Abstract
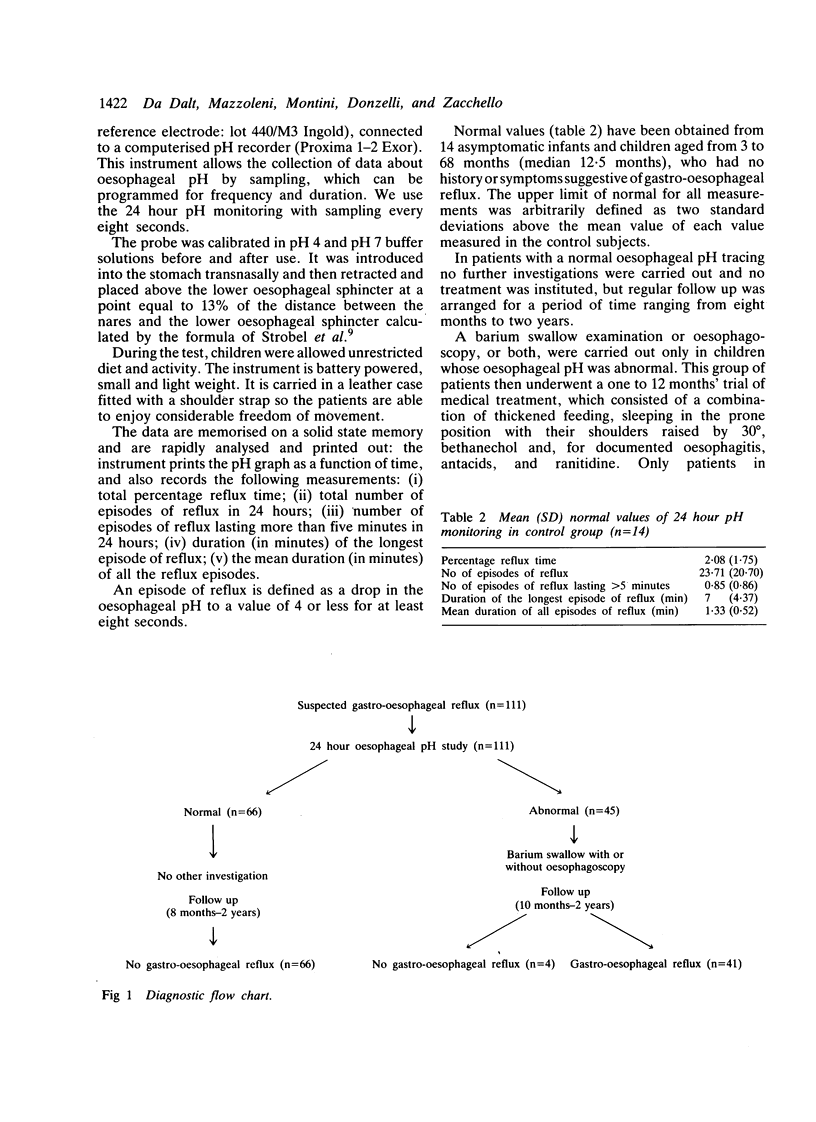
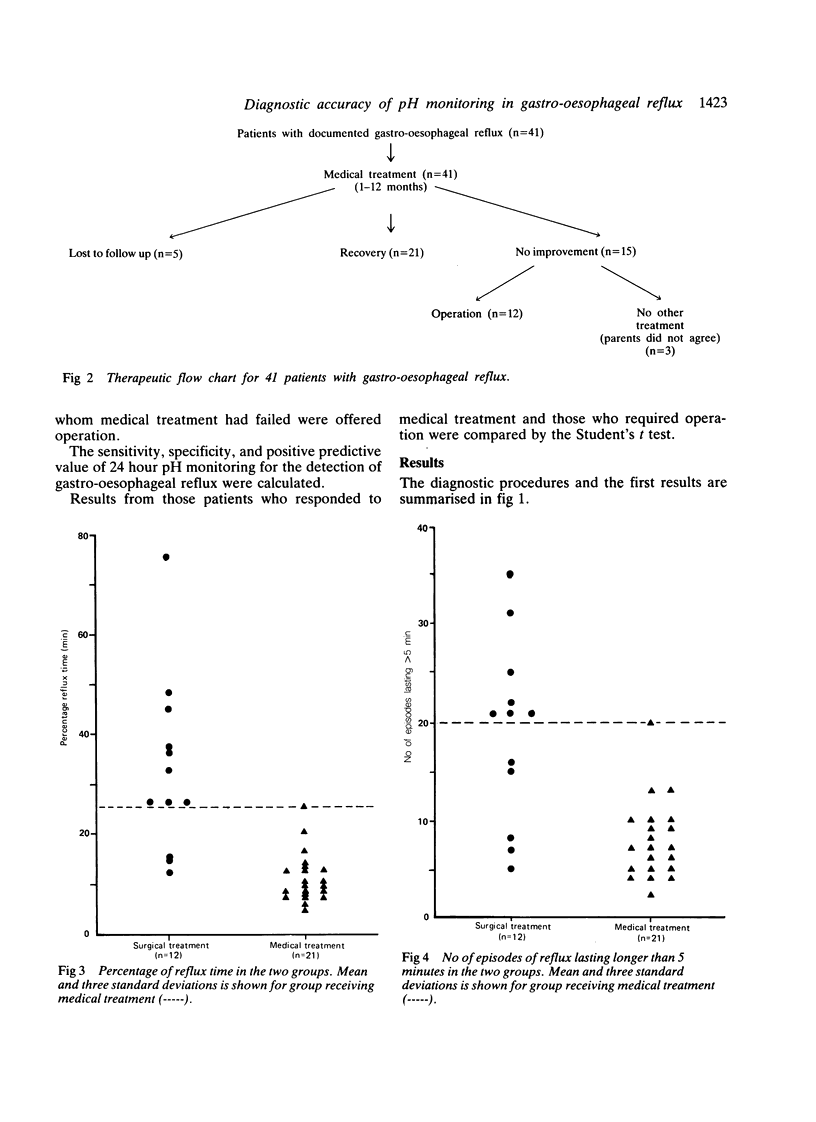
One hundred and eleven children admitted with suspected gastro-oesophageal reflux were studied, with 24 hour oesophageal pH monitoring as the first line of investigation. Barium swallow examination, or oesophagoscopy, or both, were carried out only in children with abnormal pH, who subsequently had a trial of 1-12 months medical treatment. All patients were followed up for eight months to two years. A final diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux was made in 41 patients, in all of whom the pH study was abnormal (100% sensitivity). The final diagnosis was different in 70 patients; 66 of these had a normal pH (94% specificity). All children with gastro-oesophageal reflux were treated with drugs. All those with a percentage reflux time of more than 27 and more than 20 episodes of reflux lasting more than 5 minutes failed to improve and needed operation. We conclude that monitoring of the oesophageal pH should be the first line of investigation in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux and should be used together with clinical data and other investigations, to identify those children who will need operation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arasu T. S., Wyllie R., Fitzgerald J. F., Franken E. A., Siddiqui A. R., Lehman G. A., Eigen H., Grosfeld J. L. Gastroesophageal reflux in infants and children comparative accuracy of diagnostic methods. J Pediatr. 1980 May;96(5):798–803. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80545-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boix-Ochoa J. The physiologic approach to the management of gastric esophageal reflux. J Pediatr Surg. 1986 Dec;21(12):1032–1039. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(86)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne W. J., Euler A. R., Ashcraft E., Nash D. G., Seibert J. J., Golladay E. S. Gastroesophageal reflux in the severely retarded who vomit: criteria for and results of surgical intervention in twenty-two patients. Surgery. 1982 Jan;91(1):95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARRE I. J. The natural history of the partial thoracic stomach (hiatus hernia) in children. Arch Dis Child. 1959 Aug;34:344–353. doi: 10.1136/adc.34.176.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. H., Kushner D. C., Schwartz A. N. Gastroesophageal reflux in children: results of a standardized fluoroscopic approach. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983 Jul;141(1):53–56. doi: 10.2214/ajr.141.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. R., Hurd D. M., Johnstone M. S. Nissen fundoplication and pyloroplasty in the management of gastro-oesophageal reflux in children. Br J Surg. 1987 Jun;74(6):488–490. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Wang C. I., Wernly J. A., Pellegrini C. A., Little A. G., Klementschitsch P., Bermudez G., Johnson L. F., Skinner D. B. Technique, indications, and clinical use of 24 hour esophageal pH monitoring. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980 May;79(5):656–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. F., Haynes J., Jones J. A., Stower M. J., Kapila L. Ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring in children as an indicator for surgery. J Pediatr Surg. 1986 Mar;21(3):221–223. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(86)80838-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams J. S., Ricci A., Jr, Leichtner A. M. Clinical and laboratory correlates of esophagitis in young children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):52–56. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198801000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Herbst J. J., Oliveros M. A., Stewart D. R. Evaluation of gastroesophageal reflux surgery in children. Pediatrics. 1977 Jan;59(1):62–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Jolley S. G., Herbst J. J., Cordell L. J. Surgical selection of infants with gastroesophageal reflux. J Pediatr Surg. 1981 Aug;16(4 Suppl 1):587–594. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(81)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leape L. L., Ramenofsky M. L. Surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in children. Results of Nissen's fundoplication in 100 children. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Oct;134(10):935–938. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130220013004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramenofsky M. L., Powell R. W., Curreri P. W. Gastroesophageal reflux. pH probe-directed therapy. Ann Surg. 1986 May;203(5):531–536. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198605000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindlbeck N. E., Heinrich C., König A., Dendorfer A., Pace F., Müller-Lissner S. A. Optimal thresholds, sensitivity, and specificity of long-term pH-metry for the detection of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jul;93(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger P. K., Donahue P. E., Schmid B., Layden T. J. Limitations of 24-hour intraesophageal pH monitoring in the hospital setting. Gastroenterology. 1985 Oct;89(4):797–804. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90575-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M., Peiffert B., Pierre E., Barthelme H. L'intervention de Nissen chez l'enfant encéphalopathe. Chir Pediatr. 1986;27(3):138–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd R. W., Wren J., Evans S., Lander M., Ong T. H. Gastroesophageal reflux in children. Clinical profile, course and outcome with active therapy in 126 cases. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1987 Feb;26(2):55–60. doi: 10.1177/000992288702600201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitz L., Kirtane J. Results and complications of surgery for gastro-oesophageal reflux. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Aug;60(8):743–747. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.8.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel C. T., Byrne W. J., Ament M. E., Euler A. R. Correlation of esophageal lengths in children with height: application to the Tuttle test without prior esophageal manometry. J Pediatr. 1979 Jan;94(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80361-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


