Abstract
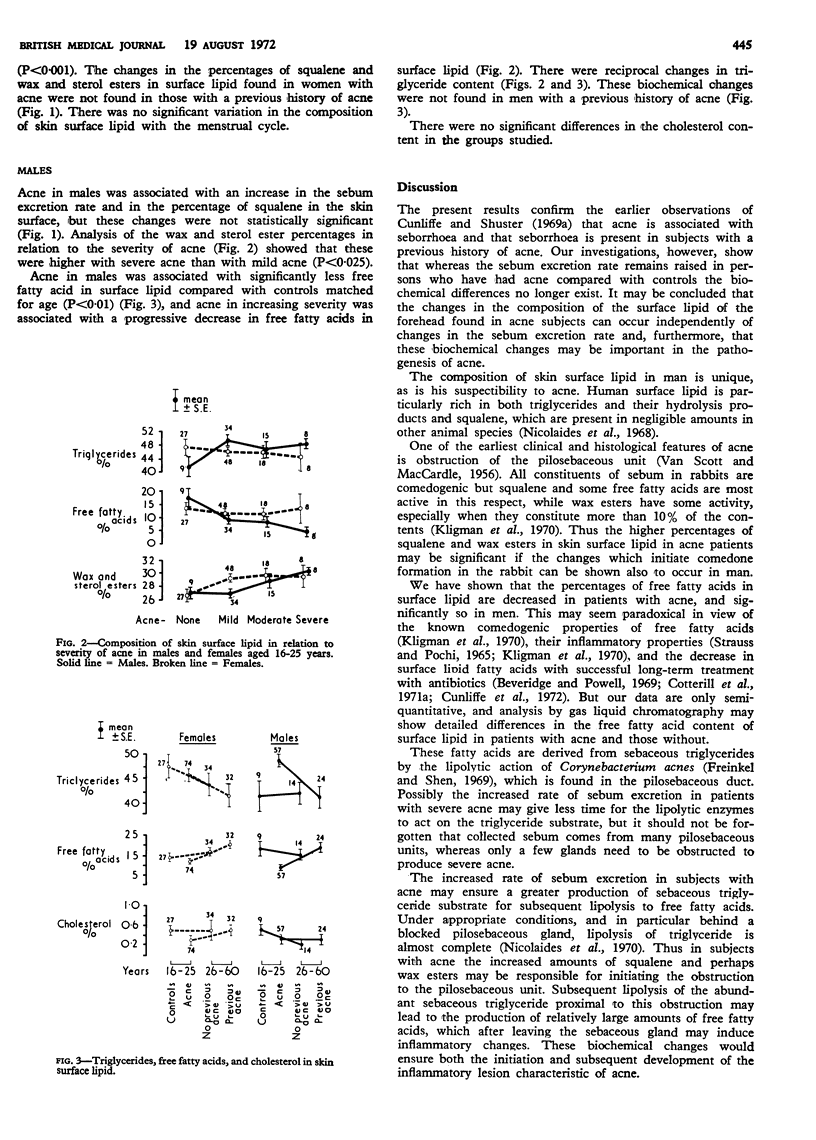
The composition of the lipid of the forehead skin surface and the sebum excretion rate were determined in 217 subjects and controls. Acne was associated with an increase in serum excretion rate and in the squalene and wax and sterol esters in surface lipid. The changes in sebum excretion rate and squalene were statistically significant only in women, but acne in men was associated with a significant decrease in the free fatty acid content or surface lipid.
The increased amounts of squalene and wax esters may lead to pilosebaceous obstruction in acne subjects. The increased sebum excretion rate in acne may ensure increased production of sebaceous triglyceride substrate available for lipolysis to irritant free fatty acids, which may then mediate the inflammatory changes of acne.
