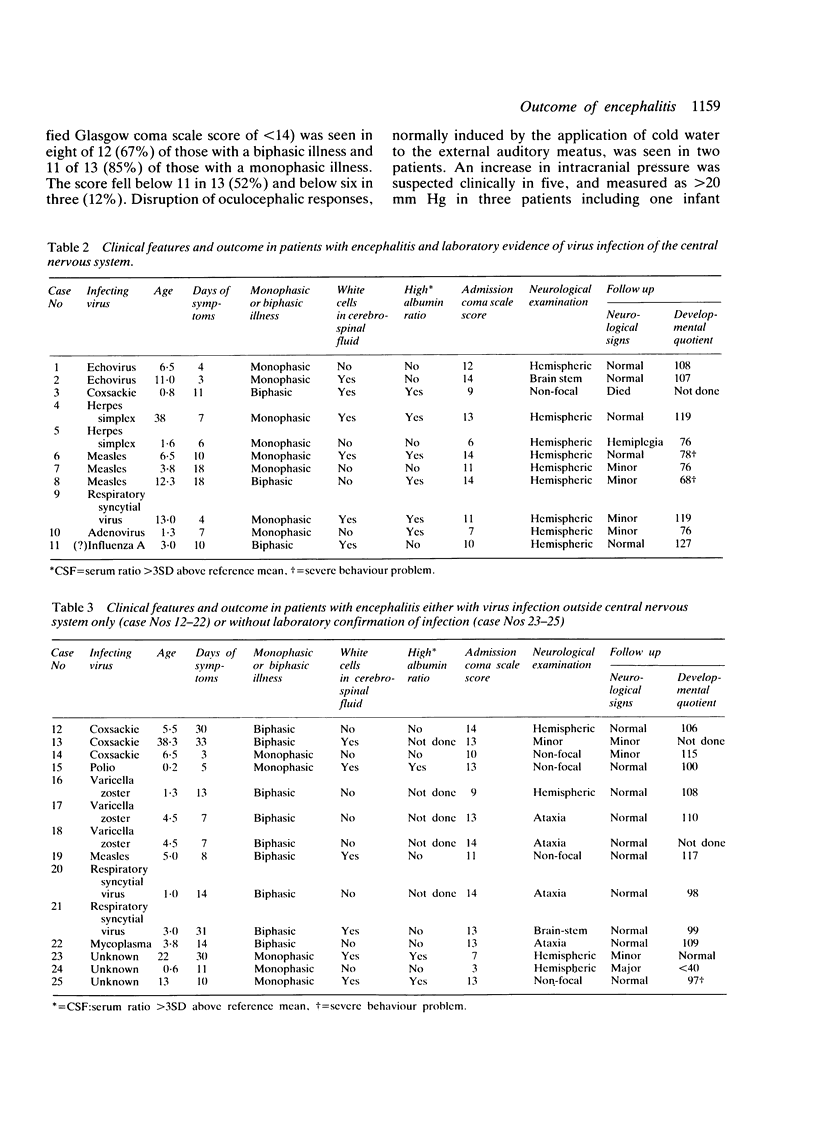
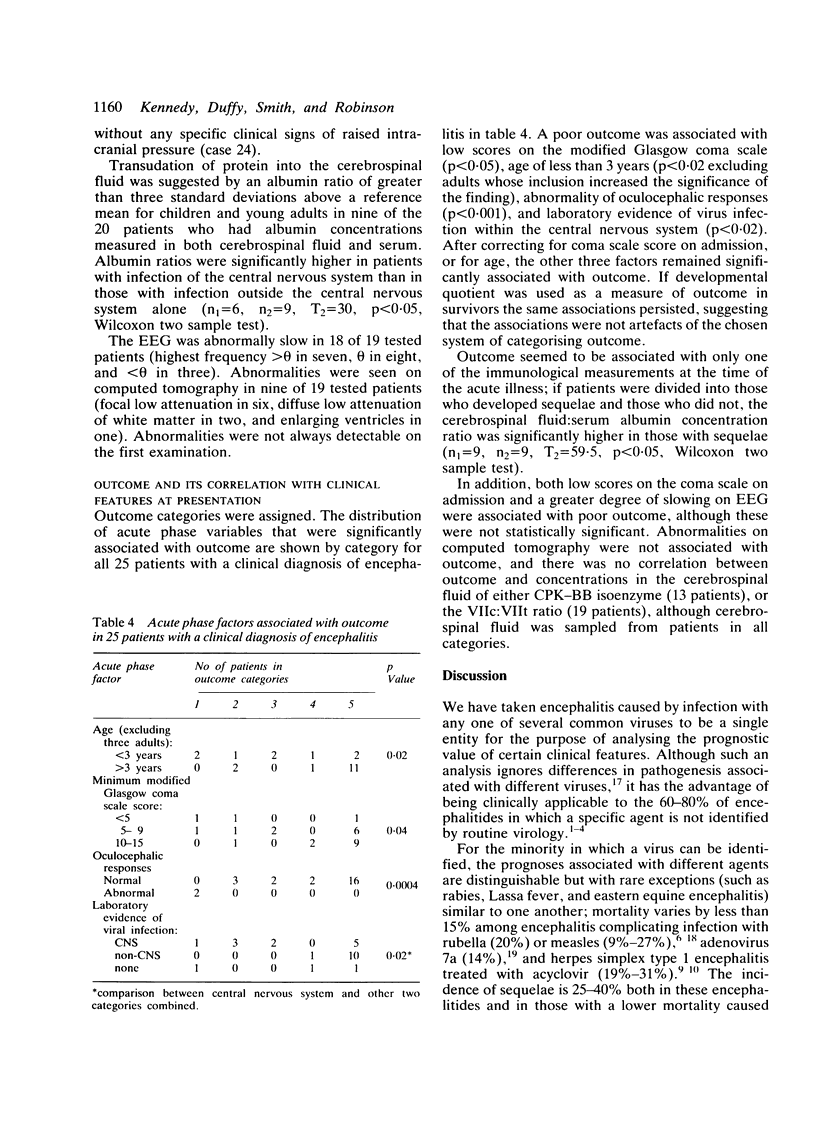
Twenty five patients with encephalitis were studied prospectively, and their clinical and virological features compared with outcome. Among 22 patients with laboratory confirmation of virus infection, evidence of direct effect on the central nervous system by the virus occurred significantly more often both in those with a monophasic illness compared with those with a biphasic illness, and in those with focal neurological signs localising in the cerebral hemispheres compared with those without such signs. Young age at presentation, low score on the Glasgow coma scale, disruption of oculocephalic responses, and laboratory evidence of virus infection within the central nervous system were significantly associated with poor outcome. Computed tomography results, concentrations of creatine phosphokinase BB isoenzyme in cerebrospinal fluid, and procoagulant activity in cerebrospinal fluid were not predictive of outcome.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOUGHTON C. R. MORBILLI IN SYDNEY. II. NEUROLOGICAL SEQUELAE OF MORBILLI. Med J Aust. 1964 Dec 5;2:908–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutt M. K., Johnston I. D. Computed tomography and EEG in herpes simplex encephalitis. Their value in diagnosis and prognosis. Arch Neurol. 1982 Feb;39(2):99–102. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510140033008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEWETT T. H., HOULT J. G. Influenzal encephalopathy and postinfluenzal encephalitis. Lancet. 1958 Jul 5;2(7036):11–15. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS J. L., MILLER H. G., STANTON J. B. Para-infectious encephalomyelitis and related syndromes; a critical review of the neurological complications of certain specific fevers. Q J Med. 1956 Oct;25(100):427–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum S. E., Reed W. P. Effect of intravascular pneumococcal challenge on vascular permeability in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):179–179. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon N. S., Fois A., Jacobi G., Minns R. A., Seshia S. S. The management of the comatose child. Neuropediatrics. 1983 Feb;14(1):3–5. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1059545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeber J. E., Stuart M. J. Spinal-fluid procoagulant activity: a sensitive indicator of central-nervous-system damage. Lancet. 1978 Aug 5;2(8084):285–288. