Abstract
Metabolic decompensation may occur in patients with disorders of intermediary metabolism during intercurrent illness. To prevent complications it is normal practice to change the diet to an 'emergency regimen'. The mainstay of this is a high carbohydrate intake, using soluble glucose polymer, given as frequent drinks by day and during the night. Additional therapy is given for some disorders. Practical details of the treatment are outlined.
Full text
PDF

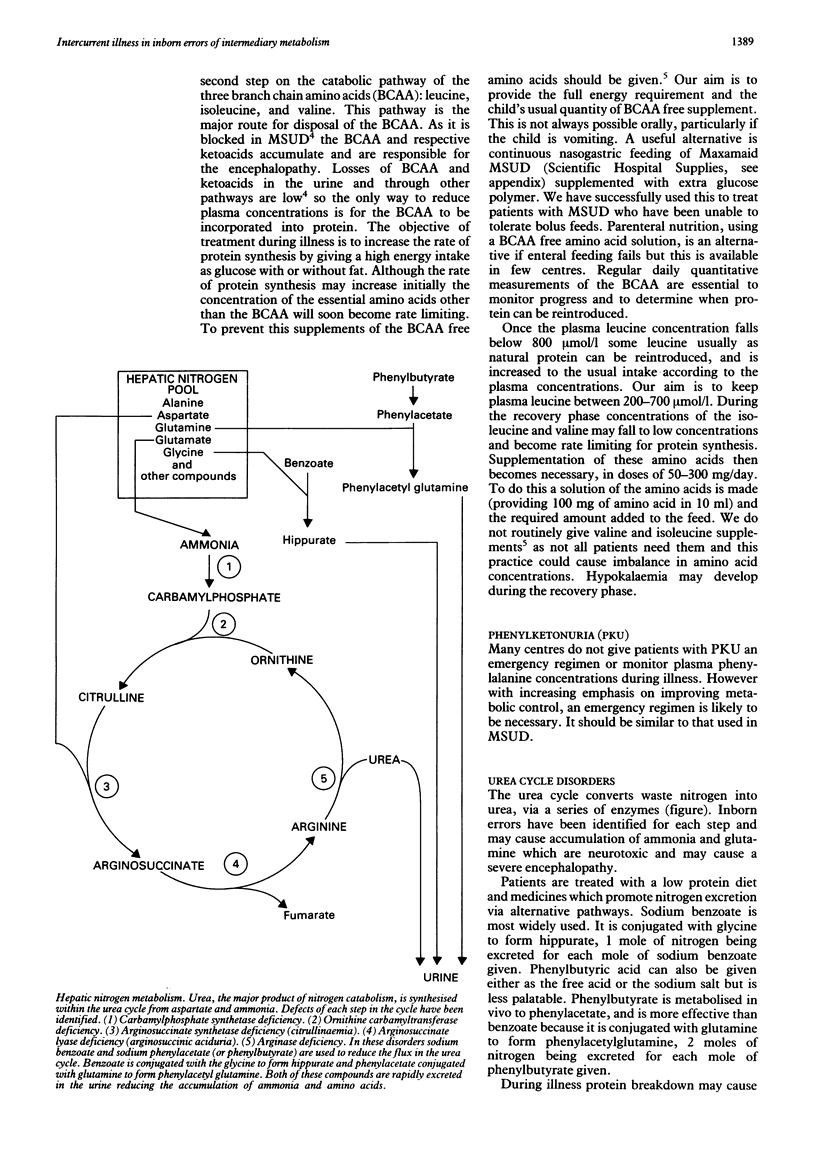

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- D'Angio C. T., Dillon M. J., Leonard J. V. Renal tubular dysfunction in methylmalonic acidaemia. Eur J Pediatr. 1991 Feb;150(4):259–263. doi: 10.1007/BF01955526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie M. J., Edwards R. H., Halliday D., Matthews D. E., Wolman S. L., Millward D. J. Muscle protein synthesis measured by stable isotope techniques in man: the effects of feeding and fasting. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Dec;63(6):519–523. doi: 10.1042/cs0630519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. N., Francis D. E., Halliday D. Acute illness in maple syrup urine disease: dynamics of protein metabolism and implications for management. J Pediatr. 1991 Jul;119(1 Pt 1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. N., Walter J. H., Bresson J. L., Ford G. C., Lyonnet S. L., Chalmers R. A., Saudubray J. M., Leonard J. V., Halliday D. Sources of propionate in inborn errors of propionate metabolism. Metabolism. 1990 Nov;39(11):1133–1137. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90084-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