Full text
PDF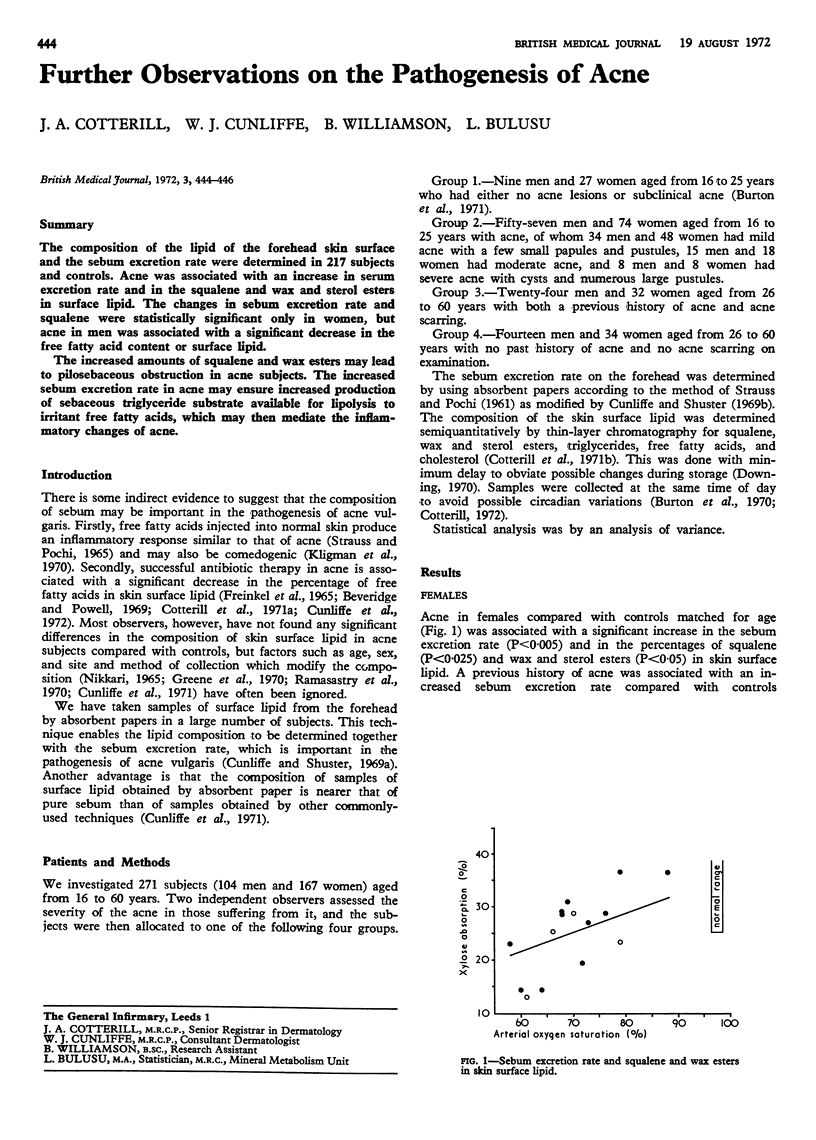

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beveridge G. W., Powell E. W. Sebum changes in acne vulgaris treated with tetracycline. Br J Dermatol. 1969 Jul;81(7):525–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1969.tb16027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton J. L., Cunliffe W. J., Shuster S. Circadian rhythm in sebum excretion. Br J Dermatol. 1970 May;82(5):497–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1970.tb02211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton J. L., Cunliffe W. J., Stafford I., Shuster S. The prevalence of acne vulgaris in adolescence. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Aug;85(2):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb07195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotterill J. A., Cunliffe W. J., Williamson B., Forster R. A. A semiquantitative method for the biochemical analysis of sebum. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Jul;85(1):35–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb07175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotterill J. A., Cunliffe W. J., Williamson B. The effect of trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole on sebum excretion rate and biochemistry in acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Aug;85(2):130–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb07197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe W. J., Cotterill J. A., Williamson B. The effect of a medicated wash on acne, sebum excretion rate and skin surface lipid composition. Br J Dermatol. 1972 Mar;86(3):311–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1972.tb02237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe W. J., Cotterill J. A., Williamson B. Variations in skin surface lipid composition with different sampling techniques. I. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Jul;85(1):40–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb07176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe W. J., Shuster S. Pathogenesis of acne. Lancet. 1969 Apr 5;1(7597):685–687. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92642-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe W. J., Shuster S. The rate of sebum excretion in man. Br J Dermatol. 1969 Sep;81(9):697–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1969.tb16211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel R. K., Shen Y. The origin of free fatty acids in sebum. II. Assay of the lipases of the cutaneous bacteria and effects of pH. J Invest Dermatol. 1969 Dec;53(6):422–427. doi: 10.1038/jid.1969.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel R. K., Strauss J. S., Yip S. Y., Pochi P. E. Effect of tetracycline on the composition of sebum in acne vulgaris. N Engl J Med. 1965 Oct 14;273(16):850–854. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196510142731604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. S., Downing D. T., Pochi P. E., Strauss J. S. Anatomical variation in the amount and composition of human skin surface lipid. J Invest Dermatol. 1970 Mar;54(3):240–247. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12280318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligman A. M., Wheatley V. R., Mills O. H. Comedogenicity of human sebum. Arch Dermatol. 1970 Sep;102(3):267–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaides N., Ansari M. N., Fu H. C., Lindsay D. G. Lipid compsition on comedones compared with that of human skin surface in acne patients. J Invest Dermatol. 1970 Jun;54(6):487–495. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaides N., Fu H. C., Rice G. R. The skin surface lipids of man compared with those of eighteen species of animals. J Invest Dermatol. 1968 Aug;51(2):83–89. doi: 10.1038/jid.1968.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasastry P., Downing D. T., Pochi P. E., Strauss J. S. Chemical composition of human skin surface lipids from birth to puberty. J Invest Dermatol. 1970 Feb;54(2):139–144. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12257164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. S., Pochi P. E. Intracutaneous injection of sebum and comedones. Histological observations. Arch Dermatol. 1965 Oct;92(4):443–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN SCOTT E. J., MACCARDLE R. C. Keratinization of the duct of the sebaceous gland and growth cycle of the hair follicle in the histogenesis of acne in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1956 Dec;27(6):405–429. doi: 10.1038/jid.1956.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


