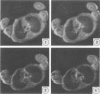
Abstract
Echo planar imaging (an extremely fast method of magnetic resonance imaging) was used to measure lung volume in a group of nine infants, all of whom had had respiratory problems. The mean echo planar imaging estimate of total lung volume was 44 +/- 9 ml/kg. In each case the right lung was larger than the left (ratio 52.8:47.2%). The mean thoracic gas volume was 36 +/- 8 ml/kg. The entire sequence of images of the thorax (about 400) takes five minutes to complete, infants require no sedation, and there are no side effects.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chrispin A., Small P., Rutter N., Coupland R. E., Doyle M., Chapman B., Coxon R., Guilfoyle D., Cawley M., Mansfield P. Transectional echo planar imaging of the heart in cyanotic congenital heart disease. Pediatr Radiol. 1986;16(4):293–297. doi: 10.1007/BF02386865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., BEDELL G. N., MARSHALL R., COMROE J. H., Jr A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume: a comparison with a nitrogen washout method for measuring functional residual capacity in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):322–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI103281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison D. M., Morgan M. D., Millar A. B. Estimation of regional gas and tissue volumes of the lung in supine man using computed tomography. Thorax. 1986 Aug;41(8):620–628. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.8.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey S., Beardsmore C. S., Maayan C., Bar-Yishay E. Can thoracic gas volume be measured in infants with airways obstruction? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Feb;133(2):245–251. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. Alveolar ventilation, diffusing capacity and the A-a PO2 difference in the newborn infant. Respir Physiol. 1968 Mar;4(2):168–192. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(68)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagneaux D., Mossay C., Geubelle F., Christiaens G. Alveolar data in healthy, awake neonates during spontaneous ventilation: a preliminary investigation. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1988;5(4):225–231. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950050409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON N. M., PROD'HOM L. S., CHERRY R. B., LIPSITZ P. J., SMITH C. A. Pulmonary function in the newborn infant. I. Methods: ventilation and gaseous metabolism. Pediatrics. 1962 Dec;30:963–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C., Chapman B., Coxon R., Howseman A., Jaroszkiewicz G., Stehling M., Mansfield P., Milner A. D., Swarbrick A., Small P. Evaluation of infants by echo planar imaging after repair of diaphragmatic hernia. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Feb;63(2):186–189. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C., Small P., Chapman B., Coxon R., Glover P., Turner R., Jaroszkiewicz G., Howseman A., Mansfield P., Coupland R. Determination of individual and total lung volumes using nuclear magnetic resonance echo-planar imaging. Ann Radiol (Paris) 1987;30(7):470–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford M. Measurement of airway resistance and thoracic gas volume in infancy. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Aug;49(8):611–615. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.8.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocks J., Levy N. M., Godfrey S. A new apparatus for the accurate measurement of airway resistance in infancy. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Jul;43(1):155–159. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.43.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]