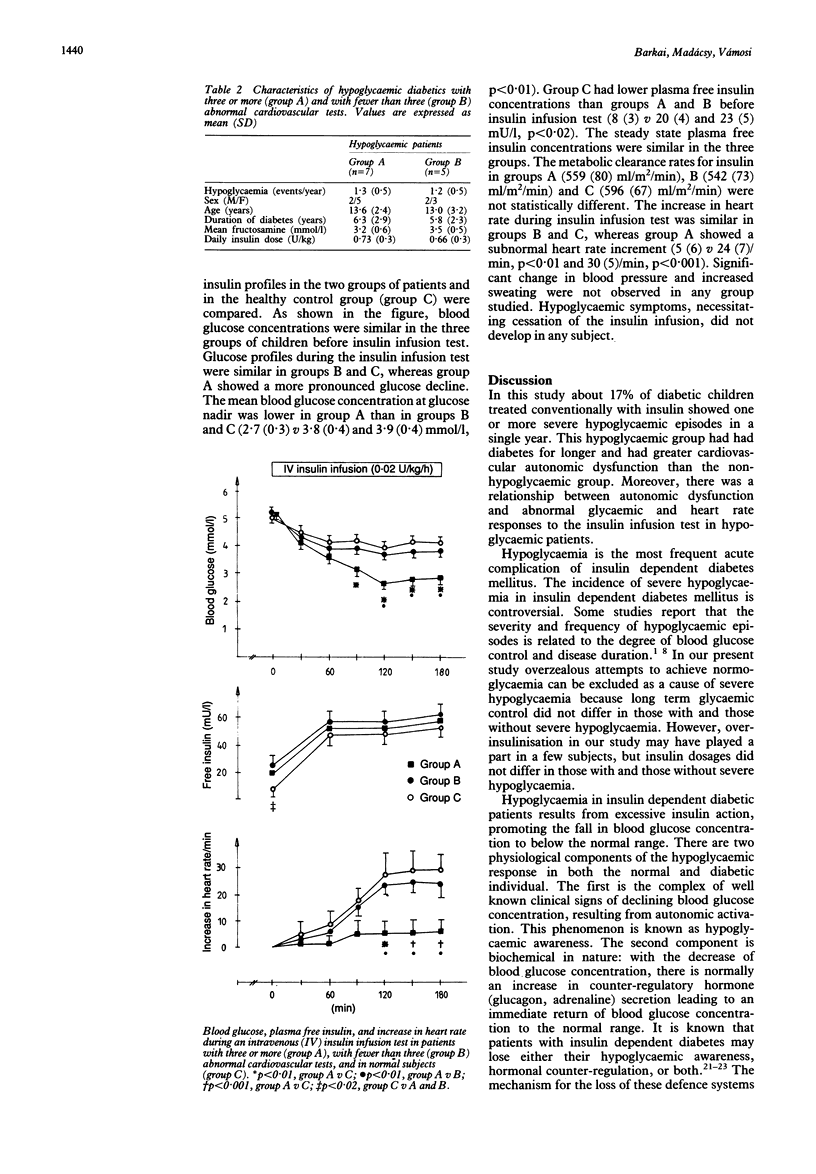
Abstract
The aims of the present study were to investigate the relationship between severe hypoglycaemia and autonomic dysfunction in diabetic children, and to assess the glycaemic response to an insulin infusion test. In a one year period, 12 of 69 diabetic patients (17%) experienced at least one severe episode of hypoglycaemia, defined as an event which required outside assistance. All patients underwent five cardiovascular autonomic tests. Seven of the hypoglycaemic patients showed three or more abnormal autonomic tests. Among the 57 non-hypoglycaemic diabetics, there was no patient with three or more abnormal tests. In hypoglycaemic diabetics with and without autonomic dysfunction, and in eight healthy age matched subjects an insulin infusion test was performed. A pronounced blood glucose decline and a subnormal increase in heart rate during insulin infusion were obtained in patients with autonomic dysfunction. Thus, severe hypoglycaemia may be due to impaired defence mechanisms against blood glucose decline in diabetic children with autonomic dysfunction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barkai L., Jr, Madácsy L., Vincze P. Az autonóm neuropathia és retinális microangiopathia összefüggésének vizsgálata diabeteses gyermekekben. Orv Hetil. 1989 Sep 17;130(38):2037–2040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkai L., Madácsy L., Kassay L. Investigation of subclinical signs of autonomic neuropathy in the early stage of childhood diabetes. Horm Res. 1990;34(2):54–59. doi: 10.1159/000181795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G. B., Dimitriadis G. D., Pehling G. B., Baker B. A., Haymond M. W., Cryer P. E., Gerich J. E. Abnormal glucose counterregulation after subcutaneous insulin in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 28;310(26):1706–1711. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406283102605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. V., Kraegen E. W., Lazarus L. Defective blood glucose counter-regulation in diabetics is a selective form of autonomic neuropathy. Br Med J. 1977 Dec 10;2(6101):1527–1529. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6101.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Binder C., Bolli G. B., Cherrington A. D., Gale E. A., Gerich J. E., Sherwin R. S. Hypoglycemia in IDDM. Diabetes. 1989 Sep;38(9):1193–1199. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.9.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneman D., Frank M., Perlman K., Tamm J., Ehrlich R. Severe hypoglycemia in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: frequency and predisposing factors. J Pediatr. 1989 Nov;115(5 Pt 1):681–685. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80642-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT): results of feasibility study. The DCCT Research Group. Diabetes Care. 1987 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–19. doi: 10.2337/diacare.10.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing D. J., Campbell I. W., Clarke B. F. Heart rate changes in diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1981 Jan 24;1(8213):183–186. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing D. J., Clarke B. F. Diagnosis and management of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 2;285(6346):916–918. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6346.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frier B. M. Lawrence Lecture. Hypoglycaemia and diabetes. Diabet Med. 1986 Nov-Dec;3(6):513–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1986.tb00807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgewicht C., Slama G., Papoz L., Tchobroutsky G. Hypoglycaemic reactions in 172 Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1983 Feb;24(2):95–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00297389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. E., England J. D., Hess R., Rawlings S. S., Walker B. A prospective study of symptomatic hypoglycemia in young diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 1981 Nov-Dec;4(6):601–605. doi: 10.2337/diacare.4.6.