Abstract
Background
Re‐expression of the recombination‐activating genes (RAG) in peripheral B cells may be relevant in the development of autoreactive antibodies in autoimmune diseases. The presence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) as a hallmark of oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (o‐JIA, early‐onset type) indicates a breakdown in immunological tolerance.
Aim
To examine the expression of RAG genes in peripheral blood mature B lymphocytes in patients with o‐JIA.
Methods
777 memory B cells from peripheral blood, CD19+ CD27+ CD5+ or CD19+ CD27+ CD5−, isolated from three ANA+ children with o‐JIA and three healthy age‐matched children, were examined for the expression of RAG1 and RAG2 mRNA. mRNA transcripts of activation‐induced cytidine deaminase and immunoglobulin G were searched to further determine their developmental stage.
Results
mRNA was present for any of the two RAG genes in the B cells of children with JIA and controls. However, the predominance of RAG1 or RAG2 was different. A significantly decreased frequency of RAG2‐expressing memory B cells in both CD5+ and CD5− populations was noted in children with JIA (p<0.001), whereas the number of RAG1‐expressing B cells was slightly increased. The coordinate expression of both the RAG genes was a rare event, similar in the CD5+ populations (1% in controls, 2% in children with JIA), but different among the CD5− compartments (5% v 0%; p<0.01).
Conclusion
These results argue for a reduced coordinate RAG expression in the peripheral CD5− memory B cells of patients with o‐JIA. Thus, it was hypothesised that impaired receptor revision contributes to autoimmune pathogenesis in JIA.
Oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (o‐JIA)1 is one of the frequently diagnosed subtypes and is associated with human leucocyte antigen alleles and antinuclear antibodies (ANA). The contribution of ANA to the pathogenesis of JIA has been investigated poorly. As in other autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or rheumatoid arthritis, the detection of autoreactive antibodies is clinically relevant for making the diagnosis. High levels of rheumatoid factor or ANA in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or SLE suggest a pathogenetic relevance. The reason why tolerance is broken and why these antibodies are produced in JIA remains unknown.
During their early development in the bone marrow, lymphocytes undergo rearrangements of their genomic immunoglobulin loci to diversify their antibody repertoire. In this process, RAG proteins, as transcripts of the recombination‐activating genes 1 (RAG1) and 2 (RAG2), have a crucial role. Their expression is strictly limited to lymphocytes. The process of variable, diversity and joining gene segments (V(D)J) recombination results in the production of functional surface immunoglobulins. A mature B cell compartment cannot be established when RAG genes are defective.2,3,4
V(D)J rearrangement has long been considered to be restricted to early B cell precursors in the bone marrow. However, it has been shown that in the immature bone marrow stages and even outside the bone marrow microenvironment, secondary rearrangements occur to rescue lymphocytes with self‐reactive antibodies from negative selection. This salvage pathway was termed receptor editing in bone marrow and receptor revision in the periphery.5 Until now, the role of receptor revision in tolerance induction has not been fully established. Evidence shows that pathological activation of receptor revision can even lead to a breakdown in tolerance. Recently, mature B cells in germinal centres have been shown to undergo receptor revision after exposure to interleukin (IL)4 and lipopolysaccharide or CD40L and after immunisation.6,7,8,9 Others have shown RAG reinduction in circulating mature peripheral B cells on stimulation with Staphylococcusaureus Cowan 1 and IL2.10 Receptor revision in mature peripheral B cells, however, has been challenged by reports stating that RAG‐expressing peripheral lymphocytes in part exhibited an immature phenotype. Such an expression of VpreB, IL7R and TdT may result from a premature release from the bone marrow or the presence of transitional B cells.11,12,13,14
Secondary rearrangements may have an important role in autoimmune diseases. Two different mechanisms can be envisaged. Disease may be promoted by an uncontrolled creation of autoreactive antibodies in the periphery. On the other hand, receptor revision may rescue B cells that have acquired autoreactive receptors.15,16,17,18 In addition, a deficiency in receptor editing or receptor revision may be a cause for ineffective deletion of autoreactive B cells as proposed for SLE.19,20
CD5+ B cells, part of the B1 cell compartment, are suggested to have a major role in innate immunity and are found predominantly in body cavities. They produce mainly polyreactive antibodies of the immunoglobulin (Ig)M class, with a restricted repertoire. Owing to their polyreactivity, these cells have the potential to contribute to autoimmunity. This has been postulated in several reports showing raised numbers of this B cell subset in systemic autoimmune diseases,21 including JIA.22,23
To assess whether human memory B lymphocytes as defined by the expression of surface CD2724 exhibit an irregular expression of RAG genes in an autoimmune context, we examined peripheral blood CD19+ CD27+ B lymphocytes from healthy children and ANA‐positive patients with o‐JIA. With a sensitive single‐cell reverse transcriptase‐polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique, the expression of RAG1 and RAG2 was evaluated in individual CD19+ CD27+ CD5+ or CD19+ CD27+ CD5− B cells. We also searched for transcripts of IgG and activation‐induced cytidine deaminase (AID) as markers for germinal centre B cells.25,26
Patients, materials and methods
Patients
For the examination of individual B cells we took heparinised blood samples from three ANA‐positive paediatric patients diagnosed with persistent o‐JIA.1 Three age‐matched healthy children served as controls. The mean (range) age for children with o‐JIA was 4.6 (3–5) years and for controls was 4.7 (2–8) years (table 1). Parents gave informed consent. The study was conducted according to the modified Declaration of Helsinki and the ethics committee of the University of Würzburg approved the study.
