Abstract
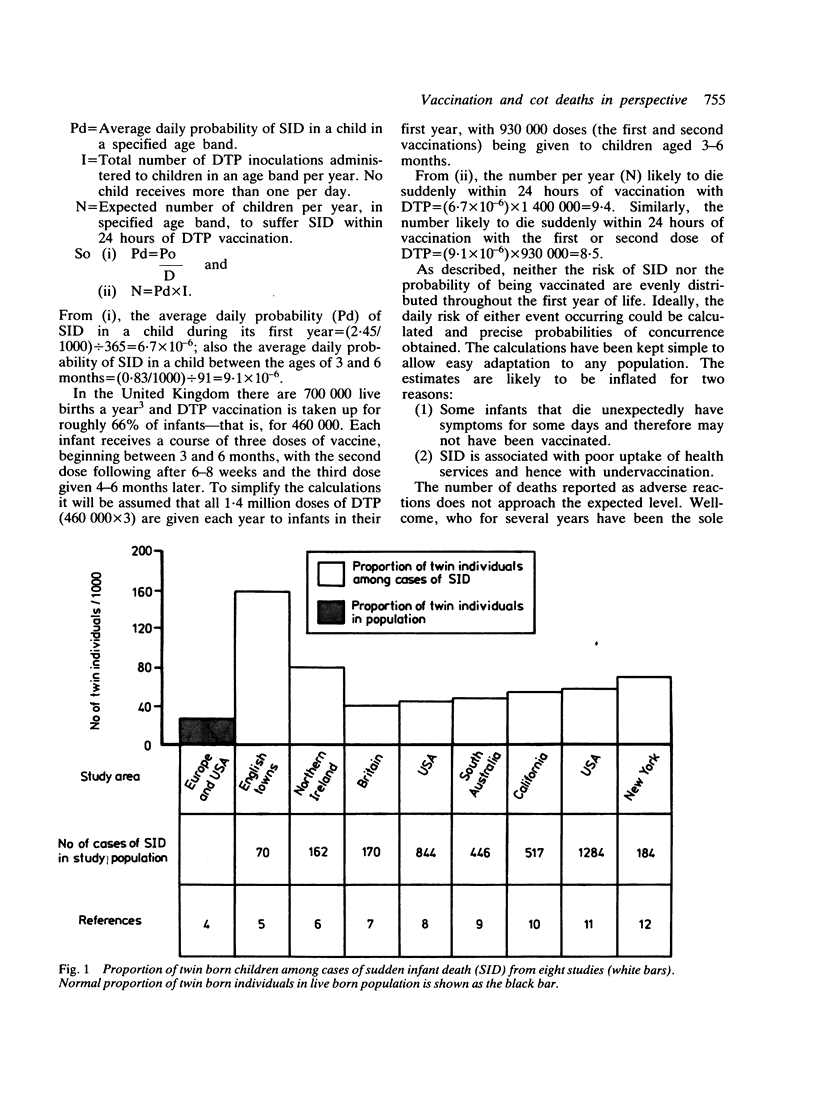
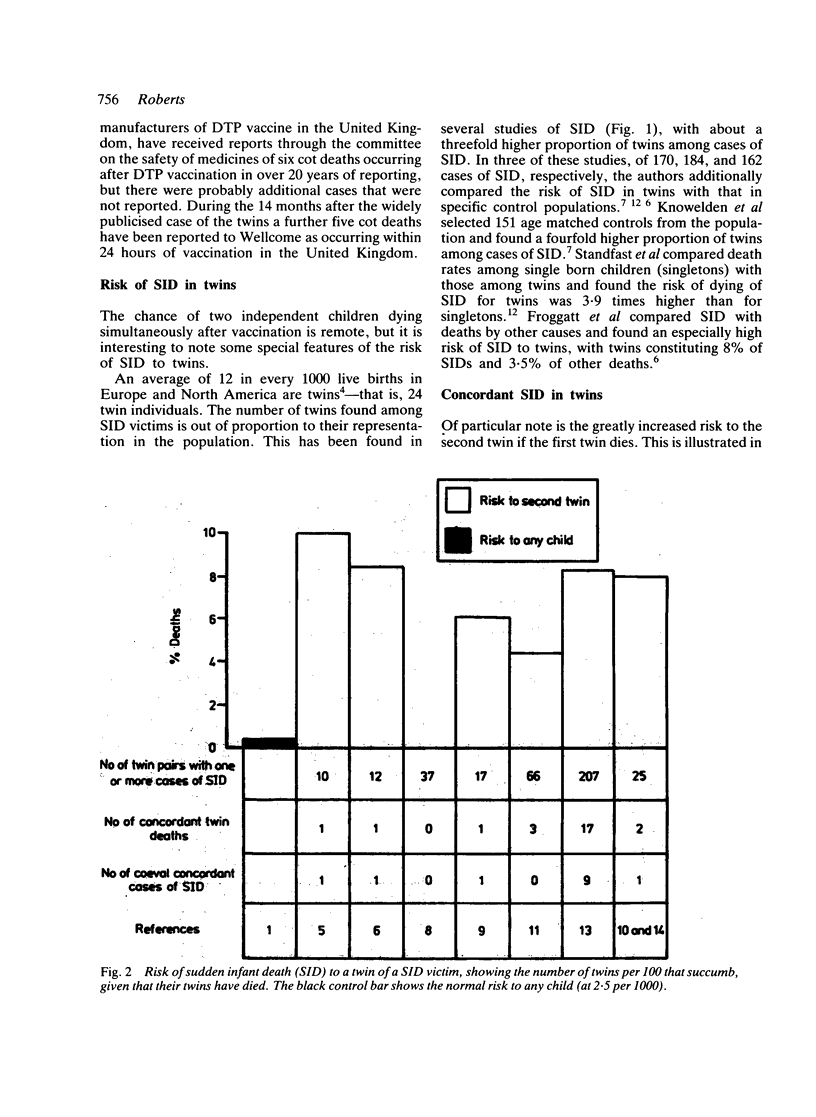
In 1985 twin boys simultaneously succumbed to sudden unexpected deaths two to three hours after vaccination with diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccine (DTP). This occurrence again raises the question of whether an association of sudden infant death (SID) with vaccination is other than temporal. Taking the incidence of SID in conjunction with rates of infant vaccination in the United Kingdom, nine infants would be expected to die, each year by chance alone, suddenly within 24 hours of (and within each 24 hour period succeeding) vaccination with DTP. Twins are at a greater risk of SID than single born infants and occasionally are found dead together. A number of studies into DTP vaccination as a risk factor in SID have shown that SID is less common in vaccinated than in unvaccinated infants.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baraff L. J., Ablon W. J., Weiss R. C. Possible temporal association between diphtheria-tetanus toxoid-pertussis vaccination and sudden infant death syndrome. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;2(1):7–11. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198301000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass M., Kravath R. E., Glass L. Death-scene investigation in sudden infant death. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 10;315(2):100–105. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607103150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black L., David R. J., Brouillette R. T., Hunt C. E. Effects of birth weight and ethnicity on incidence of sudden infant death syndrome. J Pediatr. 1986 Feb;108(2):209–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80984-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKE R. T., WELCH R. G. A STUDY IN COT DEATH. Br Med J. 1964 Dec 19;2(5424):1549–1554. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5424.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery J. L. Families in which two or more cot deaths have occurred. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):313–315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90839-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froggatt P., Lynas M. A., MacKenzie G. Epidemiology of sudden unexpected death in infants ('cot death') in Northern Ireland. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1971 Aug;25(3):119–134. doi: 10.1136/jech.25.3.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulginiti V. A. Sudden infant death syndrome, diphtheria-tetanus toxoid-pertussis vaccination and visits to the doctor: chance association or cause and effect? Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;2(1):5–6. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198301000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Heldt G., Powell N., Riley R. Small upper airway in near-miss sudden infant death syndrome infants and their families. Lancet. 1986 Feb 22;1(8478):402–407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrubec Z., Robinette C. D. The study of human twins in medical research. N Engl J Med. 1984 Feb 16;310(7):435–441. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198402163100706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irgens L. M., Skjaerven R., Peterson D. R. Prospective assessment of recurrence risk in sudden infant death syndrome siblings. J Pediatr. 