Abstract
Studies in animals demonstrate a crucial role for the amygdala in emotional and social behavior, especially as related to fear and aggression. Whereas lesion and functional-imaging studies in humans indicate the amygdala’s participation in assessing the significance of nonverbal as well as paralinguistic cues, direct evidence for its role in the emotional processing of linguistic cues is lacking. In this study, we use a modified Stroop task along with a high-sensitivity neuroimaging technique to target the neural substrate engaged specifically when processing linguistic threat. Healthy volunteer subjects were instructed to name the color of words of either threat or neutral valence, presented in different color fonts, while neural activity was measured by using H215O positron-emission tomography. Bilateral amygdalar activation was significantly greater during color naming of threat words than during color naming of neutral words. Associated activations were also noted in sensory-evaluative and motor-planning areas of the brain. Thus, our results demonstrate the amygdala’s role in the processing of danger elicited by language. In addition, the results reinforce the amygdala’s role in the modulation of the perception of, and response to, emotionally salient stimuli. The current study further suggests conservation of phylogenetically older mechanisms of emotional evaluation in the context of more recently evolved linguistic function.
Both lesion and functional-imaging studies in humans have demonstrated the amygdala’s role in the visual recognition of emotional facial expressions (1–3). Studies in humans further indicate the amygdala’s participation in assessing the significance of paralinguistic emotional stimuli (1, 4). In humans, emotional cues are also transmitted linguistically. Evidence for the amygdala’s function in the emotional processing of linguistic cues, however, has yet to be described. In this experiment, we sought to test the hypothesis that the human amygdala is involved in the emotional processing of linguistic cues specifically related to threat.
METHODS
Subjects.
Six healthy, right-handed subjects, as assessed by the Edinburgh Handedness Inventory (5), (four women and two men, mean age 26.4) took part in this study. All subjects were without past history of neurologic illness or psychiatric history, as determined by using the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM IV Disorders (6) and were not taking any medication. All subjects gave informed consent, in accordance with guidelines established by the Subcommittee on Human Studies at New York Hospital–Cornell Medical Center.
Activation Paradigm.
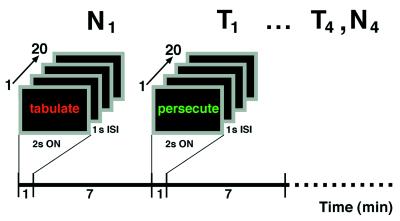
During the scanning session, there was a total of 12 scans—four repetitions of three conditions (activation, control, and rest). During each of the activation and control trials, subjects viewed a blocked trial of 20 nonrepeating words counterbalanced within and across subjects. Word font consisted of one of five colors (red, green, white, blue, or yellow) which was pseudorandomly generated such that no color was consecutively repeated. Words were categorized by valence, as confirmed by forced-choice classification by 10 naive viewers. All blocked conditions of either threat-valence or neutral-valence words were matched for word length, syllable number, and part of speech (see Table 1 for complete word list). Subjects were instructed to name the color of each word as it was displayed on a computer screen with stimulus parameters of 2 seconds on-time, and 1 second of interstimulus interval (see Fig. 1 for study design). By using a control task that differed from the activation task only by emotional valence, our modified Stroop paradigm was designed explicitly to dissociate the emotional processing of a threat valence, linguistic probe from the selective attention aspect of the task (7).
Table 1.
