Abstract
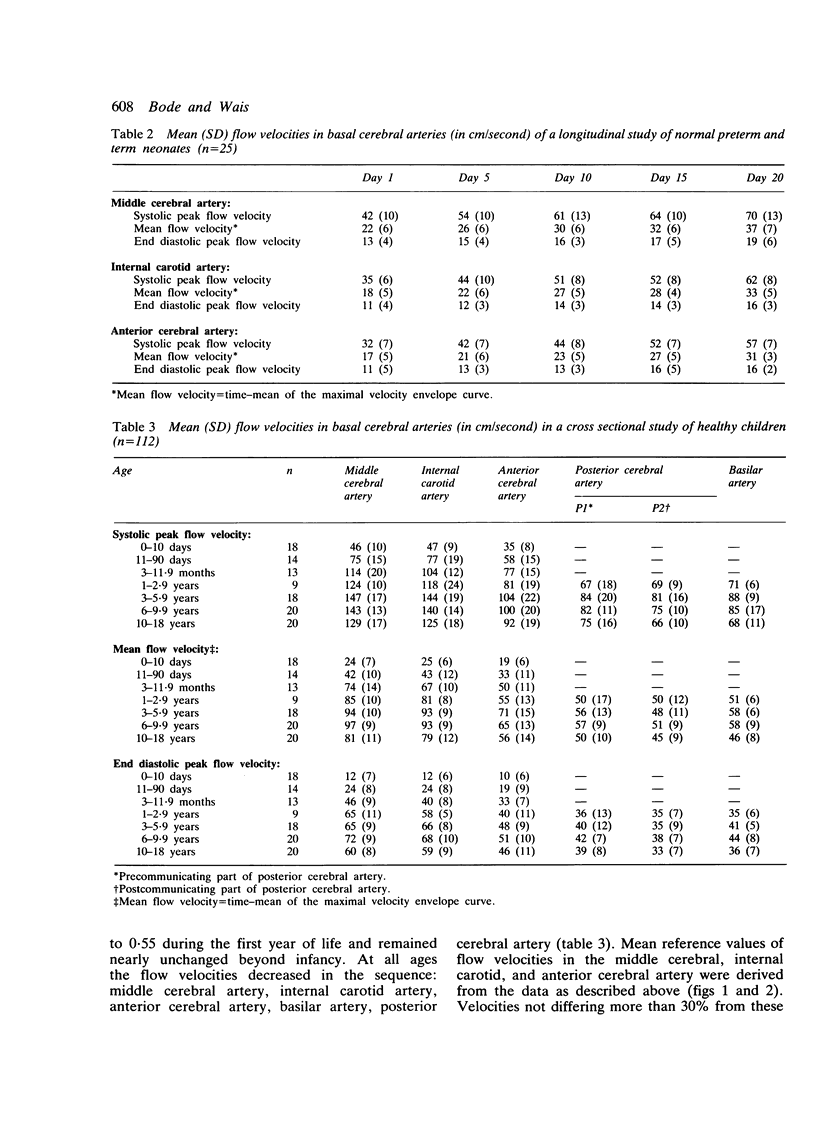
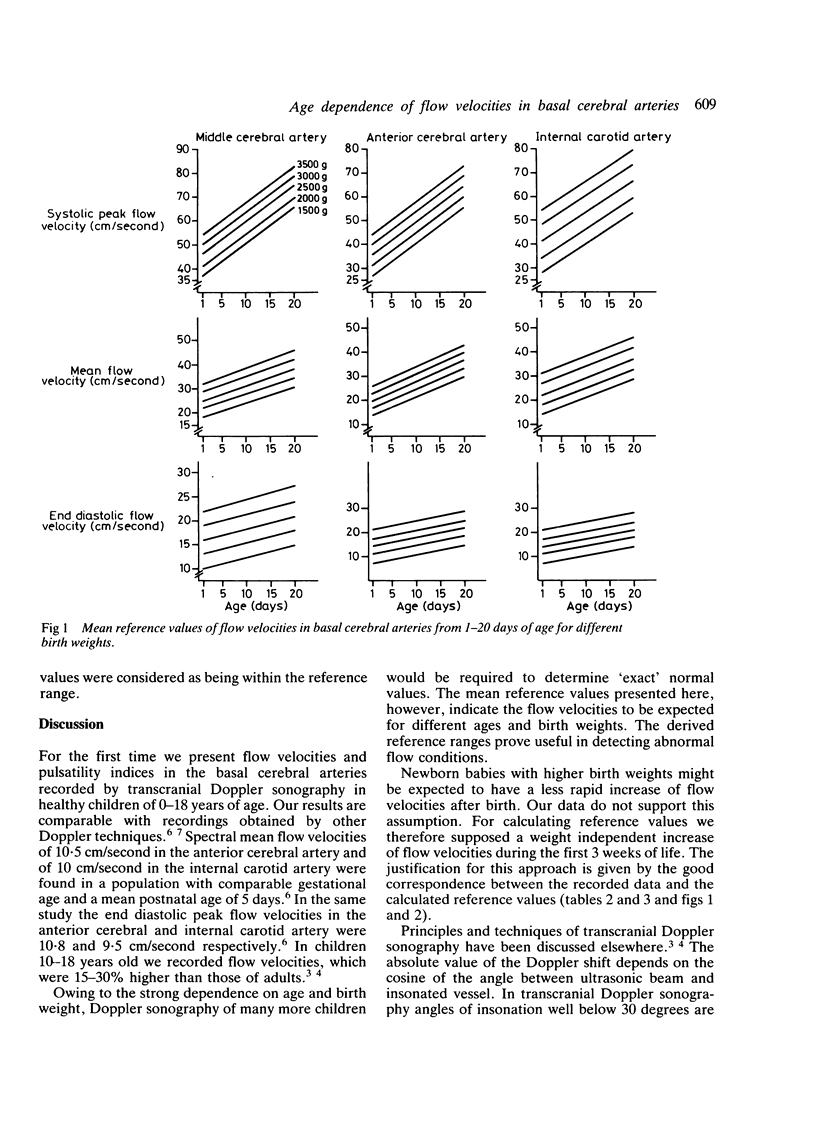
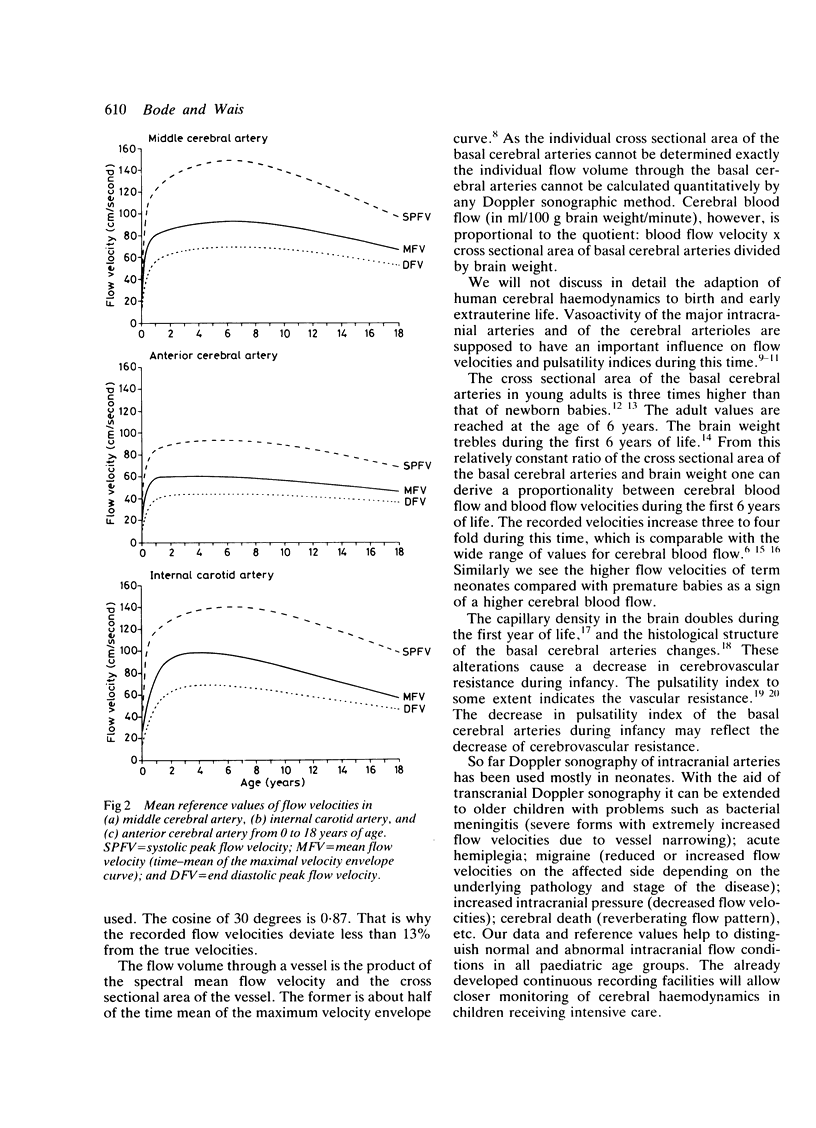
Flow velocities in the basal cerebral arteries were studied by transcranial Doppler sonography. A longitudinal study was undertaken on 25 healthy newborn babies during the first 20 days of life, and a cross sectional study was performed on 112 healthy children between 1 day and 18 years of age. A rapid linear increase of flow velocities was found within the first 20 days with higher velocities in neonates of higher birth weight and gestational age. Maximal values were recorded at the age of 5 to 6 years. After that the velocities decreased linearly to 70% of their maximum at the age of 18 years. Reference values were derived from the data considering age and birth weight. The increasing flow velocities probably reflect the increasing cerebral blood flow during the first years of life. Our results also support the hypothesis of a decrease in cerebrovascular resistance during infancy. With the technique of transcranial Doppler sonography and the introduced reference values normal and abnormal intracranial flow velocities can now be assessed by non-invasive methods in all paediatric age groups.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaslid R., Markwalder T. M., Nornes H. Noninvasive transcranial Doppler ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg. 1982 Dec;57(6):769–774. doi: 10.3171/jns.1982.57.6.0769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnolds B. J., von Reutern G. M. Transcranial Doppler sonography. Examination technique and normal reference values. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1986 Feb;12(2):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(86)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAKEMORE W. S., FORSTER R. E., MORTON J. W., OGILVIE C. M. A standardized breath holding technique for the clinical measurement of the diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jan;36(1 Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI103402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bada H. S., Hajjar W., Chua C., Sumner D. S. Noninvasive diagnosis of neonatal asphyxia and intraventricular hemorrhage by Doppler ultrasound. J Pediatr. 