Table 1 Patient details at the time of sampling.
| Patient number | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 5 | 3 | 4 |
| Active joints (n) | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| ESR (mm at the end of the first hour) | 7 | 14 | 20 |
| Hb (g/dl) | 12.5 | 11.8 | 12.8 |
| Thr (per μl) | 306 000 | 349 000 | 421 000 |
| ANA | 1:640 | 1:640 | 1:2.560 |
| Drugs | – | Naproxen | Naproxen, methotrexate |
| Duration of disease (months) | 37 | 4 | 35 |
ANA, antinuclear antibodies; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; Hb, haemoglobin; Thr, thrombocytes.
Preparation of B cells from tonsil tissue for detection of AID mRNA
A tonsil from a healthy child was obtained after tonsillectomy. Suspensions of tonsillar mononuclear cells were prepared by collagenase digestion (Worthington Biochemical, Lakewood, New Jersey, USA) of the tissue for 30 min, followed by Ficoll–Hypaque density gradient centrifugation.7 Subsequently, cells were stained with anti‐CD19 (isothiocyanate‐labelled, Caltag, Burlingame, California, USA), anti‐IgD (fluorescein isothiocyanate‐labelled, Caltag) and anti‐CD38 (PE‐labelled, BD Pharmingen, San Diego, California, USA), and sorted.
Preparation of B cells from peripheral blood
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from heparinised blood samples were separated by the Ficoll–Hypaque density gradient. For single‐cell sorting, cells were three‐colour stained and incubated for 20 min with anti‐CD19 (isothiocyanate‐labelled, Caltag), anti‐CD27 (fluorescein isothiocyanate‐labelled, BD Pharmingen) and anti‐CD5 (PE‐labelled, Caltag) antibodies, followed by two washing steps. Isotype‐matched antibodies served as controls.
Single‐cell sorting
Using a FACSVantage Flow Cytometer (Becton Dickinson, San Diego, California, USA) equipped with a single‐cell deposition unit, the two populations of CD19+ CD27+ CD5+ and CD19+ CD27+ CD5− cells were identified and individual cells from each population were deposited in 96‐well PCR plates, as described previously.7,17 Tonsillar IgD+ CD38++ B cells were sorted as individual B cells to examine AID gene expression.
Preparation of RNA and cDNA from sorted single cells
Before sorting cells into 96‐well plates, each well was provided with 10 μl of lysis solution (4.85 μl aqua, 2 μl 5× first‐strand buffer (Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany); 1 μl 0.1 M dithiothreitol (Invitrogen); 1 μl 1% Nonidet‐NP40 (Sigma, St Louis, Missouri, USA); 10 units of RNAsin ribonuclease inhibitor (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA); 0.8 μl 10 mM deoxynucleotide triphosphate (dNTP; Sigma); 0.1 μg oligo‐(dT)12–18 (Amersham Pharmacia Biotec, Piscataway, New Jersey, USA). RNA to cDNA was reverse transcribed as described previously by using Superscript II RNase H‐RT (Invitrogen).7,17 cDNA was stored at −72°C before further processing.
