Abstract
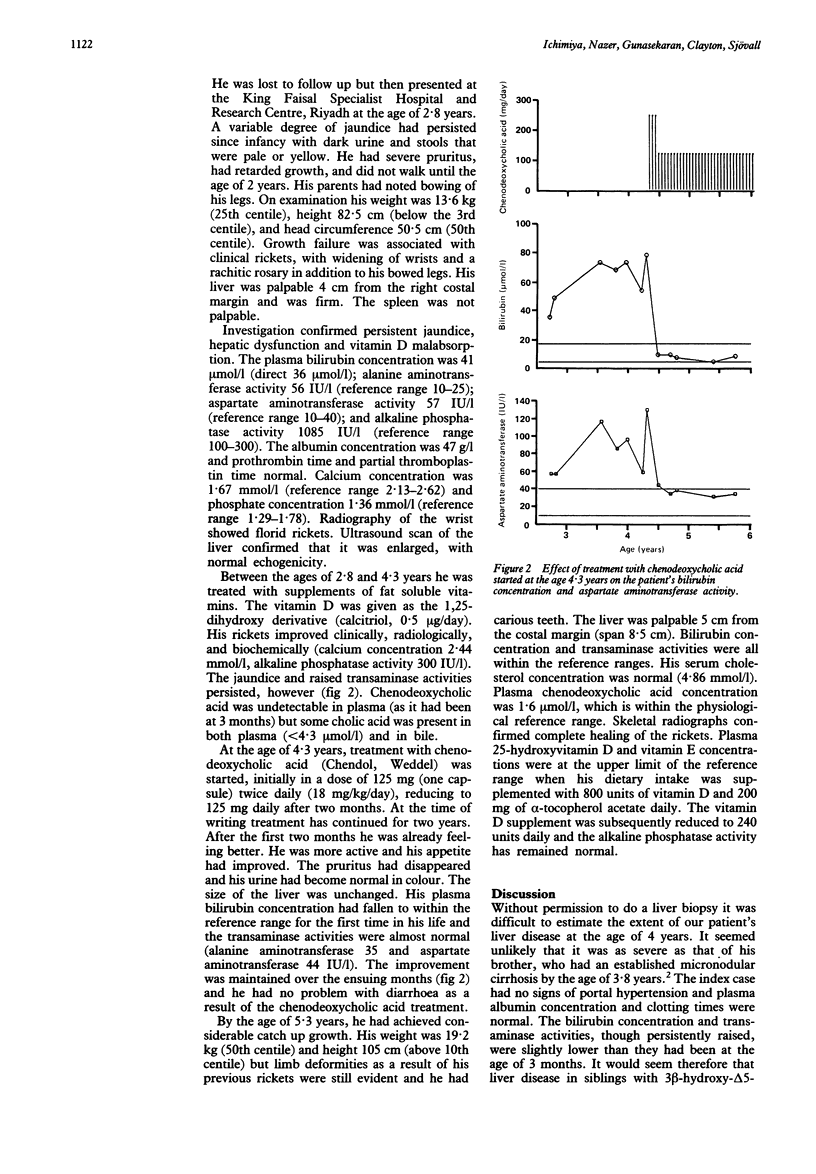
Deficiency of 3 beta-hydroxy-delta 5-C27-steroid dehydrogenase, the second enzyme in the sequence that catalyses the synthesis of bile acids from cholesterol, leads to chronic liver disease in childhood as well as to malabsorption of fat and fat soluble vitamins. A 4 year old boy with this condition has been successfully treated by oral administration of a bile acid--chenodeoxycholic acid. He had been jaundiced since birth, grew poorly because of rickets, and had severe pruritus. Plasma transaminase activities were persistently raised. Chenodeoxycholic acid 125 mg twice daily for two months, and then 125 mg daily, cured his jaundice and pruritus, returned his transaminase activities to normal, and eliminated the need for calcitriol for prevention of rickets. On this treatment he has so far remained well for two years. A diagnosis of 3 beta-hydroxy-delta 5-C27-steroid dehydrogenase deficiency should be considered in any child with unexplained chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis, especially if the liver disease is accompanied by a clinically obvious malabsorption of fat soluble vitamins. A simple colorimetric test of the urine confirms the diagnosis and effective treatment can be started.
