Abstract
In 8 out of 32 juvenile patients suffering from chronic polyarthritis and in one patient with dermatomyositis, raised transaminase levels were found; the salicylate level was above 35 mg/100 ml in all except one. Reduction in the salicylate level led to a prompt fall in the serum transaminases. Despite a rise in alkaline phosphatase in three cases there was no other evidence of liver dysfunction in the children. Only one of the adults showed a rise in transaminase levels, and she had mild cirrhosis.
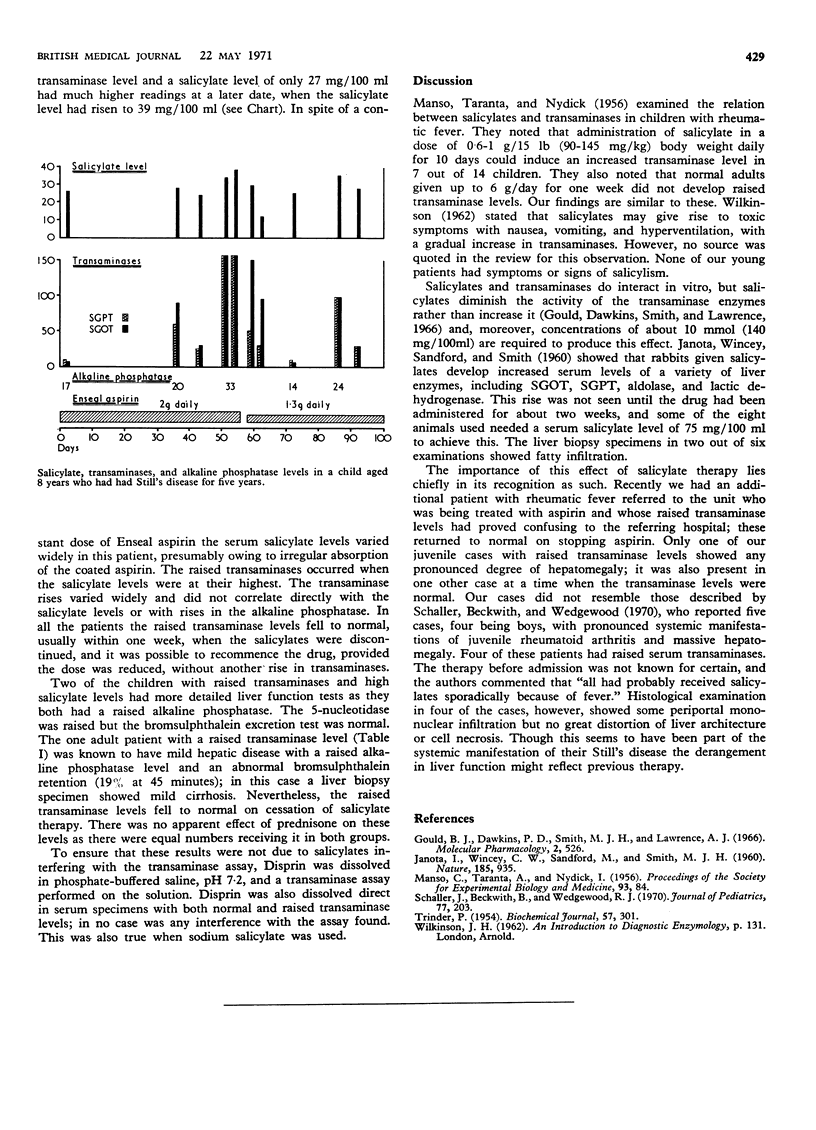
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- JANOTA I., WINCEY C. W., SANDIFORD M., SMITH M. J. Effect of salicylate on the activity of plasma enzymes in the rabbit. Nature. 1960 Mar 26;185:935–936. doi: 10.1038/185935a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller J., Beckwith B., Wedgwood R. J. Hepatic involvement in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Pediatr. 1970 Aug;77(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRINDER P. Rapid determination of salicylate in biological fluids. Biochem J. 1954 Jun;57(2):301–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0570301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


