Abstract
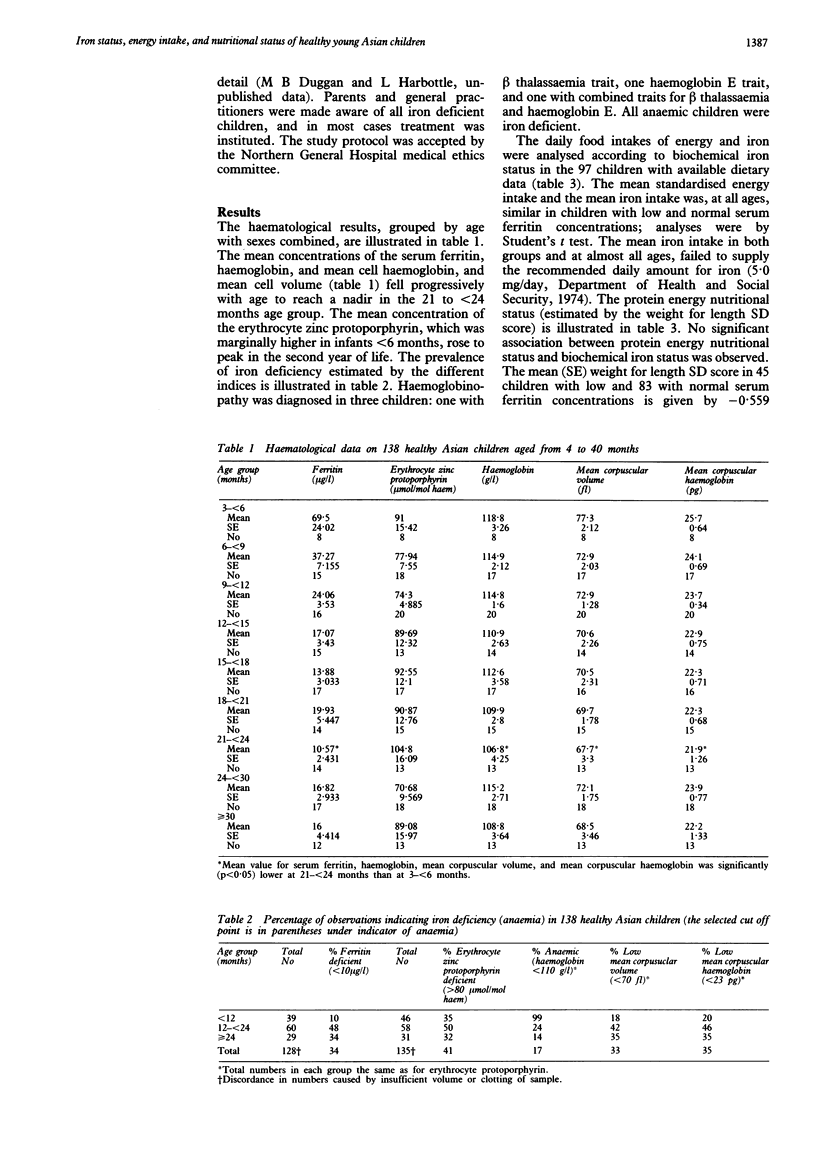
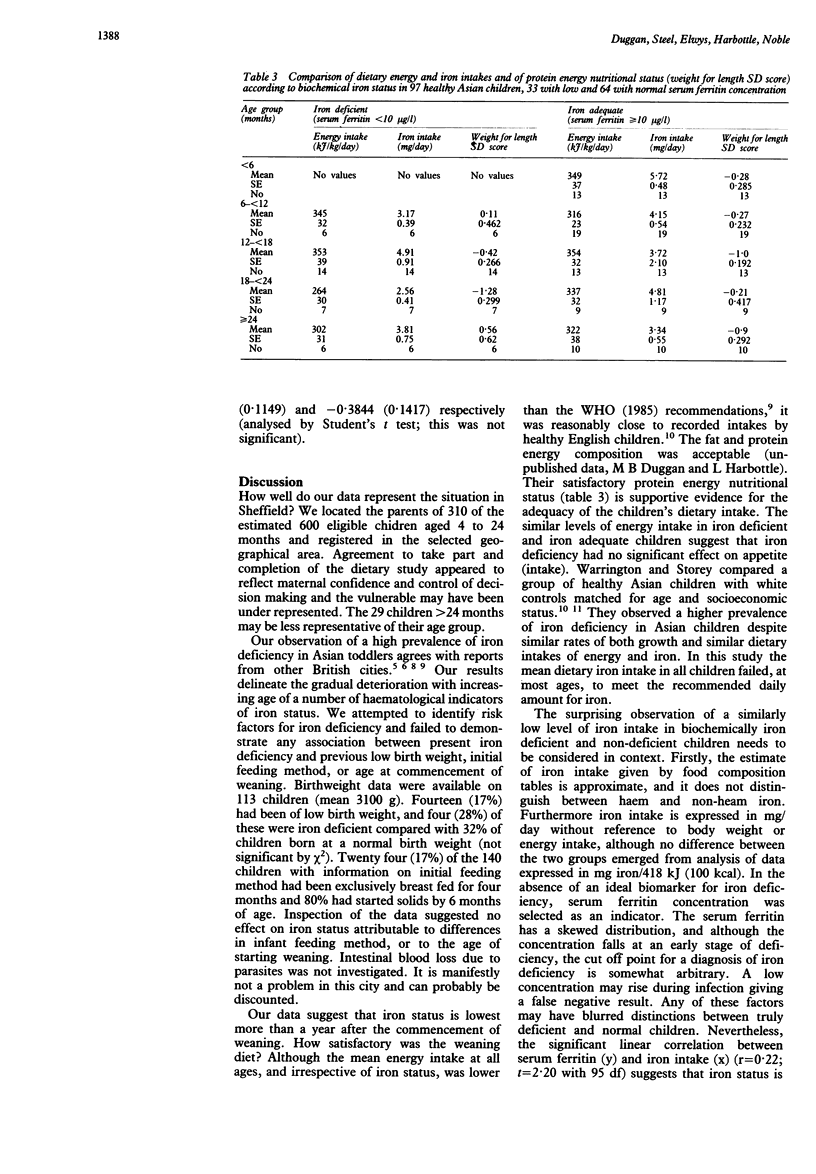
The iron status, dietary intake, and protein energy nutritional status of healthy Asian children ranging in age from 4 to 40 months was investigated. The serum ferritin, erythrocyte zinc protoporphyrin, haemoglobin and mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentrations, and mean corpuscular volume were determined in a community study of 138 children. Protein energy nutritional status was estimated by anthropometry and a four or five day weighed dietary inventory was completed by 97 children. Concentrations of the serum ferritin, haemoglobin, and mean corpuscular haemoglobin, and the mean corpuscular volume decreased progressively with increasing age. The mean values for these four indices were significantly lower in toddlers between 21 and 23 months age than in infants less than 6 months old. The mean erythrocyte zinc protoporphyrin was high in the first six months, later falling and rising again to peak in the 21 to 23 month age group. Thirty five per cent of children were iron deficient (serum ferritin concentration less than 10 micrograms/l) and low values for the mean corpuscular volume and mean corpuscular haemoglobin were observed in 33% and 35% respectively and 17% were anaemic (haemoglobin concentration less than 110 g/l). No association was observed between biochemical iron status and the dietary intake of energy or iron. Nor was there an association between protein energy nutritional status and iron status. Screening for iron deficiency in communities at risk is recommended and nutrition education using trained link workers is preferred to prophylactic iron treatment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aukett M. A., Parks Y. A., Scott P. H., Wharton B. A. Treatment with iron increases weight gain and psychomotor development. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Sep;61(9):849–857. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.9.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhardt P. Iron deficiency in young Bradford children from different ethnic groups. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Jan 11;292(6513):90–93. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6513.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindulis H., Scott P. H., Belton N. R., Wharton B. A. Combined deficiency of iron and vitamin D in Asian toddlers. