Abstract
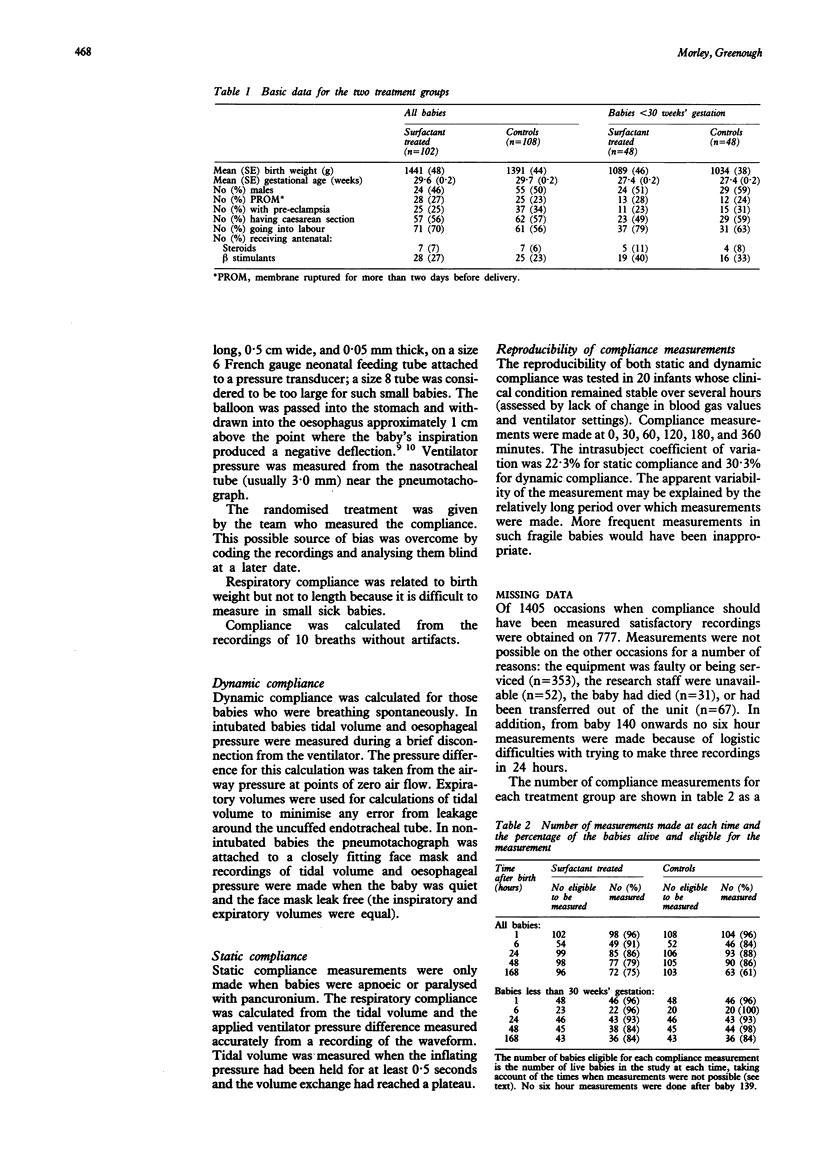
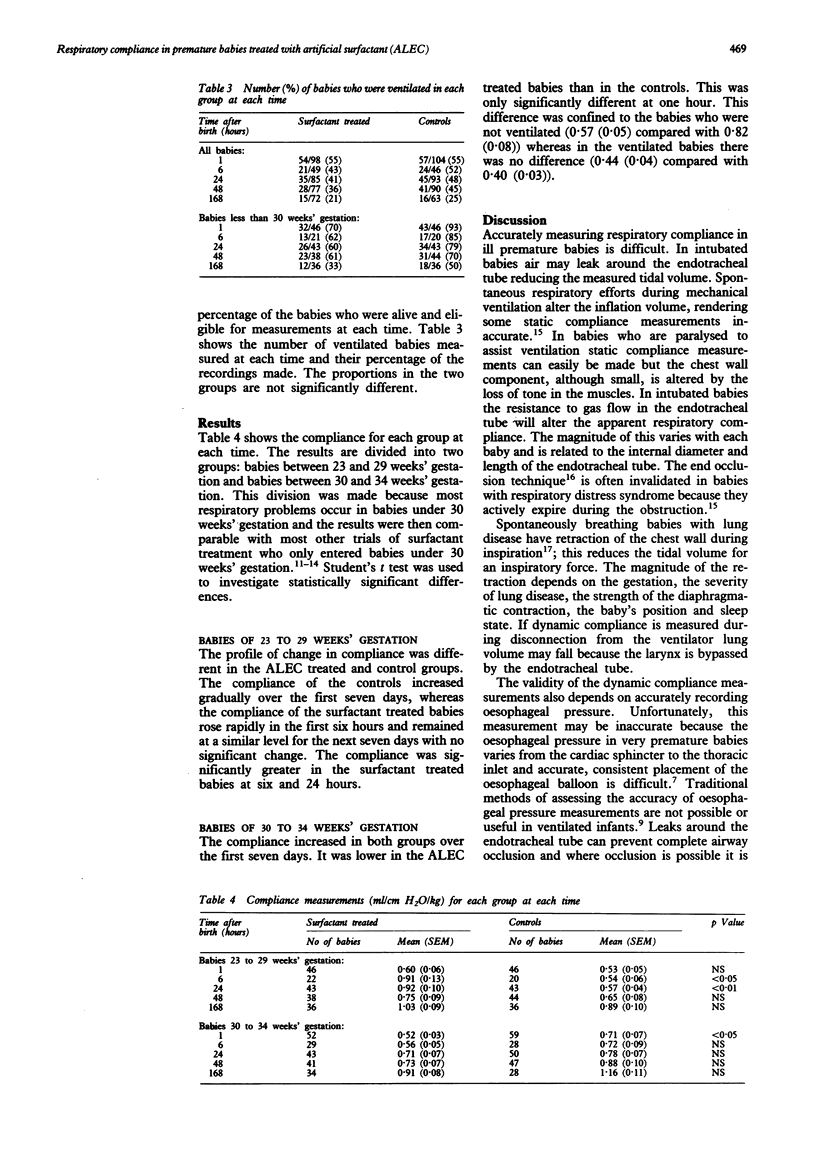
In a randomised trial of artificial surfactant (ALEC) given at birth to 294 babies less than 34 weeks' gestation, the respiratory compliance was measured at 1, 6, 24, 48, and 168 hours after birth. In babies less than 29 weeks' gestation ALEC significantly improved the mean (SEM) compliance at 6 hours from 0.54 (0.06) to 0.91 (0.13) ml/cm H2O/kg and at 24 hours from 0.57 (0.04) to 0.92 (0.10) ml/cm H2O/kg. The improvements at 1, 48, and 168 hours were not significant. In babies of over 29 weeks' gestation the compliance was lower in the ALEC treated babies. This was significant only at one hour: 0.52 (0.03) compared with 0.71 (0.07) ml/cm H2O/kg and only occurred in babies who were not ventilated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangham A. D., Morley C. J., Phillips M. C. The physical properties of an effective lung surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 21;573(3):552–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beardsmore C. S., Helms P., Stocks J., Hatch D. J., Silverman M. Improved esophageal balloon technique for use in infants. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Oct;49(4):735–742. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.4.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. M., Veness-Meehan K., Notter R. H., Bhutani V. K., Kendig J. W., Shapiro D. L. Changes in pulmonary mechanics after the administration of surfactant to infants with respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 25;319(8):476–479. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808253190804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. J., Clyman R. I., Heymann M. A., Clements J. A., Mauray F., Kitterman J., Ballard P. Effects of a protein-free, synthetic surfactant on survival and pulmonary function in preterm lambs. J Pediatr. 1985 Nov;107(5):775–780. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enhorning G., Shennan A., Possmayer F., Dunn M., Chen C. P., Milligan J. Prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome by tracheal instillation of surfactant: a randomized clinical trial. Pediatrics. 1985 Aug;76(2):145–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenough A., Morley C. J. Oesophageal pressure measurements in ventilated preterm babies. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Nov;57(11):851–855. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.11.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenough A., Morley C., Davis J. Interaction of spontaneous respiration with artificial ventilation in preterm babies. J Pediatr. 1983 Nov;103(5):769–773. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80483-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Jacobs H., Jobe A. Surfactant function in respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1983 Mar;102(3):443–447. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80673-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong M. S., Egan E. A., Notter R. H., Shapiro D. L. Double-blind clinical trial of calf lung surfactant extract for the prevention of hyaline membrane disease in extremely premature infants. Pediatrics. 1985 Oct;76(4):585–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann B. Combination of saline instillation with artificial ventilation damages bronchial surfactant. Lancet. 