Full text
PDF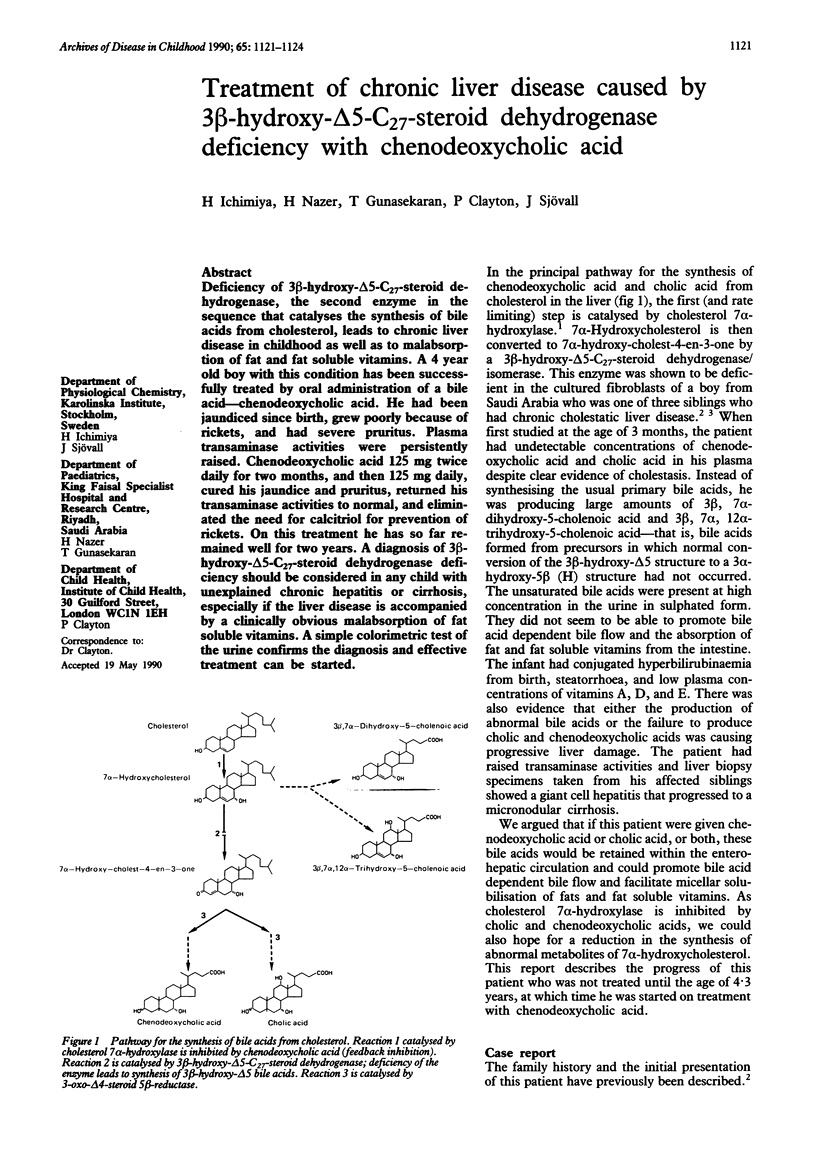


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Grundy S. M., Cleary P. A., Small D. M., Lachin J. M., Schoenfield L. J. National Cooperative Gallstone Study: the effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on lipoproteins and apolipoproteins. Gastroenterology. 1982 Apr;82(4):638–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batta A. K., Shefer S., Batta M., Salen G. Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on biliary and urinary bile acids and bile alcohols in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis; monitoring by high performance liquid chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jun;26(6):690–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Gustafsson J. A. Mechanism of microbial transformation of cholesterol into coprostanol. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Aug 16;21(3):428–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton P. T., Leonard J. V., Lawson A. M., Setchell K. D., Andersson S., Egestad B., Sjövall J. Familial giant cell hepatitis associated with synthesis of 3 beta, 7 alpha-dihydroxy-and 3 beta,7 alpha, 12 alpha-trihydroxy-5-cholenoic acids. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1031–1038. doi: 10.1172/JCI112915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton P. T., Patel E., Lawson A. M., Carruthers R. A., Tanner M. S., Strandvik B., Egestad B., Sjövall J. 3-Oxo-delta 4 bile acids in liver disease. Lancet. 1988 Jun 4;1(8597):1283–1284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo C., Roda A., Roda E., Piceni Sereni L., Brega A., Fugazza R., Giunta A. Bile acid malabsorption in cystic fibrosis with and without pancreatic insufficiency. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Sep;3(4):556–562. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198409000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. L., Anderson D. W., Boyer J. L., Ishak K., Klatskin G., Lachin J. M., Phillips M. J. A prospective morphologic evaluation of hepatic toxicity of chenodeoxycholic acid in patients with cholelithiasis: the National Cooperative Gallstone Study. Hepatology. 1982 Mar-Apr;2(2):187–201. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greim H., Trülzsch D., Czygan P., Rudick J., Hutterer F., Schaffner F., Popper H. Mechanism of cholestasis. 6. Bile acids in human livers with or without biliary obstruction. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):846–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M., Hernandez C. R., Hylemon P. B., Kubaska W. M., Hartman C., Vlahcevic Z. R. Regulation of bile acid synthesis. I. Effects of conjugated ursodeoxycholate and cholate on bile acid synthesis in chronic bile fistula rat. Hepatology. 1988 Mar-Apr;8(2):358–365. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman B. J., Wolthers B. G., van der Molen J. C., Nagel G. T., Waterreus R. J., Oosterhuis H. J. Capillary gas chromatographic determinations of urinary bile acids and bile alcohols in CTX patients proving the ineffectivity of ursodeoxycholic acid treatment. Clin Chim Acta. 1984 Sep 15;142(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(84)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maislos M., Silver J., Fainaru M. Intestinal absorption of vitamin D sterols: differential absorption into lymph and portal blood in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jun;80(6):1528–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. J., Fisher R. L., Anderson D. W., Lan S. P., Lachin J. M., Boyer J. L. Ultrastructural evidence of intrahepatic cholestasis before and after chenodeoxycholic acid therapy in patients with cholelithiasis: the national cooperative gallstone study. Hepatology. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):209–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Suchy F. J., Welsh M. B., Zimmer-Nechemias L., Heubi J., Balistreri W. F. Delta 4-3-oxosteroid 5 beta-reductase deficiency described in identical twins with neonatal hepatitis. A new inborn error in bile acid synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2148–2157. doi: 10.1172/JCI113837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikvall K. Purification and properties of a 3 beta-hydroxy-delta 5-C27-steroid oxidoreductase from rabbit liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3376–3380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolthers B. G., Volmer M., van der Molen J., Koopman B. J., de Jager A. E., Waterreus R. J. Diagnosis of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX) and effect of chenodeoxycholic acid therapy by analysis of urine using capillary gas chromatography. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jun 30;131(1-2):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


