Abstract
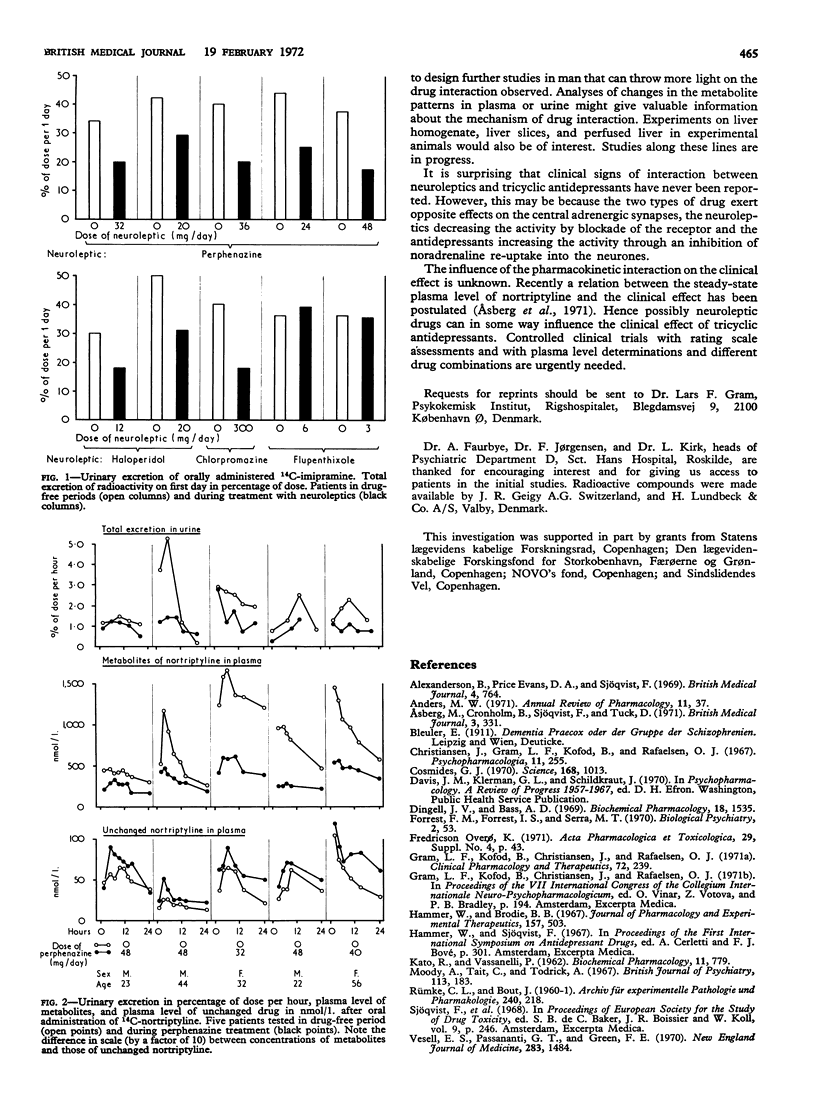
Total urinary excretion of radioactivity after oral or intravenous administration of a test dose of 14C-imipramine was measured in eight patients. They were tested before, during, and after treatment with neuroleptics. Excretion diminished while the patients were being treated with perphenazine, haloperidol, or chlorpromazine, though not during flupenthixol treatment.
Total urinary excretion of radioactivity and plasma levels of metabolites and unchanged drug were measured in five patients after a test dose of 14C-nortriptyline. Each patient was tested before and again during perphenazine treatment. In all patients perphenazine treatment caused: (1) decrease of total urinary excretion, (2) decreased plasma level of metabolites, and (3) increased plasma level of unchanged nortriptyline.
These results indicate that neuroleptics inhibit the metabolism of tricyclic antidepressants in man.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexanderson B., Evans D. A., Sjöqvist F. Steady-state plasma levels of nortriptyline in twins: influence of genetic factors and drug therapy. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 27;4(5686):764–768. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5686.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders M. W. Enhancement and inhibition of drug metabolism. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1971;11:37–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.11.040171.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asberg M., Crönholm B., Sjöqvist F., Tuck D. Relationship between plasma level and therapeutic effect of nortriptyline. Br Med J. 1971 Aug 7;3(5770):331–334. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5770.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J., Gram L. F., Kofod B., Rafaelsen O. J. Imipramine metabolism in man. A study of urinary metabolites after administration of radioactive imipramine. Psychopharmacologia. 1967 Aug 4;11(3):255–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00405231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosmides G. J. Pharmacology-toxicology. Science. 1970 May 22;168(3934):1013–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3934.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingell J. V., Bass A. D. Inhibition of the hepatic metabolism of amphetamine by desipramine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Jun;18(6):1535–1538. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90271-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest F. M., Forrest I. S., Serra M. T. Modification of chlorpromazine metabolism by some other drugs frequently administered to psychiatric patients. Biol Psychiatry. 1970 Jan;2(1):53–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram L. F., Kofod B., Christiansen J., Rafaelsen O. J. Imipramine metabolism: pH-dependent distribution and urinary excretion. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1971 Mar-Apr;12(2):239–244. doi: 10.1002/cpt1971122part1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer W. M., Brodiet B. B. Application of isotope derivative technique to assay of secondary amines: estimation of desipramine by acetylation with H3-acetic anhydride. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Sep;157(3):503–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATO R., VASSANELLI P. Induction of increased meprobamate metabolism in rats pretreated with some neurotropic drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1962 Aug;11:779–794. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(62)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody J. P., Tait A. C., Todrick A. Plasma levels of imipramine and desmethylimipramine during therapy. Br J Psychiatry. 1967 Feb;113(495):183–193. doi: 10.1192/bjp.113.495.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S., Passananti G. T., Greene F. E. Impairment of drug metabolism in man by allopurinol and nortriptyline. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 31;283(27):1484–1488. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012312832703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