1979 Nov;95(5 Pt 1):775–779. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80735-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bada H. S., Sumner D. S. Transcutaneous Doppler ultrasound: pulsatility index, mean flow velocity, end diastolic flow velocity, and cerebral blood flow. J Pediatr. 1984 Mar;104(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)81102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batton D. G., Hellmann J., Maisels M. J. Doppler-pulsatility index. Pediatrics. 1983 Feb;71(2):298–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIEMER K., HENN R. THE CAPILLARY DENSITY IN THE FRONTAL LOBE OF MATURE AND PREMATURE INFANTS. Biol Neonat. 1964;7:270–279. doi: 10.1159/000239929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbing J., Sands J. Quantitative growth and development of human brain. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Oct;48(10):757–767. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.10.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayton M. R., Skidmore R. Vasoactivity of the major intracranial arteries in newborn infants. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Mar;62(3):236–240. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.3.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis-Hansen B. Perinatal brain injury and cerebral blood flow in newborn infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1985 May;74(3):323–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen T. O., Greitz T. Normal size of the internal carotid, middle cerebral and anterior cerebral arteries. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1970 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1177/028418517001000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. H., Griffin E. A., Drumm J. E., Fitzgerald D. E., Duignan N. M. Continuous wave Doppler ultrasound in evaluation of cerebral blood flow in neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Sep;58(9):677–681. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.9.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisen G., Johansen K., Ellison P. H., Fredriksen P. S., Mali J., Friis-Hansen B. Cerebral blood flow in the newborn infant: comparison of Doppler ultrasound and 133xenon clearance. J Pediatr. 1984 Mar;104(3):411–418. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)81108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSLER O. Elastic tissue contents of the medial layer of the cerebral arteries. Differences between young and adult individuals. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1962;335:39–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00957609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorch G., Pfannschmidt J., Rabe H. Die nicht invasive Untersuchung der intrazerebralen Zirkulation bei Früh- und Neugeborenen mit der gepulsten Dopplersonographie. Grundlagen, Messtechnik, Referenzwerte. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1986 Nov;134(11):804–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch J. R., Traystman R. J., Rogers M. C. Cerebral blood flow measurement techniques in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1985 May;75(5):887–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEYDEL H. G. THE DIAMETERS OF THE CEREBRAL ARTERIES OF THE HUMAN FETUS. Anat Rec. 1964 Sep;150:79–88. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091500108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. P., Reid J. M. Quantitation of carotid stenosis with continuous-wave (C-W) Doppler ultrasound. Stroke. 1979 May-Jun;10(3):326–330. doi: 10.1161/01.str.10.3.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strassburg H. M., Niederhoff H., Sauer M. Die Doppler-sonographische Registrierung der Durchblutung intracranieller Gefässe beim Säugling. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1982 Aug;130(8):608–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