External and nested PCR amplification
AID was amplified at 94°C for 3 min, 36 cycles of 30 s at 94°C, 60 s at 60°C and 90 s at 72°C, followed by a final extension step of 3 min at 72°C. The following primers (5′–3′) were used:
External, sense: GAGGCAAGAAGACACTCTGG27
External, antisense: GTGACATTCCTGGAAGTTGC27
Nested, sense: TACTTCTGTGAGGACCGCAA
Nested, antisense: CATACAGGGGCAAAAGGATG
Oligonucleotide ACTTTCAAAGCCTGGGAAGG used for detection.
IgG transcripts of β‐actin, RAG1, RAG2 exon 2a, RAG2 exon 2b and IgG were amplified under the same conditions using the same oligonucleotides as described earlier.7,17 In brief, 1.5 μl of cDNA was used to carry out external PCR for each gene, followed by 5 μl from external product for the nested PCR. Wells without reverse transcriptase and without cDNA served as negative controls and did not yield a product. cDNA from tonsil extracts was used as a positive control. The exclusion of genomic DNA amplification was carried out as described previously.7,17
Detection of amplified cDNA by Southern blotting
Nested PCR products were transferred to a nylon membrane (ZetaProbe, BioRad, Hercules, California, USA) by Alkaline Dot‐Blot (BioRad), followed by DNA crosslinking under the influence of ultraviolet light. Membranes were then incubated in a hybridisation buffer containing DIG‐deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP)‐labelled (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) oligonucleotides specific for the amplified sequences. DIG‐dUTP was later detected by the chemoluminescent reaction, using alkaline phosphatase‐coupled anti‐DIG‐dUTP antibody and CSPD (Roche). Results were visualised by exposure to photographic film. Blots were analysed on a digital detection unit (BioRad) using QuantityOne Software (BioRad).
Statistical analysis
The χ2 test and Fisher's exact test were used to analyse statistical differences between the total of single cells from three patients and three controls. Levels of significance and high significance were set at p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively. Only B cells positive for β‐actin were considered for analysis.
Results
Expression of RAG genes and IgG mRNA in CD27+ CD5+ B cells
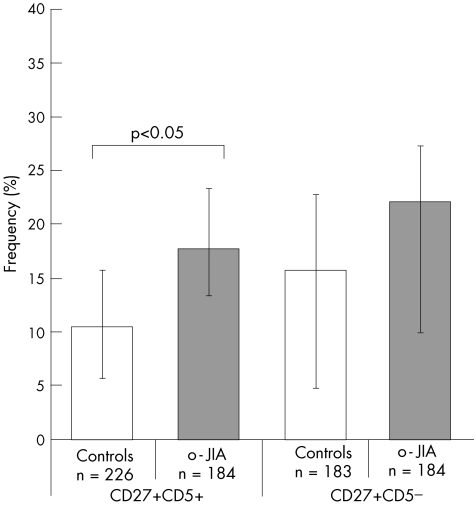
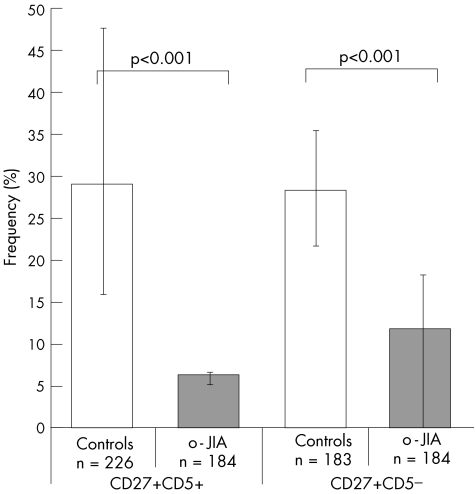
When we compared 226 B cells isolated from controls and 184 from patients with o‐JIA, we found a low frequency of RAG1‐expressing cells in controls and a higher number in patients with o‐JIA (mean 11% v 18%; p<0.05; fig 1). Examination for RAG2 mRNA expression showed a mean of 29% positive cells in controls, whereas lower levels were seen in patients with JIA (mean 6.5%; p<0.001; fig 2). Transcripts of either of the RAG genes were detectable to a considerable extent in each donor sample from both healthy children and children with JIA (mean 37% v 20%), with a significant reduction in transcripts from children with JIA (p<0.001). This was mainly attributed to the low RAG2 expression.