1984 Mar;104(3):349–351. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)81093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A., Blum D., Muller M. F., Montauk L., Bochner A., Monod N., Plouin P., Samson-Dollfus D., Delagree E. H. Sudden infant death syndrome in a twin: a comparison of sibling histories. Pediatrics. 1986 Jul;78(1):146–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keens T. G., Ward S. L., Gates E. P., Andree D. I., Hart L. D. Ventilatory pattern following diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis immunization in infants at risk for sudden infant death syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Oct;139(10):991–994. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140120037024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus J. F., Borhani N. O. Post-neonatal sudden unexplained death in Califoria: a cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Jun;95(6):497–510. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer E. A., Jr, Jones P. K., Adelson L. DTP and SIDS. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;2(6):492–493. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198311000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. R., Chinn N. M., Fisher L. D. The sudden infant death syndrome: repetitions in families. J Pediatr. 1980 Aug;97(2):265–267. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80491-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. R., Sabotta E. E., Daling J. R. Infant mortality among subsequent siblings of infants who died of sudden infant death syndrome. J Pediatr. 1986 Jun;108(6):911–914. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80926-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock T. M., Miller E., Mortimer J. Y., Smith G. Symptoms after primary immunisation with DTP and with DT vaccine. Lancet. 1984 Jul 21;2(8395):146–149. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards I. D., McIntosh H. T. Confidential inquiry into 226 consecutive infant deaths. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Oct;47(255):697–706. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.255.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smialek J. E. Simultaneous sudden infant death syndrome in twins. Pediatrics. 1986 Jun;77(6):816–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southall D. P., Talbert D. G., Johnson P., Morley C. J., Salmons S., Miller J., Helms P. J. Prolonged expiratory apnoea: a disorder resulting in episodes of severe arterial hypoxaemia in infants and young children. Lancet. 1985 Sep 14;2(8455):571–577. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90583-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiers P. S. Estimated rates of concordancy for the Sudden Infant Death Syndrome in twins. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Jul;100(1):1–7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standfast S. J., Jereb S., Janerich D. T. The epidemiology of sudden infant death in upstate New York: II: birth characteristics. Am J Public Health. 1980 Oct;70(10):1061–1067. doi: 10.2105/ajph.70.10.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. M., Emergy J. L. Immunization and cot deaths. Lancet. 1982 Sep 25;2(8300):721–721. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90745-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


