Abstract
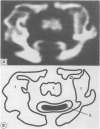
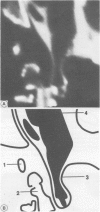
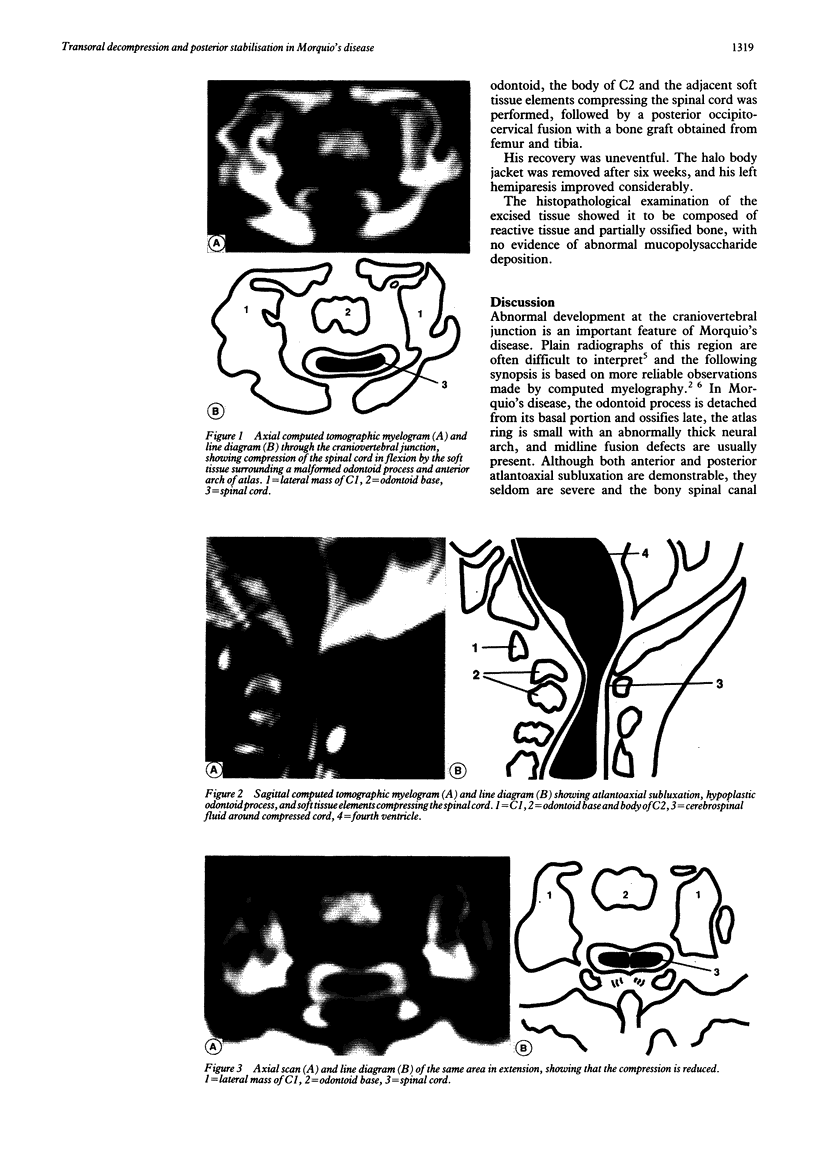
A 3.5 year old boy with Morquio's disease was referred with a persisting left hemiparesis four months after a fall and was found to have craniocervical junction compression due to atlantoaxial subluxation and significant anterior soft tissue compression. Transient unconsciousness at the time of the fall was probably due to medullary concussion as a result of hyperextension, not a head injury. Spinal cord compression due to atlantoaxial subluxation at the craniovertebral junction is a major cause of disability and death in these patients. Once cervical myelopathy appears, early posterior occipitocervical fusion has been advocated in order to arrest the progression of neurological disability and this is successful in most cases. This conventional approach was considered unsafe because of the significant anterior compression. A combined anterior transoral decompression with posterior fusion to deal with this particularly difficult problem is described.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beighton P., Craig J. Atlanto-axial subluxation in the Morquio syndrome. Report of a case. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1973 Aug;55(3):478–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethem D., Winter R. B., Lutter L., Moe J. H., Bradford D. S., Lonstein J. E., Langer L. O. Spinal disorders of dwarfism. Review of the literature and report of eighty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981 Dec;63(9):1412–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockard H. A. Anterior approaches to lesions of the upper cervical spine. Clin Neurosurg. 1988;34:389–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockard H. A., Calder I., Ransford A. O. One-stage transoral decompression and posterior fixation in rheumatoid atlanto-axial subluxation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990 Jul;72(4):682–685. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.72B4.2380227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. K., Harwood-Nash D. C., Fitz C. R., Chuang S. H. CT metrizamide myelography of the cervical spine in Morquio syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1982 Nov-Dec;3(6):666–669. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. J. Orthopedic aspects of bone dysplasias. Orthop Clin North Am. 1976 Apr;7(2):445–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. D. Atlanto-axial dislocations. Brain. 1968;91(4):655–684. doi: 10.1093/brain/91.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. E., Croley T. F. Morquio syndrome and anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1979 Sep;51(3):261–262. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197909000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopits S. E. Orthopedic complications of dwarfism. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976 Jan-Feb;(114):153–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson S. J. Dysplasia of the odontoid process in Morquio's syndrome causing quadriparesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977 Apr;59(3):340–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. A., Murphy M. J., Southwick W. O., Ogden D. A. Radiology of postnatal skeletal development. XIII. C1-C2 interrelationships. Skeletal Radiol. 1986;15(6):433–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00355100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. M., Kendall B. E., Crockard H. A., Ransford A. The odontoid process in Morquio-Brailsford's disease. The effects of occipitocervical fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991 Sep;73(5):851–858. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.73B5.1910048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]