1987 Jun 13;1(8546):1375–1375. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90676-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeSouef P. N., England S. J., Bryan A. C. Total resistance of the respiratory system in preterm infants with and without an endotracheal tube. J Pediatr. 1984 Jan;104(1):108–111. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80605-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeSouëf P. N., Lopes J. M., England S. J., Bryan M. H., Bryan A. C. Influence of chest wall distortion on esophageal pressure. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Aug;55(2):353–358. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt T. A., Hallman M., Bloom B. T., Berry C., Benirschke K., Sahn D., Key T., Edwards D., Jarvenpaa A. L., Pohjavuori M. Prophylactic treatment of very premature infants with human surfactant. N Engl J Med. 1986 Sep 25;315(13):785–790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198609253151301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner A. D., Vyas H., Hopkin I. E. Effect of exogenous surfactant on total respiratory system compliance. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Apr;59(4):369–371. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.4.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley C. J., Greenough A., Miller N. G., Bangham A. D., Pool J., Wood S., South M., Davis J. A., Vyas H. Randomized trial of artificial surfactant (ALEC) given at birth to babies from 23 to 34 weeks gestation. Early Hum Dev. 1988 May;17(1):41–54. doi: 10.1016/s0378-3782(88)80056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley C., Robertson B., Lachmann B., Nilsson R., Bangham A., Grossmann G., Miller N. Artificial surfactant and natural surfactant. Comparative study of the effects on premature rabbit lungs. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Oct;55(10):758–765. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.10.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olinsky A., Bryan A. C., Bryan M. H. A simple method of measuring total respiratory system compliance in newborn infants. S Afr Med J. 1976 Jan 31;50(5):128–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. L., Notter R. H., Morin F. C., 3rd, Deluga K. S., Golub L. M., Sinkin R. A., Weiss K. I., Cox C. Double-blind, randomized trial of a calf lung surfactant extract administered at birth to very premature infants for prevention of respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1985 Oct;76(4):593–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simbruner G., Coradello H., Lubec G., Pollak A., Salzer H. Respiratory compliance of newborns after birth and its prognostic value for the course and outcome of respiratory disease. Respiration. 1982;43(6):414–423. doi: 10.1159/000194512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimura M., Matsui I., Kobayashi N. Child abuse of one of a pair of twins in Japan. Lancet. 1990 Nov 24;336(8726):1298–1299. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92975-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A., Elliott J., Silverman M. Pulmonary compliance in sick low birthweight infants. How reliable is the measurement of oesophageal pressure? Arch Dis Child. 1983 Nov;58(11):891–896. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.11.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


