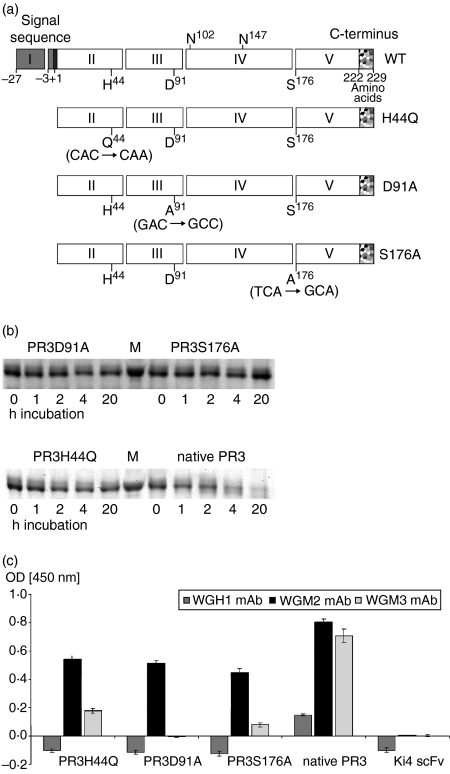
Figure 1.
Design, expression and characterization of mutated PR3. (a) Design of mutated PR3. Schematic representation of the PR3 variants. The signal sequence, prosequences, and C-terminal sequence are shown as grey, black and speckled boxes, respectively. Exons are indicated with the exon number in the box. The amino acids H44, D91 and S176 forming the catalytic triad and the two glycosylation sites on N102 and N147 are marked at the wild-type PR3. PR3 variants are listed below, the introduced point mutations are written in parenthesis. (b) Enzymatic activity of rPR3; 500 ng PR3 variants were incubated with 500 ng PR3H44Q-Ang fusion protein as substrate for 1, 2, 4 and 20 hr at room temperature. Then, protein decomposition was measured by SDS–PAGE analysis. Proteins were visualized by Coomassie staining. (c) Affinity of rPR3 variants to anti-PR3 mAb. The rPR3 constructs were tested by direct ELISA using WGH1, WGM2, or WGM3 mAb. Bound antibody was detected by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody. Therefore rPR3 was coated with a final concentration of 100 ng. The anti-CD30 scFv fragment was used as a non-specific control. Error bars represent SD values of triplicates.