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepburn D. A., Patrick A. W., Eadington D. W., Ewing D. J., Frier B. M. Unawareness of hypoglycaemia in insulin-treated diabetic patients: prevalence and relationship to autonomic neuropathy. Diabet Med. 1990 Sep-Oct;7(8):711–717. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1990.tb01475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilsted J., Madsbad S., Krarup T., Sestoft L., Christensen N. J., Tronier B., Galbo H. Hormonal, metabolic, and cardiovascular responses to hypoglycemia in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes. 1981 Aug;30(8):626–633. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.8.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeldtke R. D., Boden G., Shuman C. R., Owen O. E. Reduced epinephrine secretion and hypoglycemia unawareness in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Apr;96(4):459–462. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher T. D., Tanenberg R. J., Greenberg B. Z., Hoffman J. E., Doe R. P., Goetz F. C. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):196–200. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlhauser I., Berger M., Sonnenberg G., Koch J., Jörgens V., Schernthaner G., Scholz V., Pädagogin D. Incidence and management of severe hypoglycemia in 434 adults with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1985 May-Jun;8(3):268–273. doi: 10.2337/diacare.8.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A., Tideholm B., Kalén J., Katzman P. Incidence of severe hypoglycemia and its causes in insulin-treated diabetics. Acta Med Scand. 1988;224(3):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1988.tb19370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikawa N., Umetsu M., Sakurada M., Sato H., Toyota T., Goto Y. Discrimination between cardiac para- and sympathetic damage in diabetics. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1985 Dec;1(4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(85)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Werner P. L., Hollander P., Ensinck J. W. Evaluation of the control of glucagon secretion by the parasympathetic nervous system in man. Metabolism. 1979 May;28(5):549–552. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J., Clarke P., Gale E. A., Dave S. H., Tattersall R. B. Insulin-induced hypoglycaemia in an accident and emergency department: the tip of an iceberg? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 23;285(6349):1180–1182. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6349.1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. M., Atchison J., Puczynski S., Puczynski M., Arslanian S., Becker D. Mild hypoglycemia associated with deterioration of mental efficiency in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr. 1990 Jul;117(1 Pt 1):32–38. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82440-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltész G., Acsádi G. Association between diabetes, severe hypoglycaemia, and electroencephalographic abnormalities. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Jul;64(7):992–996. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.7.992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). Design and methodologic considerations for the feasibility phase. The DCCT Research Group. Diabetes. 1986 May;35(5):530–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