Word List
| Neutral words
|
Threat words
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| moderate | consider | circle | categorize | persecute | assassinate | conspiracy | mutilate |
| list | review | delegate | mitten | threat | bruise | loathe | bloodstain |
| reside | brushing | plastic | parking | destroy | hijack | assault | injure |
| sweater | custom | arrange | cups | whisper | gun | harass | hate |
| dial | stretch | gesture | inhabit | slaughter | pursue | investigation | contaminate |
| forward | license | spin | paper | death | rape | trap | torture |
| transfer | designate | ceiling | compute | bludgeon | suffocate | capture | hostage |
| accompany | bookcase | render | brushes | hit | wound | damage | suspicion |
| wheel | enlist | form | randomize | attach | abhor | beat | follow |
| locate | number | carbonate | fan | spy | failure | suspect | blindfold |
| objective | sheets | desk | instruct | prisoner | kidnap | annihilate | imprison |
| walking | reside | participate | calendar | distrust | suspicious | deceive | whip |
| hats | syllable | candle | percent | bully | poison | bullet | mislead |
| reclaim | trunk | wash | collecting | torment | molest | kill | blame |
| sample | rotate | column | bowl | evil | knife | corruption | strangle |
| generate | towel | tabulate | formation | execute | disturb | arrest | danger |
| invent | demonstrate | sideline | cardboard | whipcord | betrayal | suffer | intrude |
| label | pen | revise | translate | condemn | stab | chase | conspire |
| retrieve | journey | placement | navigate | opposition | abuse | punish | stare |
| folder | reiterate | trend | repeat | steal | sinister | overthrow | accuse |
Figure 1.
Stimulus parameters and experimental design. During the scanning session, four blocked trials of 20 words of either threat (T) or neutral (N) valence were displayed in one of five pseudorandomly generated colors with 2 second on-time and 1 second interstimulus interval. Image acquisition lasted 90 seconds. Stimulus presentation lasted 60 seconds, starting with the rise of the whole-brain time-activity curve.
Positron-Emission Tomography (PET) Scan Acquisition.
During each scan, subjects received a total of 8 MBq/kg H215O through a forearm cannula by using a high-sensitivity slow-bolus technique (8). The distribution of H215O was measured as an index of neuronal activity by using a General Electric Advance PET scanner in three-dimensional mode. Images were reconstructed into 35 planes using a Hanning filter, resulting in 4.5-mm transaxial and 5.2-mm axial resolution (full-width at half-maximum). Image acquisition lasted 90 seconds. Stimulus presentation lasted 60 seconds, starting with the rise of the whole-brain time-activity curve.
Statistical Analysis.
PET data were analyzed by using statistical parametric mapping (SPM96) software from the Wellcome Department of Cognitive Neurology, London (9, 10). The images were realigned to correct for slight head movement and spatially normalized to a standard stereotactic coordinate space (voxel size 2 × 2 × 4). The scans were then smoothed by using a 15-mm Gaussian filter. Regional cerebral blood flow was adjusted to a global mean of 50 ml per 100 gm per min. Predetermined contrasts of the condition effects at each voxel were assessed by using a multiple-regressions analysis including normalization for global blood flow according to the General Linear Model. Probability was determined according to the theory of random fields (9). Given our a priori hypotheses concerning amygdalar activation, a threshold of P < 0.01, uncorrected, was used.
Behavioral Analysis. Before scanning, color naming was assessed with 1 run of 10 trials of an incongruent classical Stroop interference task (color naming of color words of differing color font) with identical stimulus on-time and interstimulus interval to the scanning task. All subjects performed this prescan task with 100% proficiency.
During the scanning session, reaction-time measures in milliseconds, as defined by time from stimulus presentation onset to start of verbal response, were recorded by computer. A mixed-effect random regression model was used to compare the reaction times across the two word types (11).