Figure 1 Frequencies of memory B cells expressing recombination‐activating gene 1 (RAG1) mRNA in children with oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (o‐JIA). Individual peripheral B cells isolated from three children with o‐JIA and three age‐matched healthy children bearing the indicated phenotype (CD19+ CD27+ CD5+ or CD19+ CD27+ CD5−) were sorted by fluorescence‐activated cell sorter. Only β‐actin‐positive (n) B cells were analysed. The frequency of cells expressing RAG1 mRNA in the total cohort was determined by single‐cell polymerase chain reaction and is indicated on the y axis. The bars indicate the range among individual patients.
Figure 2 Frequencies of memory B cells expressing recombination‐activating gene 2 (RAG2) mRNA in children with oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (o‐JIA). Individual peripheral B cells isolated from three children with o‐JIA and three age‐matched healthy children bearing the indicated phenotype (CD19+ CD27+ CD5+ or CD19+ CD27+ CD5−) were sorted by fluorescence‐activated cell sorter. Only β‐actin‐positive (n) B cells were analysed. The frequency of cells expressing RAG1 mRNA in the total cohort was determined by single‐cell polymerase chain reaction and is indicated on the y axis. The bars indicate the range among individual patients.
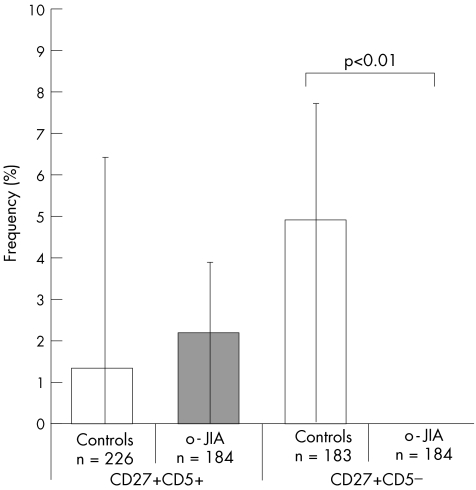
A coordinate expression of both RAG1 and RAG2 in individual cells was found only in a few cells in this B cell population, irrespective of whether controls or patients were analysed (1% in controls, 2% in patients with o‐JIA; fig 3).
Figure 3 Frequencies of memory B cells expressing recombination‐activating genes 1 and 2 (RAG1 and RAG2) mRNA isolated from children with oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (o‐JIA). Individual peripheral B cells isolated from three children with o‐JIA and three age‐matched healthy children bearing the indicated phenotype (CD19+ CD27+ CD5+ or CD19+ CD27+ CD5−) were sorted by fluorescence‐activated cell sorter. Only β‐actin‐positive (n) B cells were analysed. The frequency of cells expressing RAG1 mRNA in the total cohort was determined by single‐cell polymerase chain reaction and is indicated on the y axis. The bars indicate the range among individual patients.
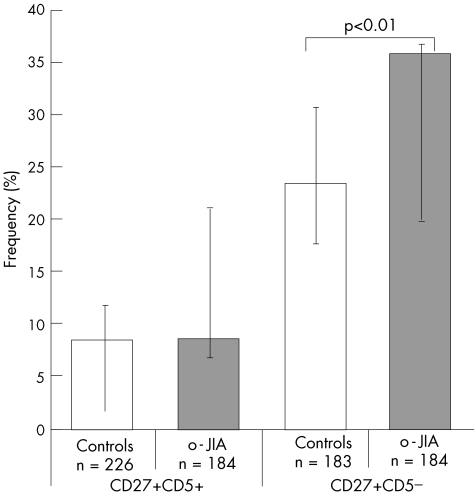
The frequency of CD27+ CD5+ B cells expressing IgG mRNA was 8% and 9% among patients and controls, and the difference was not significant (fig 4). None of the RAG double‐positive cells was positive for IgG mRNA in controls or in patients with o‐JIA (table 2).
Figure 4 Frequencies of immunoglobulin G mRNA expressing CD27+ memory B cells isolated from children with oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (o‐JIA). Individual peripheral B cells isolated from three children with o‐JIA and three age‐matched healthy children bearing the indicated phenotype (CD19+ CD27+ CD5+ or CD19+ CD27+ CD5−) were sorted by fluorescence‐activated cell sorter. Only β‐actin‐positive (n) B cells were analysed. The frequency of cells expressing RAG1 mRNA in the total cohort was determined by single‐cell polymerase chain reaction and is indicated on the y axis. The bars indicate the range among individual patients.