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91689-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOULT J. G., FLEWETT T. H. Influenzal encephalopathy and post-influenzal encephalitis; histological and other observations. Br Med J. 1960 Jun 18;1(5189):1847–1850. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5189.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T. Selective vulnerability of neural cells to viral infections. Brain. 1980 Sep;103(3):447–472. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennard C., Swash M. Acute viral encephalitis: its diagnosis and outcome. Brain. 1981 Mar;104(Pt 1):129–148. doi: 10.1093/brain/104.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C. R., Bird D., Chrzanowska K., Stephens S., Webster A. D. The pathogenesis of virus-associated encephalopathies: a prospective study of immunological mechanisms. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Feb;42(2):218–228. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipps A., Dick G., Moodie J. W. Measles and the central nervous system. Lancet. 1983 Dec 17;2(8364):1406–1410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90932-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig H., Rabinowitz S. G., Day E., Miller V. Post-infectious encephalomyelitis after successful treatment of herpes simplex encephalitis with adenine arabinoside: ultrastructural observations. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 10;300(19):1089–1093. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905103001906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskiniemi M., Donner M., Pettay O. Clinical appearance and outcome in mumps encephalitis in children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1983 Jul;72(4):603–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1983.tb09778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskiniemi M., Manninen V., Vaheri A., Sainio K., Eistola P., Karli P. Acute encephalitis. A survey of epidemiological, clinical and microbiological features covering a twelve-year period. Acta Med Scand. 1981;209(1-2):115–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M., Hjelm M., Kay J. D., Pincott J. R., Gould J. D., Dinwiddie R., Matthew D. J. Haemorrhagic shock and encephalopathy: a new syndrome with a high mortality in young children. Lancet. 1983 Jul 9;2(8341):64–67. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER H. M., Jr, JOHNSON R. T., CRAWFORD I. P., DASCOMB H. E., ROGERS N. G. Central nervous system syndromes of "vital" etiology. A study of 713 cases. Am J Med. 1960 Aug;29:334–347. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane J. A., Mitchell A. A., Walsh J. M., Robertson J. J. Spiramycin the the prevention of postoperative staphylococcal infection. Lancet. 1968 Jan 6;1(7532):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pampiglione G., Harden A. Resuscitation after cardiocirculatory arrest. Prognostic evaluation of early electroencephalographic findings. Lancet. 1968 Jun 15;1(7555):1261–1265. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman N., Stevenson J. E., Graham P. J. Prevalence of behaviour problems in 3-year-old children: an epidemiological study in a London borough. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1975 Oct;16(4):277–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1975.tb00362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter M. A children's behaviour questionnaire for completion by teachers: preliminary findings. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1967 May;8(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1967.tb02175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seshia S. S., Seshia M. M., Sachdeva R. K. Coma in childhood. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1977 Oct;19(5):614–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1977.tb07995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Similä S., Jouppila R., Salmi A., Pohjonen R. Encephaloningitis in children associated with an adenovirus type 7 epidemic. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1970 May;59(3):310–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1970.tb09009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sköldenberg B., Forsgren M., Alestig K., Bergström T., Burman L., Dahlqvist E., Forkman A., Frydén A., Lövgren K., Norlin K. Acyclovir versus vidarabine in herpes simplex encephalitis. Randomised multicentre study in consecutive Swedish patients. Lancet. 1984 Sep 29;2(8405):707–711. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92623-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Bortolussi R. Acute viral infection of the central nervous system in children: an 8-year review. Can Med Assoc J. 1981 Sep 15;125(6):585–589. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Alford C. A., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Luby J. P., Aoki F. Y., Hanley D., Nahmias A. J., Soong S. J. Vidarabine versus acyclovir therapy in herpes simplex encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 16;314(3):144–149. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601163140303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


