Abstract
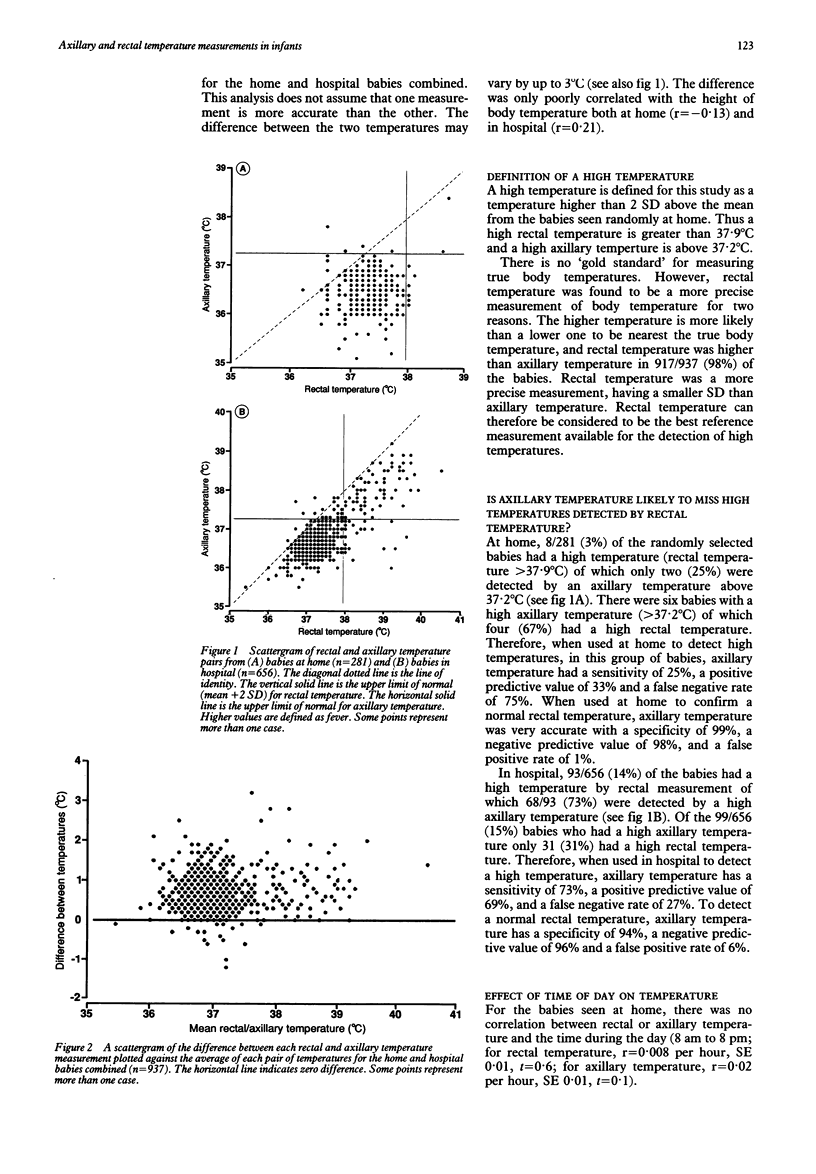
Rectal and axillary temperatures were measured during the daytime in 281 infants seen randomly at home and 656 at hospital under 6 months old, using mercury-in-glass thermometers. The normal temperature range derived from the babies at home was 36.7-37.9 degrees C for rectal temperature and 35.6-37.2 degrees C for axillary temperature. Rectal temperature was higher than axillary in 98% of the measurements. The mean (SD) difference between rectal and axillary temperatures was 0.7 (0.5) degrees C, with a range of 3 degrees C. When used in hospital to detect high temperature, axillary temperature had a sensitivity of 73% compared with rectal temperature. This is too insensitive for accurate detection of an infant's high temperature. Rectal temperature measurement is safer than previously suggested: perforation has occurred in less than one in two million measurements. If an infant's temperature needs to be taken, rectal temperature should be used.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. S., Petersen S. A., Wailoo M. P. Factors influencing the body temperature of 3-4 month old infants at home during the day. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Dec;65(12):1308–1310. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.12.1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrus D. H. A comparison of rectal and axillary temperatures by electronic thermometer measurement in preschool children. Pediatr Nurs. 1983 Nov-Dec;9(6):424–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANBY J. P. Rectal perforation: a hazard of rectal temperatures. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1963 May;2:223–224. doi: 10.1177/000992286300200503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAAS L. Neonatal perforation of the colon. Arch Dis Child. 1958 Aug;33(170):362–363. doi: 10.1136/adc.33.170.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresch M. J. Axillary temperature as a screening test for fever in children. J Pediatr. 1984 Apr;104(4):596–599. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80558-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. T., Ong G. B. Broken and retained rectal thermometers in infants and young children. Aust Paediatr J. 1981 Jun;17(2):93–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1981.tb01912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messaritakis J., Anagnostakis D., Laskari H., Katerelos C. Rectal-skin temperature difference in septicaemic newborn infants. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Apr;65(4 Spec No):380–382. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.4_spec_no.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar G. W., Read R. C. Studies during open-heart surgery on the special characteristics of rectal temperature. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Mar;36(3):333–336. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.3.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales L., Rovira J., Mongard M., Sancho M. A., Bach A. Intraspinal migration of a rectal foreign body. J Pediatr Surg. 1983 Oct;18(5):634–635. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(83)80381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley C. J., Thornton A. J., Cole T. J., Hewson P. H., Fowler M. A. Baby Check: a scoring system to grade the severity of acute systemic illness in babies under 6 months old. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Jan;66(1):100–105. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogren J. M. The inaccuracy of axillary temperatures measured with an electronic thermometer. Am J Dis Child. 1990 Jan;144(1):109–111. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1990.02150250121048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRISH R. A., SHERMAN R. T., WILSON H. SPONTANEOUS RUPTURE OF THE GASTRO-ENTERIC TRACT IN THE NEWBORN: A REPORT OF 13 CASES AND DESCRIPTION OF A CHARACTERISTIC X-RAY FINDING. Ann Surg. 1964 Feb;159:244–251. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196402000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGNITZ R. H. Accidental transanal perforation of the rectum; an obscure cause of peritonitis in infancy and childhood. AMA J Dis Child. 1957 Mar;93(3):255–258. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1957.02060040257010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shann F., Mackenzie A. Axillary or rectal temperatures in children. Lancet. 1981 Aug 8;2(8241):310–310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90563-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiddy F. G., Benson E. A. Rectal perforation by thermometer. Lancet. 1969 Oct 11;2(7624):805–806. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90525-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. E., Kiely E. M., Agrawal M., Brereton R. J., Spitz L. Neonatal gastrointestinal perforation. J Pediatr Surg. 1989 Sep;24(9):888–892. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(89)80589-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton A. J., Morley C. J., Green S. J., Cole T. J., Walker K. A., Bonnett J. M. Field trials of the Baby Check score card: mothers scoring their babies at home. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Jan;66(1):106–110. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARWICK W. J., GIKAS P. W. Neonatal transanal perforation of the rectum. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 Jun;97(6):869–870. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010871018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON A. W. 'SPONTANEOUS' RUPTURE OF THE RECTUM. Proc R Soc Med. 1965 Aug;58:615–616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wailoo M. P., Petersen S. A., Whittaker H., Goodenough P. Sleeping body temperatures in 3-4 month old infants. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Apr;64(4):596–599. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.4.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waskerwitz S., Berkelhamer J. E. Outpatient bacteremia: clinical findings in children under two years with initial temperatures of 39.5 degrees C or higher. J Pediatr. 1981 Aug;99(2):231–233. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80458-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. J. Rectal perforation in infant by thermometer. Case report with review of literature on rectal perforation. Am J Dis Child. 1966 Feb;111(2):197–200. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1966.02090050129012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