RESULTS
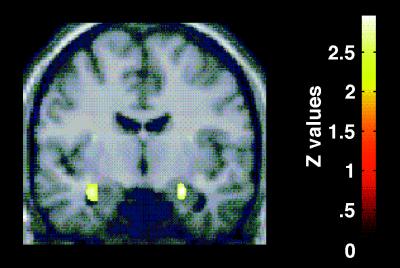
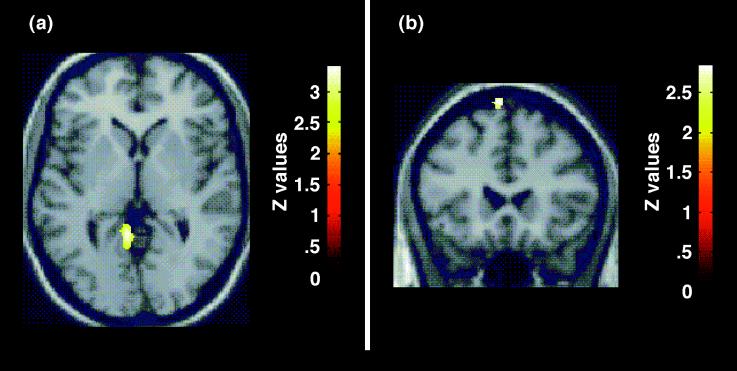
As predicted, the regional cerebral blood flow pattern produced by the color naming of threat-valence words (contrasted with neutral-valence words) demonstrated bilateral amygdalar activation (Z = 2.97 on right, Z = 2.93 on left) (Table 2, Fig. 2). In addition, left lingual gyrus [Brodmann’s area (BA) 19]/posterior parahippocampal gyrus (BA30) activation was observed (Z = 3.41) (Table 2, Fig. 3). Left premotor (BA6) activation was noted (Z = 2.93) (Table 2, Fig. 3) and must, in the absence of an a priori hypothesis, be treated with caution. There was a small but significant difference in reaction times: color naming of threat-valence words (mean = 679.28; SD =108.71; 457 observations) vs. color naming of neutral-valence words (mean = 663.26; SD = 109.24; 456 observations; b = 15.94; Z = 2.30; P = 0.022). There was no significant effect for order (b = 0.030; Z = −0.50; P = 0.62).
Table 2.
Brain regions showing significant activation in comparison of processing of threat vs. neutral words
| Area | Coordinates*(x, y, z) | Voxels* | Z score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Right amygdala | 24, −8, −18 | 58 | 2.97 |
| Left amygdala | −32, −6, −18 | 96 | 2.93 |
| Left premotor cortex (BA6) | −6, 22, 70 | 57 | 2.93 |
| Left parahippocampal/lingual gyrus (BA30/BA19) | −6, −50, 0 | 324 | 3.41 |
Coordinates of the maximally activated voxel and the number of significant voxels in the associated cluster are shown here.
Figure 2.
Selective response to processing of threat words. A statistical parametric map (SPM) showing activation of the amygdala bilaterally. The SPM is the result of a preselected contrast of brain regions with a greater neuronal response to processing of threat words compared with neutral words. The contrasts are displayed at a threshold of P < 0.01, uncorrected. The SPM is displayed on a coronal slice (y = −8 mm) of a stereotactically transformed MRI image, x = 24, y = −8, z = −18; x = −32, y = −6, z = −18.
Figure 3.
Selective response to processing of threat words. (a) An SPM showing activation in the region of the left parahippocampal/lingual gyrus (BA 30/BA 19) in the contrast of processing of threat words compared with neutral words. The SPM is displayed on an axial slice (z = 0 mm) of a stereotactically transformed MRI image. (b) An SPM showing activation in the region of the left premotor cortex (BA 6). The SPM is displayed on a coronal slice (y = 22 mm) of a stereotactically transformed MRI image. The contrasts are displayed at a threshold of P < 0.01, uncorrected.
DISCUSSION
Our results provide direct evidence that the amygdala plays a role in the processing of visually presented linguistic threat. A previous PET study, using less sensitive techniques, a Stroop task with repeating, negative words that were not threat-valenced and which did not control for selective attention, described anterior and midcingulate, but not amygdalar, activation (12). A previous functional MRI study that used an emotional Stroop counting paradigm with threat- and neutral-valence words reported anterior cingulate, but not amygdalar, activation (13). The repeating nature of the stimuli used, and/or the possible decreased signal-to-noise ratio in the mesotemporal region at the base of the brain, may account for the lack of amygdalar activity in that study.
A recent human lesion study has shown deficits in social judgment based on facial expression in patients with amygdalar lesions (1). Whereas one study of a patient with bilateral amygdalar and striatal damage describes a deficit in the auditory recognition of paralinguistically presented fear and anger as conveyed by prosody (4), another more recent study of a patient with amygdalar damage alone does not (14). Electrical stimulation of the amygdala can induce fear, often accompanied by associated visceral and autonomic responses (15–17). The amygdala contains many cells responsive to faces seen (18, 19), however, the assertion of word-specific cells within the amygdala remains to be proven (20, 21).
