Abstract
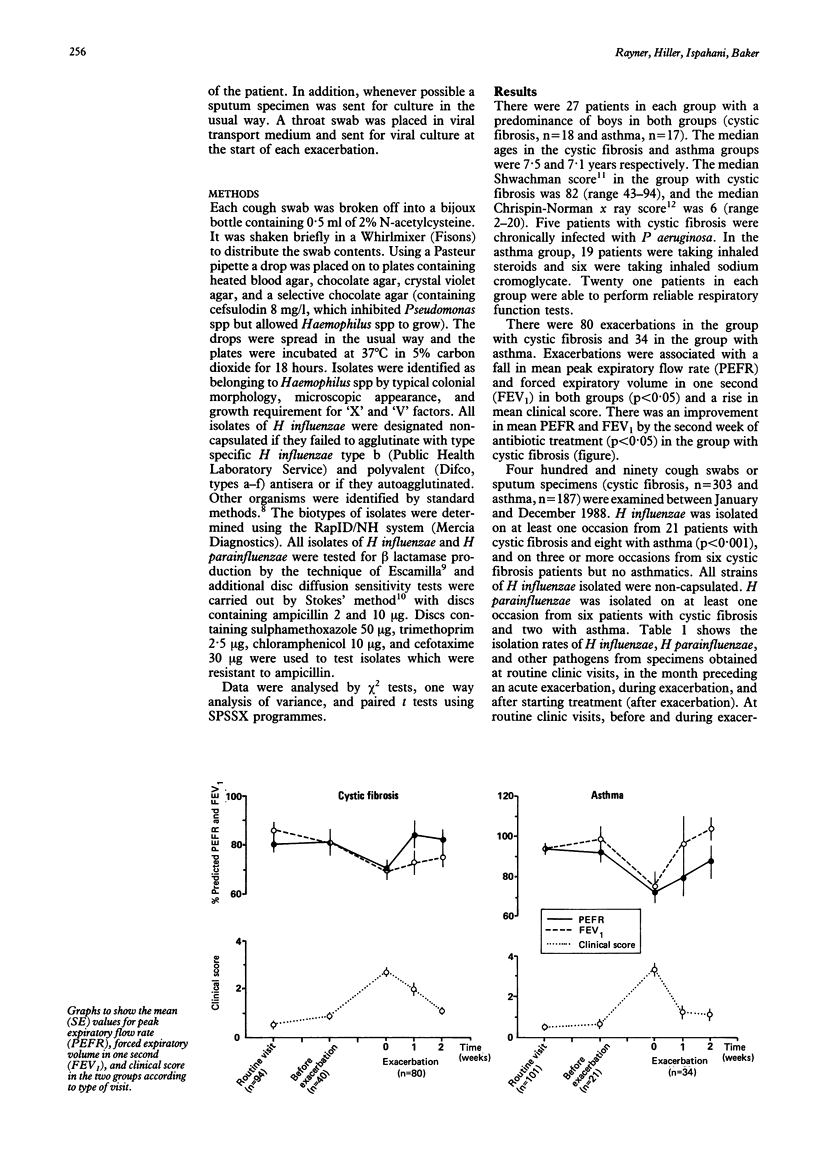
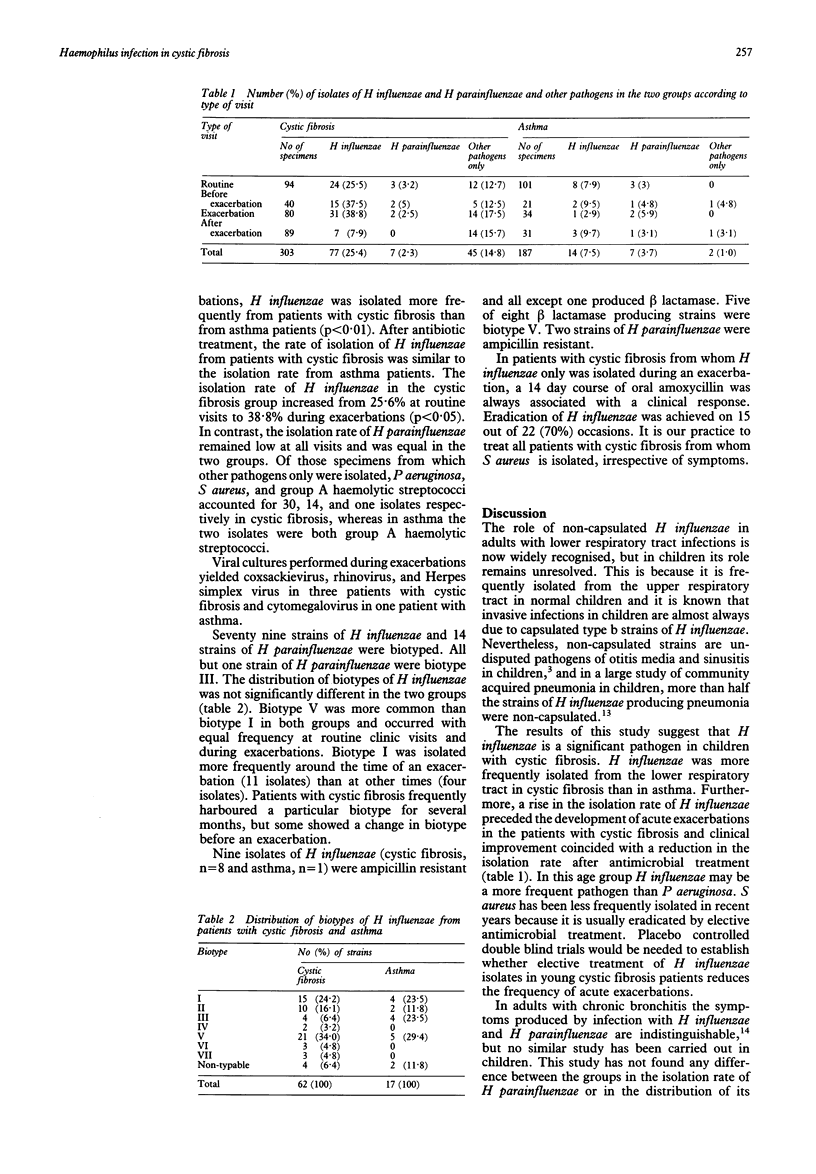
Twenty seven patients with cystic fibrosis under the age of 12 years and 27 matched patients with asthma were followed up in a prospective study for one year. The isolation rate of non-capsulated strains of Haemophilus influenzae from cough swabs and sputum specimens taken at routine clinic visits every two months was significantly greater in cystic fibrosis than in asthma. Haemophilus para-influenzae was equally common in both groups. During exacerbations the isolation rate of H influenzae in cystic fibrosis was significantly greater than at other times, whereas in asthma there was no significant difference. The distribution of biotypes of H influenzae and H parainfluenzae was similar in the two groups. In cystic fibrosis, biotype I was associated with exacerbations. Biotype V was more common than in previous studies, but was not associated with exacerbations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chrispin A. R., Norman A. P. The systematic evaluation of the chest radiograph in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Radiol. 1974;2(2):101–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01314939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole P. J., Roberts D. E., Davies S. F., Knight R. K. A simple oral antimicrobial regimen effective in severe chronic bronchial suppuration associated with culturable Haemophilus influenzae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Feb;11(2):109–113. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.2.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escamilla J. Susceptibility of Haemophilus influenza to ampicillin as determined by use of a modified, one-minute beta-lactamase test. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):196–198. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Kilian M. Haemophilus from the lower respiratory tract of patients with cystic fibrosis. Scand J Respir Dis. 1976;57(3):103–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ispahani P., Youngs E. R. Non-capsulate Haemophilus influenzae: a neglected pathogen in adults. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Jun 22;290(6485):1870–1871. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6485.1870-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A taxonomic study of the genus Haemophilus, with the proposal of a new species. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):9–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. S., Teter M. J., Gilligan P. H. Biotype of Haemophilus influenzae: correlation with virulence and ampicillin resistance. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):800–806. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressler T., Szaff M., Høiby N. Antibiotic treatment of Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Jul;73(4):541–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb09968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhind G. B., Gould G. A., Ahmad F., Croughan M. J., Calder M. A. Haemophilus parainfluenzae and H influenzae respiratory infections: comparison of clinical features. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Sep 14;291(6497):707–708. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6497.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHWACHMAN H., KULCZYCKI L. L. Long-term study of one hundred five patients with cystic fibrosis; studies made over a five- to fourteen-year period. AMA J Dis Child. 1958 Jul;96(1):6–15. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1958.02060060008002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shann F., Gratten M., Germer S., Linnemann V., Hazlett D., Payne R. Aetiology of pneumonia in children in Goroka Hospital, Papua New Guinea. Lancet. 1984 Sep 8;2(8402):537–541. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90764-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheinman B. D., Devalia J. L., Davies R. J., Crook S. J., Tabaqchali S. Synthesis of histamine by Haemophilus influenzae. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 29;292(6524):857–858. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6524.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. E., Prober C. G., Manson B., Corey M., Levison H. Association of respiratory viral infections with pulmonary deterioration in patients with cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Dec 27;311(26):1653–1658. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198412273112602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. C., Kerr E. J., Baillie M. Temporal changes in biotypes of Haemophilus influenzae isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(2):129–132. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-2-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. C., Kerr E. J., Hinks C. A. Distribution of biotypes of Haemophilus influenzae and H parainfluenzae in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jul;38(7):750–753. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.7.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


