Abstract
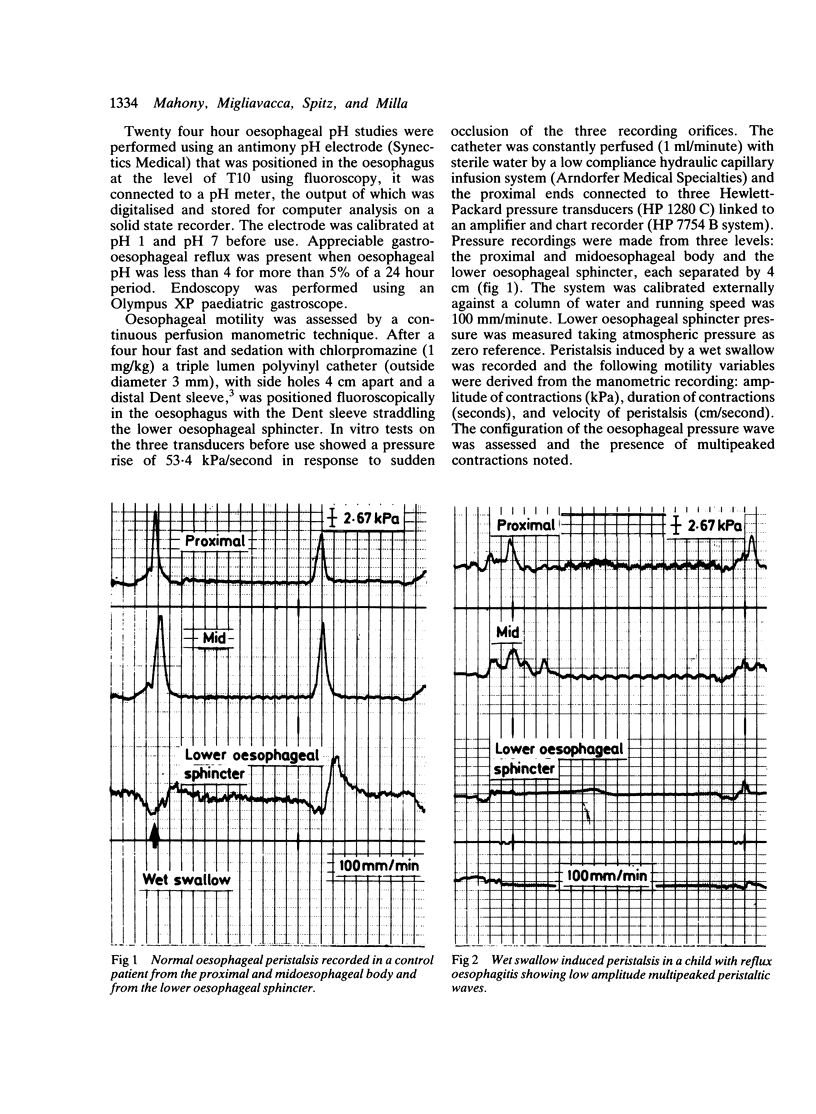
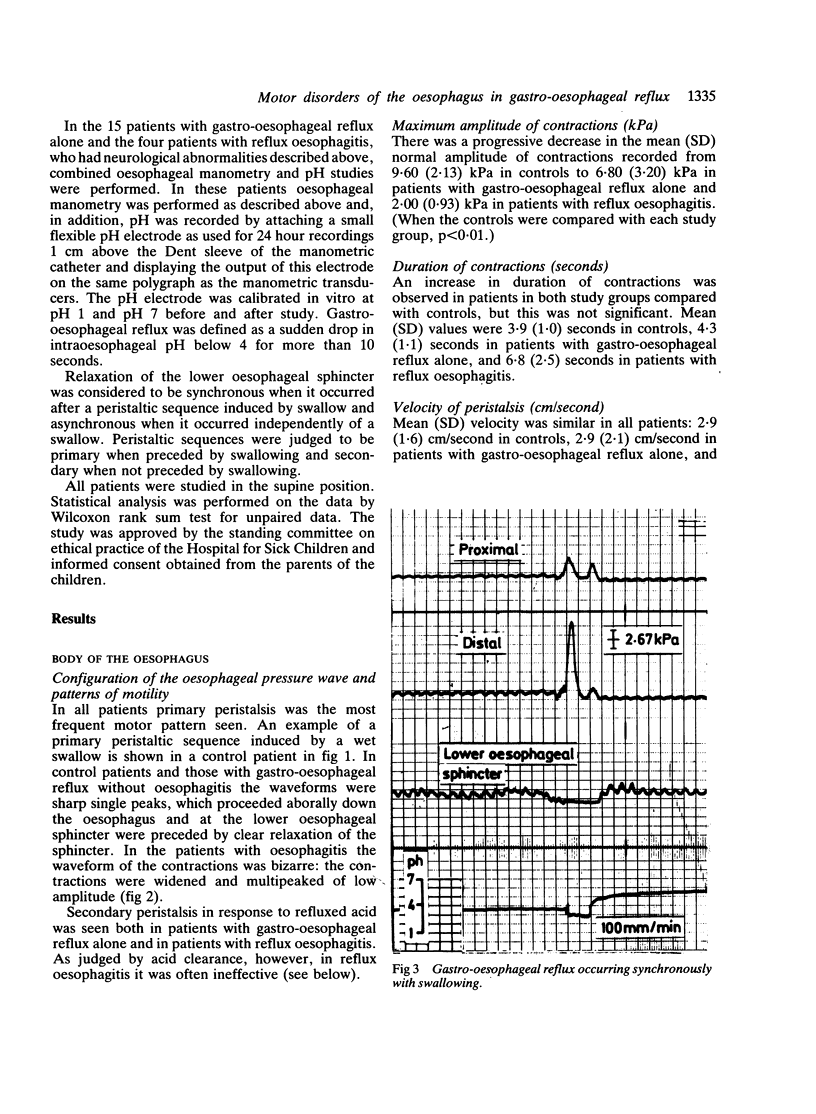
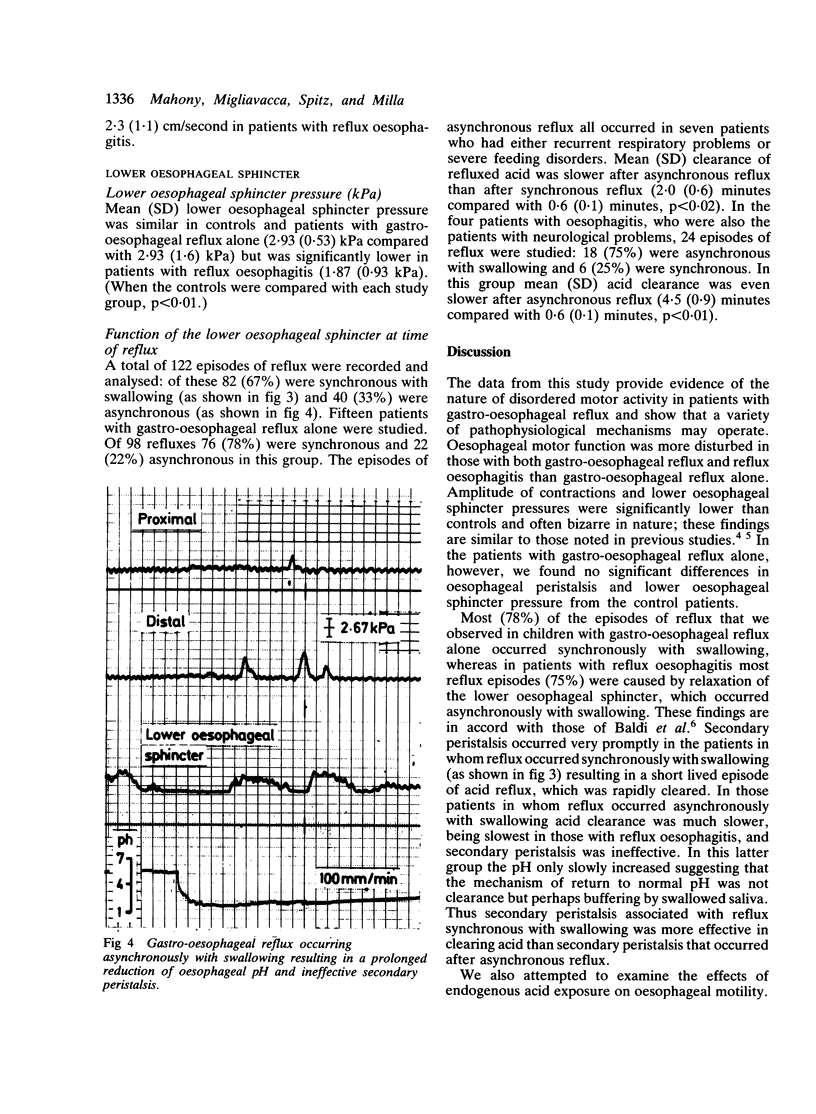
Mechanisms of gastro-oesophageal reflux were studied by oesophageal manometry and pH monitoring in 33 children: nine controls, 15 with gastro-oesophageal reflux alone, and nine with reflux oesophagitis. A total of 122 episodes of reflux were analysed in detail: 82 (67%) were synchronous with swallowing and 40 (33%) asynchronous. Infants with trivial symptoms had gastro-oesophageal reflux synchronous with swallowing, whereas those with serious symptoms had slower acid clearance and asynchronous reflux. There were significant differences in lower oesophageal sphincter pressure and amplitude of oesophageal contractions between controls and patients with both gastro-oesophageal reflux and reflux oesophagitis. In reflux oesophagitis there was a decrease in lower oesophageal sphincter pressure and the contractions had a bizarre waveform suggesting a neuropathic process.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldi F., Ferrarini F., Balestra R., Borioni D., Longanesi A., Miglioli M., Barbara L. Oesophageal motor events at the occurrence of acid reflux and during endogenous acid exposure in healthy subjects and in patients with oesophagitis. Gut. 1985 Apr;26(4):336–341. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.4.