The amygdaloid complex plays a critical role in the acquisition of a range of conditioned fear responses, as well (22–24). Visual, somatosensory, and auditory information is transmitted to the amygdala by a series of indirect, modality-specific thalamocorticoamygdalar pathways, as well as by direct thalamoamygdalar pathways (25). Within the amygdaloid complex, information processing takes place along numerous highly organized parallel pathways with extensive intraamygdaloid connections (26). The convergence of inputs in the lateral nucleus enables modulated stimulus representations to be summated (27, 28). Specific output pathways from the central nucleus and amygdalohippocampal area mediate complementary aspects of learning and behavioral expression connected with various emotional states (25). The amygdala is thus well positioned to play a role in rapid cross-modal emotional recognition.
In addition, anatomical studies of the primate amygdala demonstrate projections to virtually all levels of visual processing in the occipital and temporal cortex (29). Therefore, the amygdala is also critically placed to modulate visual input, based on affective significance, at a variety of levels along the cortical visual-processing stream. Left ventral lingual and fusiform gyrus activity has recently been described in association with the neural processing of visually presented words (30) and negatively valenced images (31). Activation in the lingual gyrus/parahippocampal gyrus on the left, in our study, may represent modulation by the amygdala of the ventral visual stream for words specifically signifying danger. In addition, although our study was not intended to engage memory, incidental encoding of episodic memory may well have occurred. Many studies have demonstrated greater incidental episodic memory for emotionally charged compared with neutral events (32, 33) and words (34). A recent PET study has shown that bilateral amygdalar activity during memory encoding correlated with enhanced episodic recognition memory for aversive visual stimuli (35). Left parahippocampal activity has been described during semantic memory tasks (36) and also in long-term encoding (37). Therefore, the bilateral amygdalar and left lingual/parahippocampal activity in our study may also represent affective modulation by the amygdala of enhanced semantic encoding in the left lingual/parahippocampal region for threat-valenced words.
Finally, the amygdala has strong connections to effector regions, including the hypothalamus, that are important for coordinating autonomic responses to complex environmental cues for conspecific survival as well as premotor and prefrontal areas that are necessary for rapid motor and behavioral responses to perceived threat (29, 38). Activation in the premotor region, in our study, may signify a preparatory component of the efferent network required for quick action to impending danger or perceived threat. This study, therefore, provides a framework for understanding the role of the amygdala in enhanced, modality-specific afferent and efferent processing required for the rapid evaluation of and response to threat. It further suggests conservation of phylogenetically older limbic mechanisms of emotional evaluation in the context of more recently evolved linguistic function.
Acknowledgments
We thank our subjects for their cooperation. We would also like to thank Ronald Blasberg, Ron Finn, and members of the Memorial-Sloan Kettering PET scanning facility. We would also like to thank the National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression and the De Witt-Wallace Fund of the New York Community Trust for their generous support.
ABBREVIATIONS
- BA
Brodmann’s area
- PET
positron emission tomography
- SPM
statistical parametric map
References
- 1.Adolphs R, Tranel D, Damasio A R. Nature (London) 1998;393:470–474. doi: 10.1038/30982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Morris J S, Friston K J, Buchel C, Frith C D, Young A W, Calder A J, Dolan R J. Brain. 1998;121:47–57. doi: 10.1093/brain/121.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Whalen P J, Rauch S L, Etcoff N L, McInerney S C, Lee M B, Jenike M A. J Neurosci. 1998;18:411–418. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-01-00411.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Scott S K, Young A W, Calder A J, Hellawell D J, Aggleton J P, Johnson M. Nature (London) 1997;385:254–257. doi: 10.1038/385254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Oldfield R C. Neuropsychologia. 1971;9:97–113. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(71)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.First M B, Spitzer R L, Gibbon M, Willaims J B W. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM IV Axis 1 Disorders. New York: New York State Psychiatric Institute; 1996. pp. 1–J21. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Stroop J R. J Exp Psychol. 1935;18:634–662. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Silbersweig D A, Stern E, Frith C D, Cahill C, Schnorr L, Grootoonk S, Spinks T, Clark J, Frackowiak R, Jones T. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993;13:617–629. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1993.