Abstract
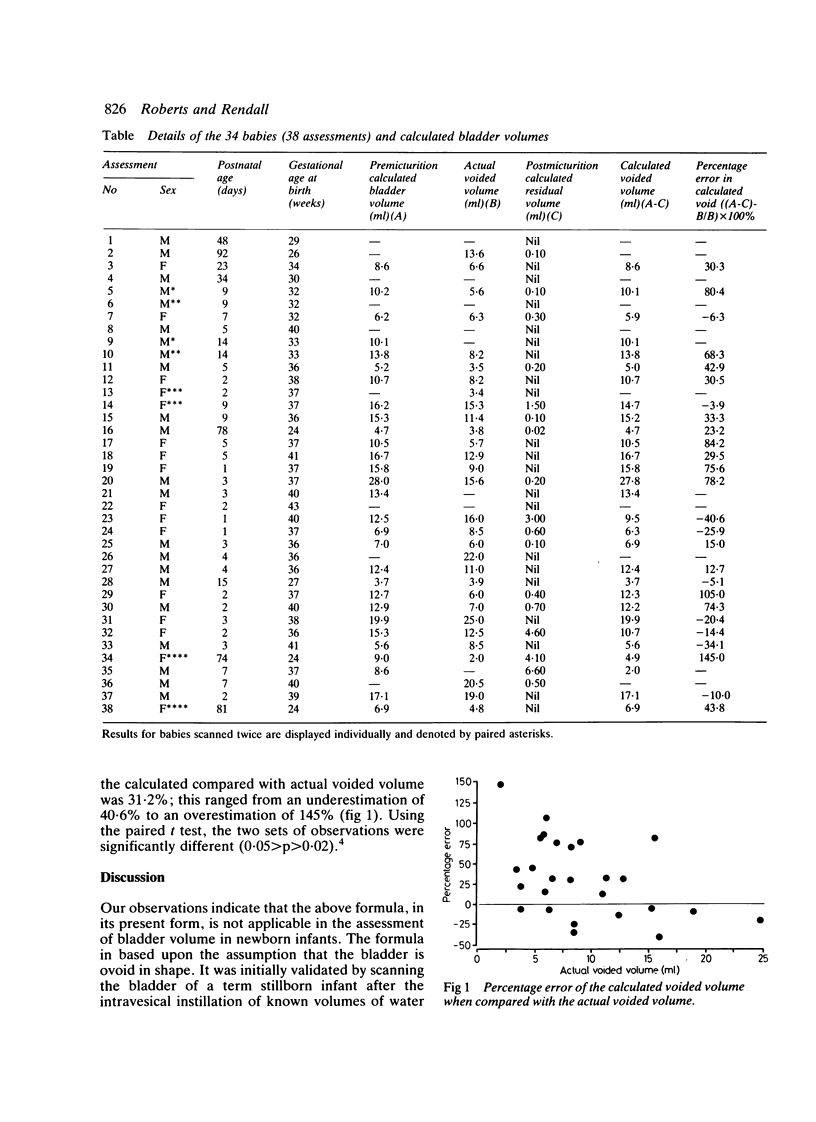
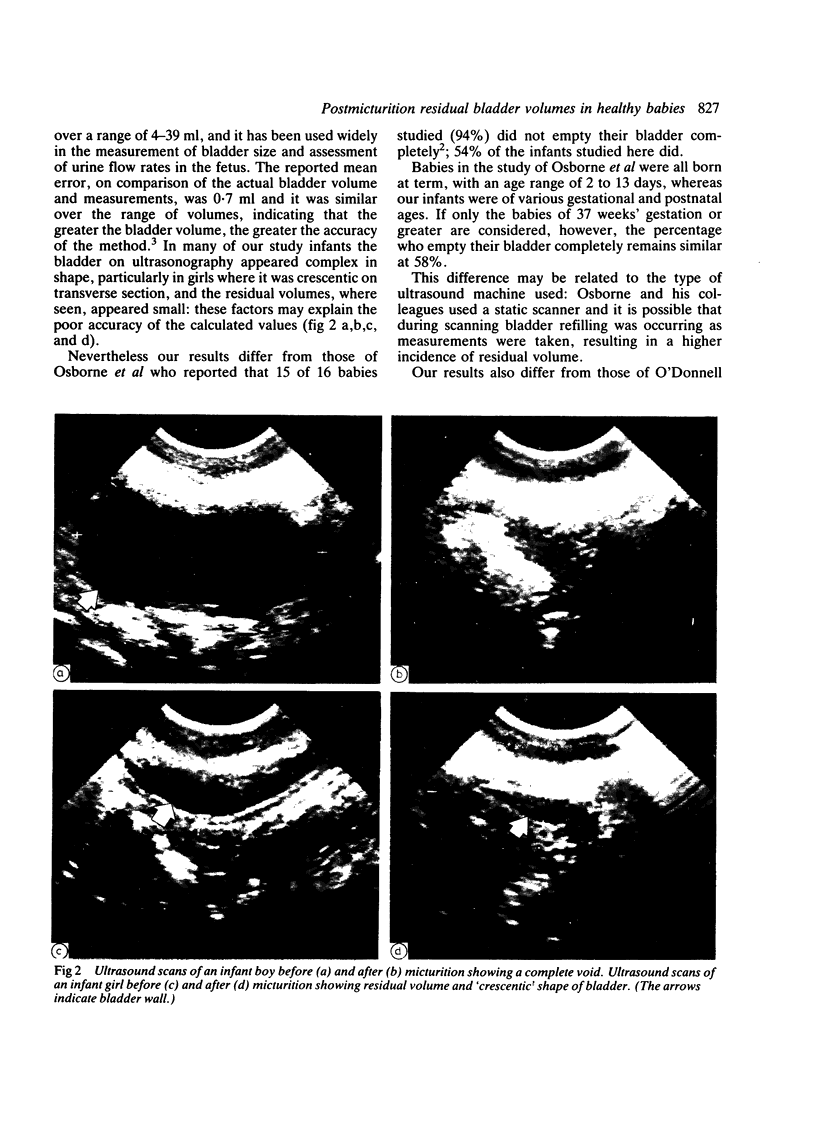
Thirty eight assessments of postmicturition residual volume were undertaken in 34 babies of various gestational and postnatal ages using abdominal ultrasonography. Twenty one (54%) babies had no detectable residual bladder volume. In all cases manual expression of the bladder failed to eliminate the residual volume. The formula widely used in the estimation of fetal bladder size and urine output is not applicable in the newborn infant.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S., Wladimiroff J. W., Dewhurst C. J. The antenatal measurement of fetal urine production. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1973 Aug;80(8):680–686. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1973.tb16049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell B., O'Connor T. P. Bladder function in infants and children. Br J Urol. 1971 Feb;43(1):25–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1971.tb04928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J., Du Mont G., Beecroft M., Ayres A. B. Bladder emptying in neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Nov;52(11):896–898. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.11.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]