Abstract
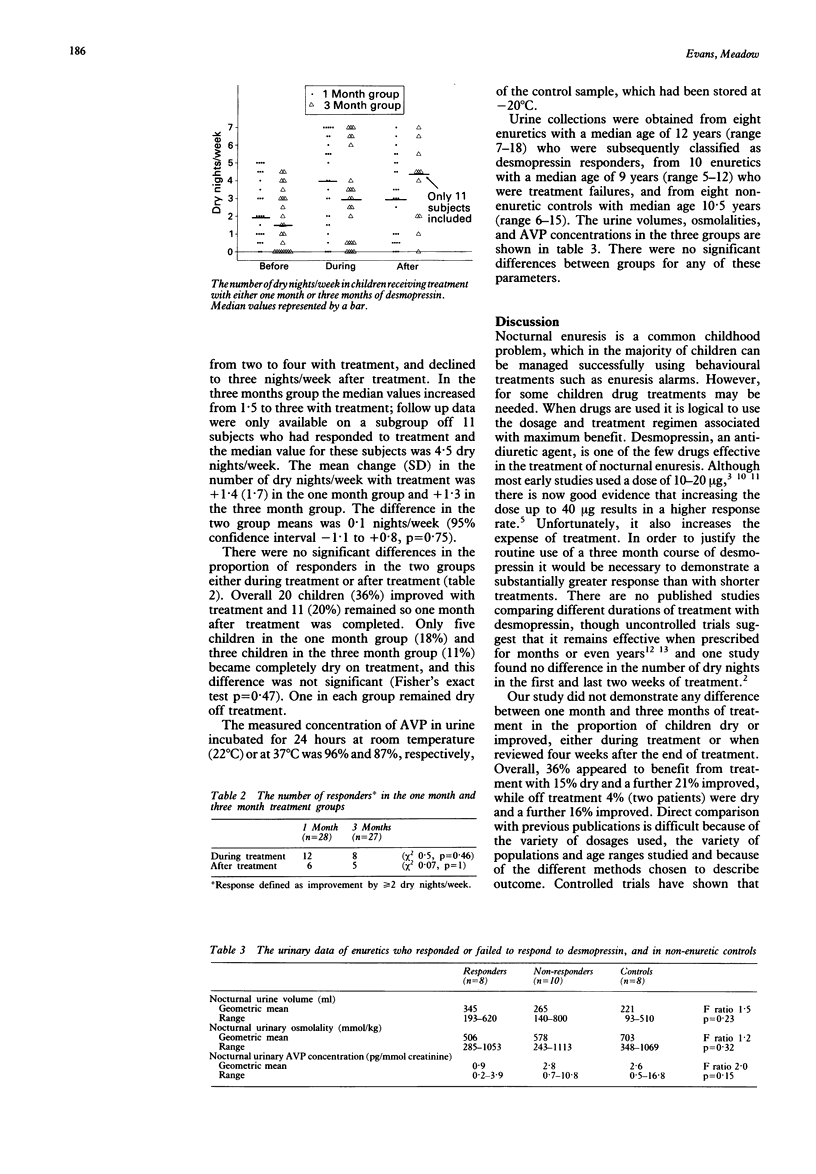
Fifty five children with nocturnal enuresis referred to a hospital enuresis clinic entered a controlled trial to compare the efficacy of one month and three month courses of intranasal desmopressin (Desmospray). There was no significant difference in outcome between the two groups. Overall 36% improved by at least two dry nights/week during treatment, but only five children (18%) in the one month group and three (11%) in the three month group became completely dry and only one in each group remained dry after treatment. To determine whether nocturnal polyuria was associated with a therapeutic response to desmopressin, the nocturnal urine volume, osmolality, and vasopressin concentration were measured in desmopressin responsive enuretics, desmopressin non-responders, and non-enuretic control children. There were no significant differences between the three groups. A three month course of desmopressin is no more effective than a one month course. Although many children will improve during treatment, only a small number become dry and most will relapse when treatment is stopped.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aladjem M., Wohl R., Boichis H., Orda S., Lotan D., Freedman S. Desmopressin in nocturnal enuresis. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Feb;57(2):137–140. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avendaño L. F., Calderón A., Macaya J., Prenzel I., Duarte E. Rotavirus viral RNA electrophoresis in hospitalized infants with diarrhea in Santiago, Chile. Pediatr Res. 1982 Apr;16(4 Pt 1):329–330. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198204000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkásová M., Birkás O., Flynn M. J., Cort J. H. Desmopressin in the management of nocturnal enuresis in children: a double-blind study. Pediatrics. 1978 Dec;62(6):970–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaere K. P., Strijbos W. E. Antidiuretic approach with DDAVP for nocturnal enuresis. Acta Urol Belg. 1986;54(4):464–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimson S. B. DDAVP and urine osmolality in refractory enuresis. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Nov;61(11):1104–1107. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.11.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische S., Yule W., Corbett J., Hand D. Childhood nocturnal enuresis: factors associated with outcome of treatment with an enuresis alarm. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1983 Feb;25(1):67–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1983.tb13723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etzioni A., Benderley A., Levi Y. Water intoxication by the oral route in an infant. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Jul;54(7):551–553. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.7.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finberg L. Water intoxication. A prevalent problem in the inner city. Am J Dis Child. 1991 Sep;145(9):981–982. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1991.02160090033016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. P., Messerli F. H., Genest J., Nowaczynski W., Boucher R., Kuchel Orofo-Oftega M. Diurnal variation of plasma vasopressin in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Aug;41(2):332–338. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating J. P., Schears G. J., Dodge P. R. Oral water intoxication in infants. An American epidemic. Am J Dis Child. 1991 Sep;145(9):985–990. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1991.02160090037018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nørgaard J. P., Pedersen E. B., Djurhuus J. C. Diurnal anti-diuretic-hormone levels in enuretics. J Urol. 1985 Nov;134(5):1029–1031. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)47581-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULTON E. M., HINDEN E. The classification of enuresis. Arch Dis Child. 1953 Oct;28(141):392–397. doi: 10.1136/adc.28.141.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsden P. D., Hindmarsh J. R., Price D. A., Yeates W. K., Bowditch J. D. DDAVP for adult enuresis--a preliminary report. Br J Urol. 1982 Jun;54(3):256–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1982.tb06970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuvemo T. DDAVP in childhood nocturnal enuresis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1978 Nov;67(6):753–755. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1978.tb16255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VULLIAMY D. The day and night output of urine in enuresis. Arch Dis Child. 1956 Dec;31(160):439–443. doi: 10.1136/adc.31.160.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanapruks V., Prapaitrakul K. Water intoxication and hyponatraemic convulsions in neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1989 May;64(5):734–735. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.5.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiriyathian S., Rosenfeld C. R., Arant B. S., Jr, Porter J. C., Faucher D. J., Engle W. D. Urinary arginine vasopressin: pattern of excretion in the neonatal period. Pediatr Res. 1986 Feb;20(2):103–108. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198602000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


