Abstract
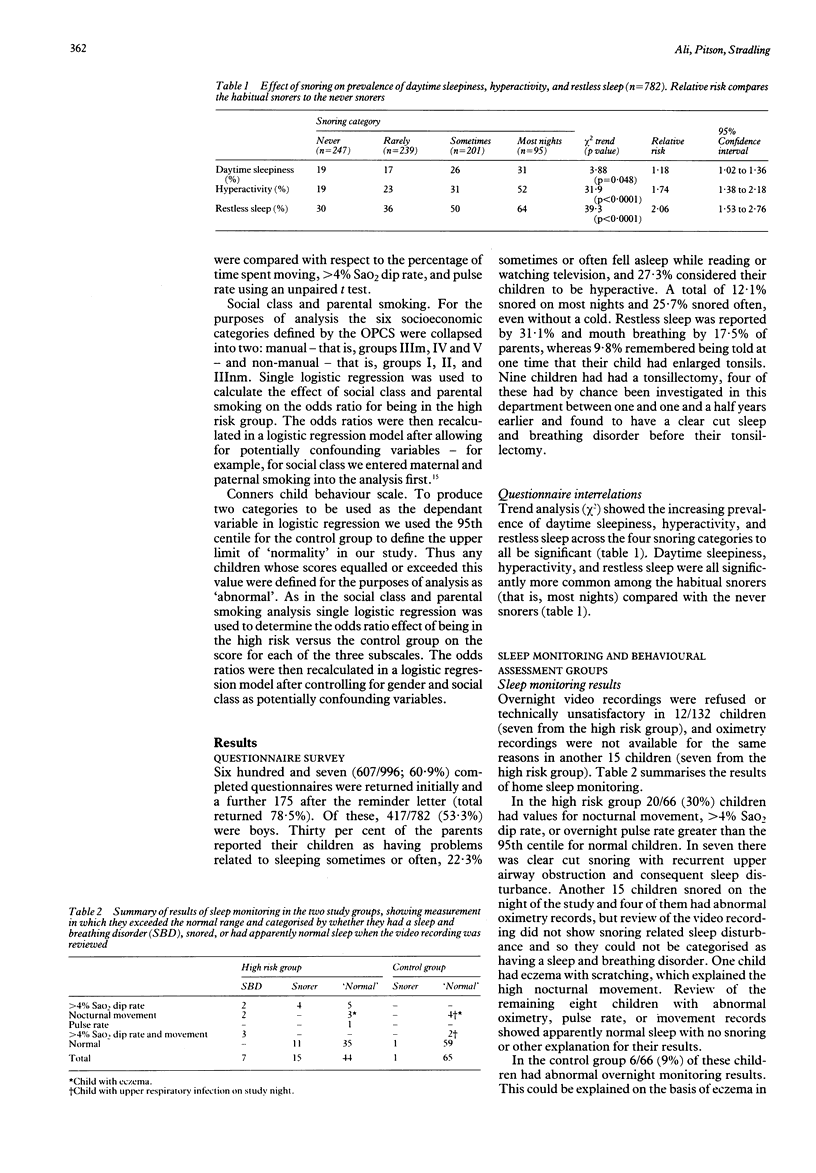
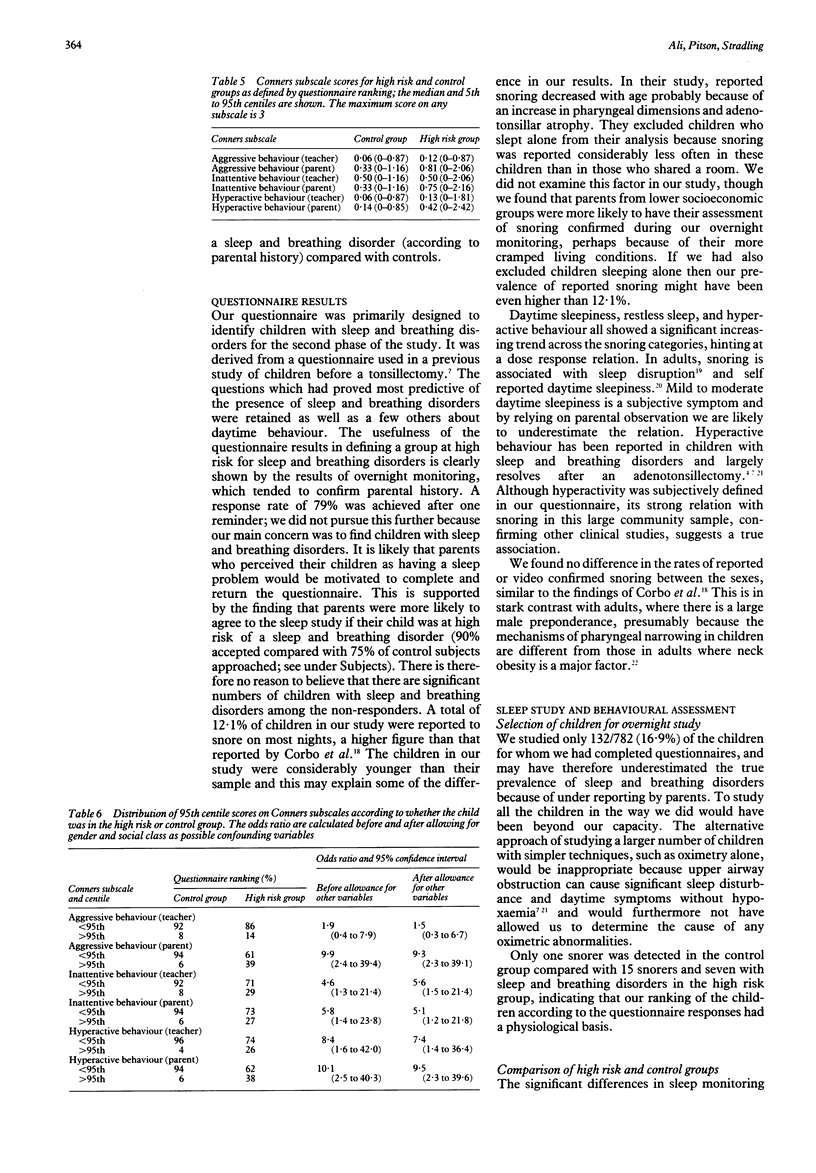
Parents of 996 children aged 4-5 years identified consecutively from the Oxford health visitor register were asked to complete a questionnaire about breathing disorders during sleep. A total of 782 (78.5%) was returned. Ninety five (12.1%) children were reported to snore on most nights. Habitual snoring was significantly associated with daytime sleepiness, restless sleep, and hyperactivity. The questionnaire responses were used to select two subgroups, one at high risk of a sleep and breathing disorder and a control group. These children (132 in total) were monitored at home with overnight video recording and oximetry, and had formal behavioural assessment using the Conners scale. Seven (7/66) children from the high risk group and none from the control group had obvious sleep disturbance consequent on snoring and upper airway obstruction. Thus our estimate of the prevalence of sleep and breathing disorders in this age group is 7/996 or 0.7%. The high risk group had significantly higher nocturnal movement, oxygen saturation dip rates, and overnight pulse rates than the controls. Maternal but not paternal smoking was associated with the high risk group. Parents and teachers thought those in the high risk group were more hyperactive and inattentive than the controls, but only their parents thought them more aggressive. Significant sleep and breathing disorders occur in about 0.7% of 4-5 year olds. Children whose parents report snoring and sleep disturbance have objective evidence of sleep disruption and show more behaviour problems than controls.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brodsky L., Moore L., Stanievich J. F. A comparison of tonsillar size and oropharyngeal dimensions in children with obstructive adenotonsillar hypertrophy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1987 Aug;13(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0165-5876(87)90091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Check W. A. Does drop in T and A's pose new issue of adenotonsillar hypertrophy? JAMA. 1982 Mar 5;247(9):1229–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conners C. K. A teacher rating scale for use in drug studies with children. Am J Psychiatry. 1969 Dec;126(6):884–888. doi: 10.1176/ajp.126.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbo G. M., Fuciarelli F., Foresi A., De Benedetto F. Snoring in children: association with respiratory symptoms and passive smoking. BMJ. 1989 Dec 16;299(6714):1491–1494. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6714.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft C. B., Brockbank M. J., Wright A., Swanston A. R. Obstructive sleep apnoea in children undergoing routine tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1990 Aug;15(4):307–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1990.tb00474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. J., Stradling J. R. The relationship between neck circumference, radiographic pharyngeal anatomy, and the obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Eur Respir J. 1990 May;3(5):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRY J. Are all "T's and A's" really necessary? Br Med J. 1957 Jan 19;1(5011):124–129. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5011.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Korobkin R., Winkle R. A review of 50 children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Lung. 1981;159(5):275–287. doi: 10.1007/BF02713925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Stoohs R., Duncan S. Snoring (I). Daytime sleepiness in regular heavy snorers. Chest. 1991 Jan;99(1):40–48. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Winkle R., Korobkin R., Simmons B. Children and nocturnal snoring: evaluation of the effects of sleep related respiratory resistive load and daytime functioning. Eur J Pediatr. 1982 Nov;139(3):165–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01377349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport J. L., Benoit M. The relation of direct home observations to the clinic evaluation of hyperactive school age boys. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1975 Apr;16(2):141–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1975.tb01263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. M., Green R. P. Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy: changing trends. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1990 Mar;99(3 Pt 1):187–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said G., Zalokar J., Lellouch J., Patois E. Parental smoking related to adenoidectomy and tonsillectomy in children. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1978 Jun;32(2):97–101. doi: 10.1136/jech.32.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradling J. R., Crosby J. H., Payne C. D. Self reported snoring and daytime sleepiness in men aged 35-65 years. Thorax. 1991 Nov;46(11):807–810. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.11.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradling J. R., Crosby J. H. Relation between systemic hypertension and sleep hypoxaemia or snoring: analysis in 748 men drawn from general practice. BMJ. 1990 Jan 13;300(6717):75–78. doi: 10.1136/bmj.300.6717.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradling J. R., Thomas G., Warley A. R., Williams P., Freeland A. Effect of adenotonsillectomy on nocturnal hypoxaemia, sleep disturbance, and symptoms in snoring children. Lancet. 1990 Feb 3;335(8684):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90068-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E., Sandberg S. Hyperactive behavior in English schoolchildren: a questionnaire survey. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1984 Mar;12(1):143–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00913466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trites R. L., Blouin A. G., Laprade K. Factor analysis of the Conners Teacher Rating Scale based on a large normative sample. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1982 Oct;50(5):615–623. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.50.5.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warley A. R., Mitchell J. H., Stradling J. R. Evaluation of the Ohmeda 3700 pulse oximeter. Thorax. 1987 Nov;42(11):892–896. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.11.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