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Sep;61(9):843–848. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.9.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. J., Armstrong D., Ali R., Loynes A. Nutritional survey of Bangladeshi children aged under 5 years in the London borough of Tower Hamlets. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Jun;58(6):428–432. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.6.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jivani S. K. The practice of infant feeding among Asian immigrants. Arch Dis Child. 1978 Jan;53(1):69–73. doi: 10.1136/adc.53.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. M. Current infant weaning practices within the Bangladeshi community in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. Hum Nutr Appl Nutr. 1987 Oct;41(5):349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills A. F. Surveillance for anaemia: risk factors in patterns of milk intake. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Apr;65(4):428–431. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.4.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picciano M. F., Deering R. H. The influence of feeding regimens on iron status during infancy. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Apr;33(4):746–753. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.4.746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter T., De Andraca I., Chadud P., Perales C. G. Iron deficiency anemia: adverse effects on infant psychomotor development. Pediatrics. 1989 Jul;84(1):7–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter T., Kovalskys J., Stekel A. Effect of mild iron deficiency on infant mental development scores. J Pediatr. 1983 Apr;102(4):519–522. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington S., Storey D. M. Comparative studies on Asian and Caucasian children. 1: Growth. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1988 Jan;42(1):61–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington S., Storey D. M. Comparative studies on Asian and Caucasian children. 2: Nutrition, feeding practices and health. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1988 Jan;42(1):69–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


