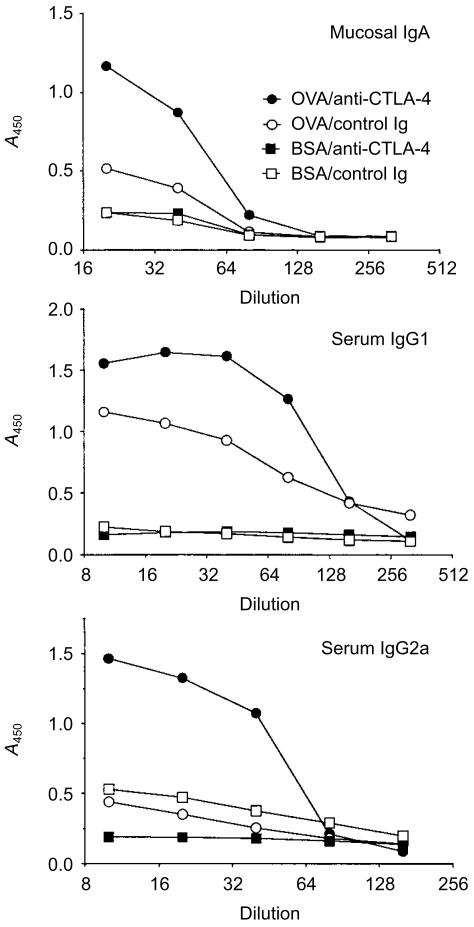
Figure 5.
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) blockade promotes specific antibody responses following mucosal exposure of ovalbumin (OVA). After transfer of transgenic cells, BALB/c mice were fed with bovine serum albumin (BSA) or ovalbumin (OVA) and injected with control immunoglobulin G (IgG) or anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody (mAb), as described in the legend to Fig. 1b. Three days after the last feeding, faeces and sera were collected from all mice, and faecal anti-OVA immunoglobulin (Ig) A, seral anti-OVA IgG1 and seral anti-OVA IgG2a were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).20 The differences between the OVA/anti-CTLA-4 group and all other groups were statistically significant (P < 0·05). The differences between the OVA/control IgG group and the BSA-treated groups were statistically significant only for serum IgG1 (P < 0·05). Data shown are representative of three separate experiments. A450, absorbance at 450 nm.