Abstract
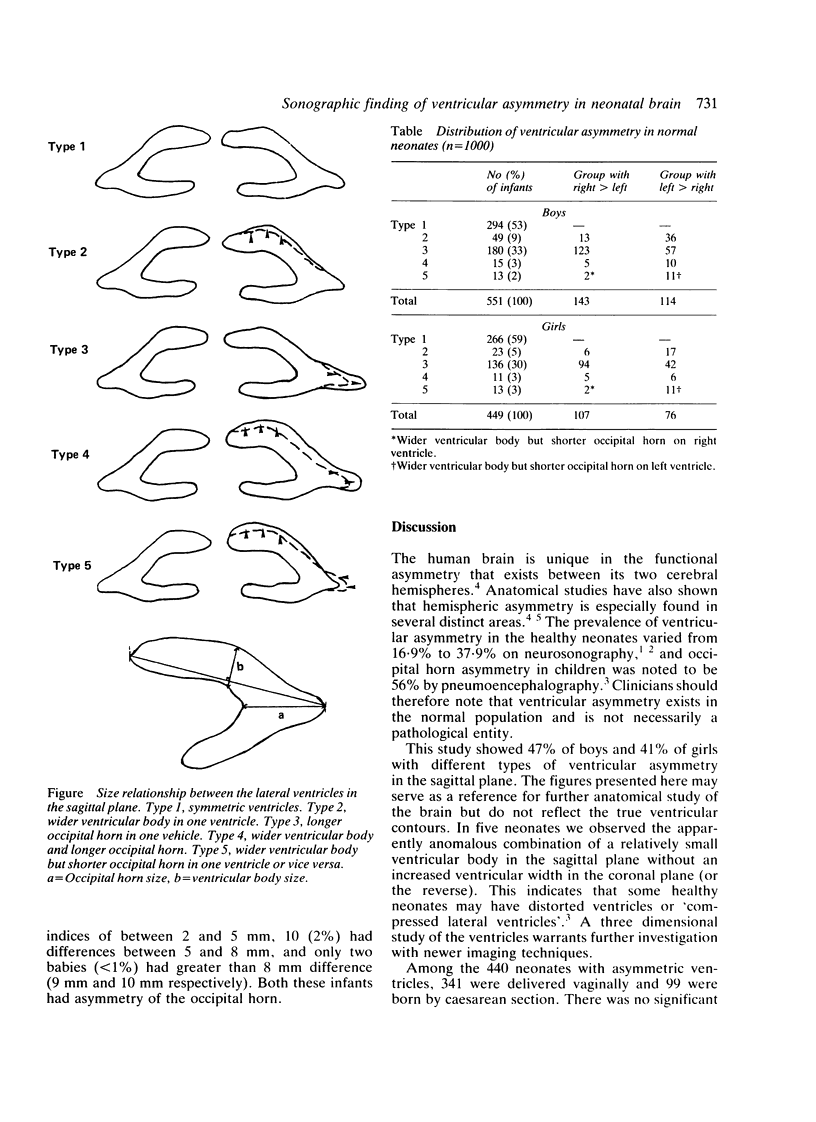
One thousand normal Chinese full term neonates underwent prospective ultrasonography examination. Asymmetry of size between the right and left lateral ventricle was observed in a similar proportion of boys: 257/551 (47%) and girls: 183/449 (41%). The mode of delivery did not significantly influence the occurrence of ventricular asymmetry. We propose four different patterns of asymmetry.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Galaburda A. M., LeMay M., Kemper T. L., Geschwind N. Right-left asymmetrics in the brain. Science. 1978 Feb 24;199(4331):852–856. doi: 10.1126/science.341314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E., Fitz C. Occipital horn asymmetry in children. Ann Neurol. 1980 Oct;8(4):437–439. doi: 10.1002/ana.410080417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada J. A., Clarke R., Hamm A. Cerebral hemispheric asymmetry in humans. Cortical speech zones in 100 adults and 100 infant brains. Arch Neurol. 1975 Apr;32(4):239–246. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490460055007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