Table 2 Fractions of IgG‐positive and IgG‐negative B cells that are positive for RAG genes.
| Healthy | o‐JIA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG pos | IgG neg | IgG pos | IgG neg | |
| CD19+ CD27+ CD5+ (n) | 19 | 207 | 16 | 168 |
| RAG1 (%) | 11 | 11 | 13 | 18 |
| RAG2 (%) | 32 | 29 | 0 | 7 |
| RAG1+RAG2 (%) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| CD19+CD27+CD5− (n) | 43 | 140 | 66 | 118 |
| RAG1 (%) | 30 (p<0.01) | 11 | 23 | 22 |
| RAG2 (%) | 33 | 27 | 14 | 11 |
| RAG1+RAG2 (%) | 9 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Ig, immunoglobulin, neg, negative; o‐JIA, oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis; pos, positive; RAG, recombination‐activating gene.
Expression of RAG genes and IgG mRNA in CD27+ CD5− B cells
In the CD27+ CD5− population, we examined 183 single B cells isolated from controls and 184 cells from children with o‐JIA. RAG1 expression showed a comparable distribution as already seen in the CD5+ subset, with an increased number among patients with JIA compared with controls (mean 22% v 16%; p = 0.12; fig 1). RAG2 expression was also found to be similar when compared with the CD5+ population (mean 28% v 12%; p<0.001; fig 2).
Although patterns of individual RAG1 or RAG2 expression were comparable, the coordinate expression of RAG1 and RAG2 was strikingly different. In both healthy children and in those with o‐JIA, 34% of all CD5− B cells expressed either of the RAG genes. A coordinate expression of RAG1 and RAG2 was seen in 5% of B cells from controls (9/183; ie, 7.2%, 7.7% and 0.0%), but not in those from children with o‐JIA (p<0.01; fig 3).
When the expression of IgG in the CD5− population was studied, we found levels of IgG‐producing B cells higher than in the CD5+ population. Particularly, a larger frequency was found in children with o‐JIA than in controls (mean 36% v 23%; p<0.01). These results are consistent with phenotypical data from peripheral CD27+ B cells, where surface IgG ranged between 22% and 55%.27
In controls, RAG1‐expressing cells were significantly over‐represented in the IgG mRNA‐positive (13/43, 30%) compared with the IgG mRNA‐negative compartment (16/140, 11%; p<0.01; table 2).
Expression of AID mRNA in peripheral B cells isolated from children with o‐JIA
To further analyse the phenotype of CD27+ B cells and to exclude the possibility of them having recently been washed out of germinal centres in the course of a general inflammation, we also searched for transcripts of AID as a germinal centre marker in individual CD27+ CD5+ and CD27+ CD5− B cells isolated from one of the patients with o‐JIA (patient 2). None among 76 (CD27+ CD5+) and 87 (CD27+ CD5−) B cells yielded a PCR product. The method was validated by carrying out PCR with the setting on individual IgD+ CD38++ germinal centre founder cells from a human tonsil, where transcripts of AID were detectable in 6/36 β‐actin‐positive cells.
Discussion
We examined mature CD27+ peripheral blood B lymphocytes for the expression of RAG genes on a single‐cell level. RAG gene expression is detectable in mature B cells. About one third of 777 B lymphocytes examined from all populations together had detectable levels of any of the RAG genes. Our results challenge recent views that RAG1 and RAG2 expression physiologically occurs only in a coordinate 1:1 relationship.28 This hypothesis, however, has been generated in the analysis of “primary” V(D)J recombination of early B cell progenitors in bone marrow. Recently, evidence is emerging that receptor revision in the periphery may be an important process that ensures tolerance.16,29 Our findings give new insights into divergent RAG1 and RAG2 expression, which are partly supported by findings that engagement of the BCR can have contrary effects in distinct developmental stages of B lymphocytes.30
We found a more than twofold and fourfold decrease in the frequency of RAG2‐expressing B cells isolated from patients with o‐JIA in CD27+ CD5+ and CD27+ CD5− populations when compared with healthy people. In contrast, RAG1 frequencies tended to be unchanged or slightly increased in those with o‐JIA. Thus, we hypothesised that RAG2 is differentially expressed in patients with o‐JIA when compared with healthy people. Finally, this resulted in a loss of coordinate RAG expression in CD5− but not in CD5+ B cells.