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cucchiara S., Staiano A., Capozzi C., Di Lorenzo C., Boccieri A., Auricchio S. Cisapride for gastro-oesophageal reflux and peptic oesophagitis. Arch Dis Child. 1987 May;62(5):454–457. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.5.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cucchiara S., Staiano A., Di Lorenzo C., D'Ambrosio R., Andreotti M. R., Prato M., De Filippo P., Auricchio S. Esophageal motor abnormalities in children with gastroesophageal reflux and peptic esophagitis. J Pediatr. 1986 Jun;108(6):907–910. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80925-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. A new technique for continuous sphincter pressure measurement. Gastroenterology. 1976 Aug;71(2):263–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J., Dodds W. J., Friedman R. H., Sekiguchi T., Hogan W. J., Arndorfer R. C., Petrie D. J. Mechanism of gastroesophageal reflux in recumbent asymptomatic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):256–267. doi: 10.1172/JCI109667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds W. J., Dent J., Hogan W. J., Helm J. F., Hauser R., Patel G. K., Egide M. S. Mechanisms of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with reflux esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 16;307(25):1547–1552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212163072503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst J. J. Gastroesophageal reflux. J Pediatr. 1981 Jun;98(6):859–870. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80576-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillemeier A. C., Grill B. B., McCallum R., Gryboski J. Esophageal and gastric motor abnormalities in gastroesophageal reflux during infancy. Gastroenterology. 1983 Apr;84(4):741–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahrilas P. J., Dodds W. J., Hogan W. J., Kern M., Arndorfer R. C., Reece A. Esophageal peristaltic dysfunction in peptic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):897–904. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90692-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo F. D., Dodds W. J., Soergel K. H., Arndorfer R. C., Helm J. F., Hogan W. J. Multipeaked esophageal peristaltic pressure waves in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gastroenterology. 1985 Feb;88(2):485–491. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90511-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony M. J., Kennedy J. D., Leaf A., Matthew D. J., Milla P. J. Brain stem glioma presenting as gastro-oesophageal reflux. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Jul;62(7):731–733. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.7.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