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Friston K J, Holmes A P, Worsley K J, Poline J P, Frith C D, Frackowiak R S J. Hum Brain Mapp. 1995;2:189–210. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Friston K J, Ashburner J, Poline J P, Frith C D, Frackowiak R S J. Hum Brain Mapp. 1995;3:165–189. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hedeker D, Gibbons R D. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 1996;49:229–252. doi: 10.1016/0169-2607(96)01723-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.George M S, Ketter T A, Parekh P I, Rosinsky N, Ring H, Casey B J, Trimble M R, Horwitz B, Herscovitch P, Post R M. Hum Brain Mapp. 1994;1:194–209. doi: 10.1002/hbm.460010305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Whalen P J, Bush G, McNally R J, Wilhelm S, McInerney S C, Jenike M A, Rauch S L. Biol Psychiatry. 1998;44:1219–1228. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(98)00251-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Anderson A, Phelps E. NeuroReport. 1998;9:3607–3613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gloor P. Brain. 1990;113:1673–1694. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.6.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Halgren E, Walter R D, Cherlow D G, Crandall P H. Brain. 1978;101:83–117. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wieser H. In: Neurobehavioral Problems in Epilepsy. Smith D B, Treiman D M, Trimble M R, editors. Vol. 55. New York: Raven; 1991. pp. 301–315. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Leonard C M, Rolls E T, Wilson F A W, Balis C G. Behav Brain Res. 1985;15:159–176. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(85)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rolls E T. Hum Neurobiol. 1984;3:209–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Heit G, Smith M E, Halgren E. Nature (London) 1988;333:773–775. doi: 10.1038/333773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Halgren E. In: The Amygdala: Neurobiological Aspects of Emotion, Memory, and Mental Dysfunction. Aggleton J P, editor. New York: Wiley; 1992. pp. 191–228. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Le Doux J. The Emotional Brain. New York: Simon and Schuster; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 23.La Bar K S, Le Doux J E, Spencer D D, Phelps E A. J Neurosci. 1995;15:6846–6855. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-10-06846.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Le Doux J E, Cicchetti P, Xagoraris A, Romanski L M. J Neurosci. 1990;10:1062–1069. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-04-01062.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gallagher M, Chiba A. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1996;6:221–227. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(96)80076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pitkanen A, Savander V, Le Doux J E. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20:517–523. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(97)01125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Savander V, Go C G, Le Doux J E, Pitkanen A. J Comp Neurol. 1995;361:345–368. doi: 10.1002/cne.903610211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pandya D N, Yeterian E H. Cereb Cortex. 1985;4:3–55. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Amaral D, Price J, Pitkanen A, Carmichael S T. In: The Amygdala: Neurobiological Aspects of Emotion, Memory, and Mental Dysfunction. Aggleton J P, editor. New York: Wiley; 1992. pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kuriki S, Takeuchi F, Hirata Y. Brian Res Cog Brain Res. 1998;6:193–203. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6410(97)00030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Taylor S, Liberzon I, Fig L, Decker L, Minoshima S, Koeppe R. Neuroimage. 1998;8:188–197. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1998.0356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.McDaniel M A, Einstein G O, De Losh E L, May C P. J Exp Psychol Learning Mem Cognit. 1995;21:422–435. doi: 10.1037//0278-7393.21.2.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mc Closky M, Wible C G, Cohen N J. J Exp Psychol Gen. 1988;117:171–181. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Craik F M, Blankenstein K R. In: Research in Psychophysiology. Venables P H, Christie M J, editors. New York: Wiley; 1975. pp. 388–417. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hamann S B, Ely T D, Grafton S T, Kilts C D. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:289–293. doi: 10.1038/6404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ricci P T, Zelkowicz B J, Nebes R D, Meltzer C C, Mintun M A, Becker J T. NeuroImage. 1999;9:88–96. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1998.0386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Alkire M T, Haier R J, Fallon J H, Cahill L. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:14506–14510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Llamas A, Avendano C, Reinoso-Suarez F. Science. 1977;195:794–796. doi: 10.1126/science.836591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]