The argument that an increased bone marrow lymphopoiesis results in a major fraction of immature RAG‐expressing B cells in the periphery during a systemic inflammatory process14 is not applicable to our results, as we studied CD27+ mature B cells. Arguably, the effects seen are caused by cell cycle dependence of RAG expression, as a larger fraction of proliferating lymphocytes can be assumed in inflammation. Relative percentages of CD27+ among CD19+ cells were comparable in patients with o‐JIA and in controls in a current flow‐cytometric analysis, with a mean of about 16–18% (data not shown). No evidence in our analysis and in previous publications23 showed an increase in total B cells isolated from patients with o‐JIA. Thus, considerably differing absolute CD27 counts are unlikely. Although the RAG2 protein is down regulated at least 20‐fold before a cell enters the S phase to protect against unselective recombination under vulnerable conditions,31,32 these changes in the RAG protein level occur primarily at a post‐translational level, with RAG2 mRNA levels remaining nearly unaffected.31 So far, it cannot be excluded that drugs had an effect on the composition of lymphocyte subsets, as we have previously shown for cyclophosphamide in SLE in children.33 However, the completely missing coordinate RAG expression in CD5− B cells isolated from patients with JIA, despite a broad spectrum in disease activity compared with a solid presence in two of three in controls, would argue for a disease‐related phenomenon.
Our results from human peripheral CD27+ B cells are concordant with recent reports on individual tonsil B cells from healthy children, in whom distinct developmental stages of germinal centre B cells were examined for RAG gene expression, with a special focus on CD5 expression29: on CD38+ IgD+ CD23+ B cells, induction of surface CD5 after stimulation with anti‐IgM and CD40L was described, followed by coordinate RAG mRNA expression. Interestingly, RAG2 transcripts appeared later than RAG1 transcripts, supporting the hypothesis of a differential regulation of these two genes, and of RAG2 as a limiting factor.29 In contrast, among early tonsil memory B cells (CD38− IgD−), nearly three times as many double‐RAG‐positive cells were found in the CD5− subgroup as in the CD5+ population (16.6 v6%). These findings are comparable to our results in peripheral CD19+ CD27+ B cells of controls: the relationship was similar, with 4.9% and 1.3% in CD5− and CD5+ B cells, respectively (p<0.05). Interestingly, the absolute frequencies of cells expressing RAG1 and RAG2 were lower in our study on peripheral B cells. Thus, a small subset of B cells expressing RAG1 and RAG2 seems to persist physiologically in the peripheral blood of children, as we have described previously in the case of adults.7 Reduced coordinate RAG expression in CD27+ CD5− B cells isolated from patients with o‐JIA may be relevant in pathogenesis, possibly disabling these B cells to carry out sufficient receptor revision.
The regulation of RAG genes is complex and tightly regulated, owing to the possible disastrous consequences of unselective DNA cleavage. It can happen at the level of transcription, post‐transcriptional mRNA and protein modification or DNA accessibility (reviewed by Schlissel34). It has been difficult so far to assess factors influencing RAG expression: it is known that BCR engagement itself can turn off the expression of V(D)J recombinase genes in mature B cells.35,36RAG can be induced again in these cells via a combination of CD40L or lipopolysaccharide and IL4 (or IL7) signalling, imitating T cell help.9,37 In contrast, in immature B cells, the opposite reaction has been documented. RAG genes have been induced after BCR engagement.38
Among CD5+ B cells, low coordinate RAG transcripts were detected in patients and in controls. In the CD5− children with JIA, we found no coordinate RAG expression at all. The CD5 molecule negatively regulates antigen receptor‐mediated growth signals by recruiting SH2‐domain‐containing protein tyrosine phosphatase‐1 into the BCR.39 Thus, CD5 action may have a stimulating role on the final coordinate RAG expression in patients with JIA by inhibiting a BCR‐mediated suppression of RAG transcription in those with JIA. This may be due to a strong challenge of autoantigens via the BCR, which, on the other hand, suppresses RAG transcription, especially in B cells lacking the CD5 molecule in patients with JIA, as shown in our analysis. Thus, we hypothesise that pathogenetic processes are imposed on mature B cells, which become engaged in autoimmunity.
In earlier studies, we have shown increased coordinate RAG expression in IgD+ B cells from peripheral blood of patients with SLE,17,33 proposing a prolonged receptor editing in B cells from patients with SLE, which have prematurely left the bone marrow. As these cells represent an earlier stage in B cell development, comparability to the currently analysed post‐switch memory B cells in patients with JIA is limited.
