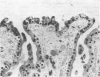
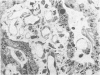
Abstract
5-Aminosalicylic acid given to rats as a single intravenous injection led to necrosis of the proximal convoluted tubules and of the renal papilla. These two lesions developed at the same time and the cortical lesions did not appear to be a consequence of the renal papillary necrosis. Since the compound possesses the molecular structure both of a phenacetin derivative and of a salicylate these observations may be relevant to the problem of renal damage incident to abuse of analgesic compounds and suggest the possibility that in this syndrome cortical lesions may develop independently of renal papillary necrosis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calder I. C., Funder C. C., Green C. R., Ham K. N., Tange J. D. Comparative nephrotoxicity of aspirin and phenacetin derivatives. Br Med J. 1971 Nov 27;4(5786):518–521. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5786.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. R., Ham K. N., Tange J. D. Kidney lesions induced in rats by p-aminophenol. Br Med J. 1969 Jan 18;1(5637):162–164. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5637.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANNGREN A., HANSSON E., SVARTZ N., ULLBERG S. Distribution and metabolism of salicyl-azo-sulfapyridine. I. A study with C-14-5-amino-salicylic acid. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Jan;173:61–72. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1963.tb16506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid-Smith P. Pathogenesis of the renal lesion associated with the abuse of analgesics. Lancet. 1967 Apr 22;1(7495):859–862. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILNE M. D., MUEHRCKE R. C., HEARD B. E. Potassium deficiency and the kidney. Br Med Bull. 1957 Jan;13(1):15–18. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]