Indeed, these findings may show two different mechanisms proposed for the role of secondary rearrangements in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, both promoting the disease by an uncontrolled creation of autoreactive antibodies. In contrast, an impaired receptor revision may result in ineffective deletion of B cells that have acquired autoreactive receptors in patients with o‐JIA. However, the consequences of these immunoregulatory abnormalities on the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases cannot be defined yet.
In conclusion, we found comparable low frequencies of RAG double‐positive CD27+ B cells in healthy children and CD5+ populations with JIA, whereas the CD5− populations showed a complete absence of RAG1‐positive and RAG2‐positive lymphocytes in peripheral memory B cells in children with o‐JIA. We obtained evidence for a lack of receptor revision in the periphery as a feature for CD27+ CD5− B cells in children with JIA, which may contribute to the autoimmune pathogenesis of the disease.
Acknowledgements
We thank U Samfaß, M Fischer, C Linden and A Wirsing for excellent technical assistance.
Abbreviations
AID - activation‐induced cytidine deaminase
ANA - antinuclear antibodies
dUTP - deoxyuridine triphosphate
o‐JIA - oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis
PCR - polymerase chain reaction
RAG - recombination‐activating gene
SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus
Footnotes
Competing interests: None.
References
- 1.Petty R E, Southwood T R, Manners P, Baum J, Glass D N, Goldenberg J.et al International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 2nd revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol 200431390–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mombaerts P, Iacomini J, Johnson R S, Herrup K, Tonegawa S, Papaioannou V E. RAG‐1‐deficient mice have no mature B and T lymphocytes. Cell 199268869–877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schwarz K, Gauss G H, Ludwig L, Pannicke U, Li Z, Lindner D.et al RAG mutations in human B cell‐negative SCID. Science 199627497–99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shinkai Y, Rathbun G, Lam K P, Oltz E M, Stewart V, Mendelsohn M.et al RAG‐2‐deficient mice lack mature lymphocytes owing to inability to initiate V(D)J rearrangement. Cell 199268855–867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tiegs S L, Russell D M, Nemazee D. Receptor editing in self‐reactive bone marrow B cells. J Exp Med 19931771009–1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Han S, Dillon S R, Zheng B, Shimoda M, Schlissel M S, Kelsoe G. V(D)J recombinase activity in a subset of germinal center B lymphocytes. Science 1997278301–305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Girschick H J, Grammer A C, Nanki T, Mayo M, Lipsky P E. RAG1 and RAG2 expression by B cell subsets from human tonsil and peripheral blood. J Immunol 2001166377–386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Han S, Zheng B, Schatz D G, Spanopoulou E, Kelsoe G. Neoteny in lymphocytes: Rag1 and Rag2 expression in germinal center B cells. Science 19962742094–2097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hikida M, Mori M, Takai T, Tomochika K, Hamatani K, Ohmori H. Reexpression of RAG‐1 and RAG‐2 genes in activated mature mouse B cells. Science 19962742092–2094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nagafuchi H, Yoshikawa H, Takeba Y, Nara K, Miura K, Kurokawa M S.et al Recombination activating genes (RAG) induce secondary Ig gene rearrangement in and subsequent apoptosis of human peripheral blood circulating B lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol 200413676–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yu W, Nagaoka H, Jankovic M, Misulovin Z, Suh H, Rolink A.et al Continued RAG expression in late stages of B cell development and no apparent re‐induction after immunization. Nature 1999400682–687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Monroe R J, Seidl K J, Gaertner F, Han S, Chen F, Sekiguchi J.et al RAG2:GFP knockin mice reveal novel aspects of RAG2 expression in primary and peripheral lymphoid tissues. Immunity 199911201–212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kuwata N, Igarashi H, Ohmura T, Aizawa S, Sakaguchi N. Cutting edge: absence of expression of RAG1 in peritoneal B‐1 cells detected by knocking into RAG1 locus with green fluorescent protein gene. J Immunol 19991636355–6359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nagaoka H, Gonzalez‐Aseguinolaza G, Tsuji M, Nussenzweig M C. Immunization and infection change the number of recombination activating gene (RAG)‐expressing B cells in the periphery by altering immature lymphocyte production. J Exp Med 20001912113–2120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Itoh K, Meffre E, Albesiano E, Farber A, Dines D, Stein P.et al Immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene replacement as a mechanism for receptor revision in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue B lymphocytes. J Exp Med 20001921151–1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang Z, Wu X, Limbaugh B H, Bridges S L., Jr Expression of recombination‐activating genes and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and secondary rearrangement of immunoglobulin kappa light chains in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum 2001442275–2284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Girschick H J, Grammer A C, Nanki T, Vazquez E, Lipsky P E. Expression of recombination activating genes 1 and 2 in peripheral B cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2002461255–1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dorner T, Foster S J, Farner N L, Lipsky P E. Immunoglobulin kappa chain receptor editing in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 1998102688–694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bensimon C, Chastagner P, Zouali M. Human lupus anti‐DNA autoantibodies undergo essentially primary V kappa gene rearrangements. EMBO J 1994132951–2962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Suzuki N, Mihara S, Sakane T. Development of pathogenic anti‐DNA antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. FASEB J 1997111033–1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Youinou P, Lydyard P M. CD5+ B cells in nonorgan‐specific autoimmune diseases: a fresh look. Lupus 200110523–525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Martini A, Massa M, De Benedetti F, Viola S, Neirotti G, Burgio R G. CD5 positive B lymphocytes in seronegative juvenile arthritis. J Rheumatol 199017932–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wouters C H, Ceuppens J L, Stevens E A. Different circulating lymphocyte profiles in patients with different subtypes of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 200220239–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Klein U, Rajewsky K, Kuppers R. Human immunoglobulin (Ig)M+IgD+ peripheral blood B cells expressing the CD27 cell surface antigen carry somatically mutated variable region genes: CD27 as a general marker for somatically mutated (memory) B cells. J Exp Med 19981881679–1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Muto T, Muramatsu M, Taniwaki M, Kinoshita K, Honjo T. Isolation, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of the human activation‐induced cytidine deaminase (AID) gene. Genomics 20006885–88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Muramatsu M, Sankaranand V S, Anant S, Sugai M, Kinoshita K, Davidson N O.et al Specific expression of activation‐induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a novel member of the RNA‐editing deaminase family in germinal center B cells. J Biol Chem 199927418470–18476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shi Y, Agematsu K, Ochs H D, Sugane K. Functional analysis of human memory B‐cell subpopulations: IgD+CD27+ B cells are crucial in secondary immune response by producing high affinity IgM. Clin Immunol 2003108128–137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schatz D G, Oettinger M A, Schlissel M S. V(D)J recombination: molecular biology and regulation. Annu Rev Immunol 199210359–383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hillion S, Saraux A, Youinou P, Jamin C. Expression of RAGs in peripheral B cells outside germinal centers is associated with the expression of CD5. J Immunol 20051745553–5561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sandel P C, Monroe J G. Negative selection of immature B cells by receptor editing or deletion is determined by site of antigen encounter. Immunity 199910289–299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lin W C, Desiderio S. Cell cycle regulation of V(D)J recombination‐activating protein RAG‐2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994912733–2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lin W C, Desiderio S. V(D)J recombination and the cell cycle. Immunol Today 199516279–289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Morbach H, Singh S, Faber C, Lipsky P, Girschick H J. Analysis of RAG expression by peripheral blood CD5+ and CD5− B cells of patients with childhood systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 200665482–487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schlissel M S. Regulating antigen‐receptor gene assembly. Nat Rev Immunol 20033890–899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hertz M, Kouskoff V, Nakamura T, Nemazee D. V(D)J recombinase induction in splenic B lymphocytes is inhibited by antigen‐receptor signalling. Nature 1998394292–295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Meffre E, Papavasiliou F, Cohen P, de Bouteiller O, Bell D, Karasuyama H.et al Antigen receptor engagement turns off the V(D)J recombination machinery in human tonsil B cells. J Exp Med 1998188765–772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hikida M, Nakayama Y, Yamashita Y, Kumazawa Y, Nishikawa S I, Ohmori H. Expression of recombination activating genes in germinal center B cells: involvement of interleukin 7 (IL‐7) and the IL‐7 receptor. J Exp Med 1998188365–372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ohmori H, Magari M, Nakayama Y, Kanayama N, Hikida M. Role for complement receptors (CD21/CD35) in the regulation of recombination activating gene expression in murine peripheral B cells. Immunol Lett 20028395–99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sen G, Bikah G, Venkataraman C, Bondada S. Negative regulation of antigen receptor‐mediated signaling by constitutive association of CD5 with the SHP‐1 protein tyrosine phosphatase in B‐1 B cells. Eur J Immunol 1999293319–3328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]