Abstract
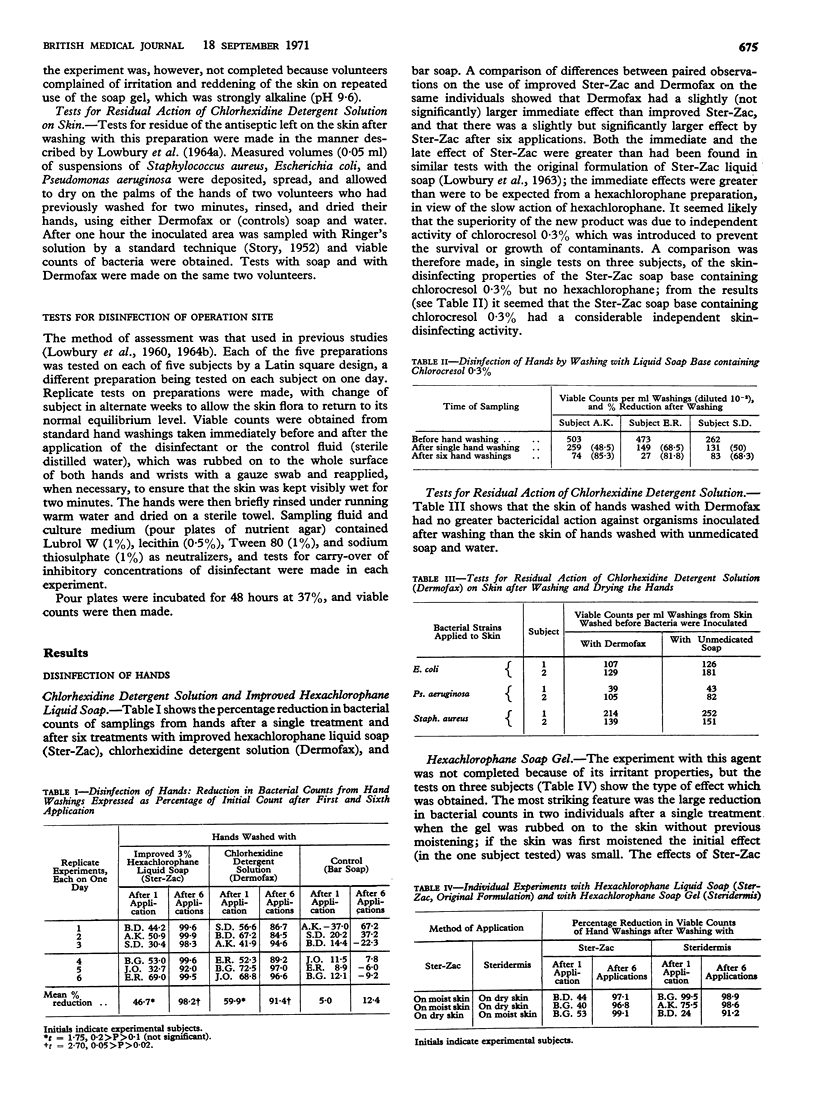
Repeated hand washing with a detergent solution containing 0·75% chlorhexidine digluconate was found to cause a large reduction in the resident skin flora which was slightly though significantly smaller than that caused by the use of 3% hexachlorophane liquid soap containing a phenolic preservative, chlorocresol 0·3%. Both agents caused a greater immediate reduction of bacteria after a single hand washing than the hexachlorophane liquid soap without a phenolic additive had shown in earlier experiments; the soap base containing chlorocresol 0·3% but no hexachlorophane was also found to cause a large reduction in skin flora. The chlorhexidine detergent solution had no residual disinfectant action on the skin after rinsing and drying the hands.
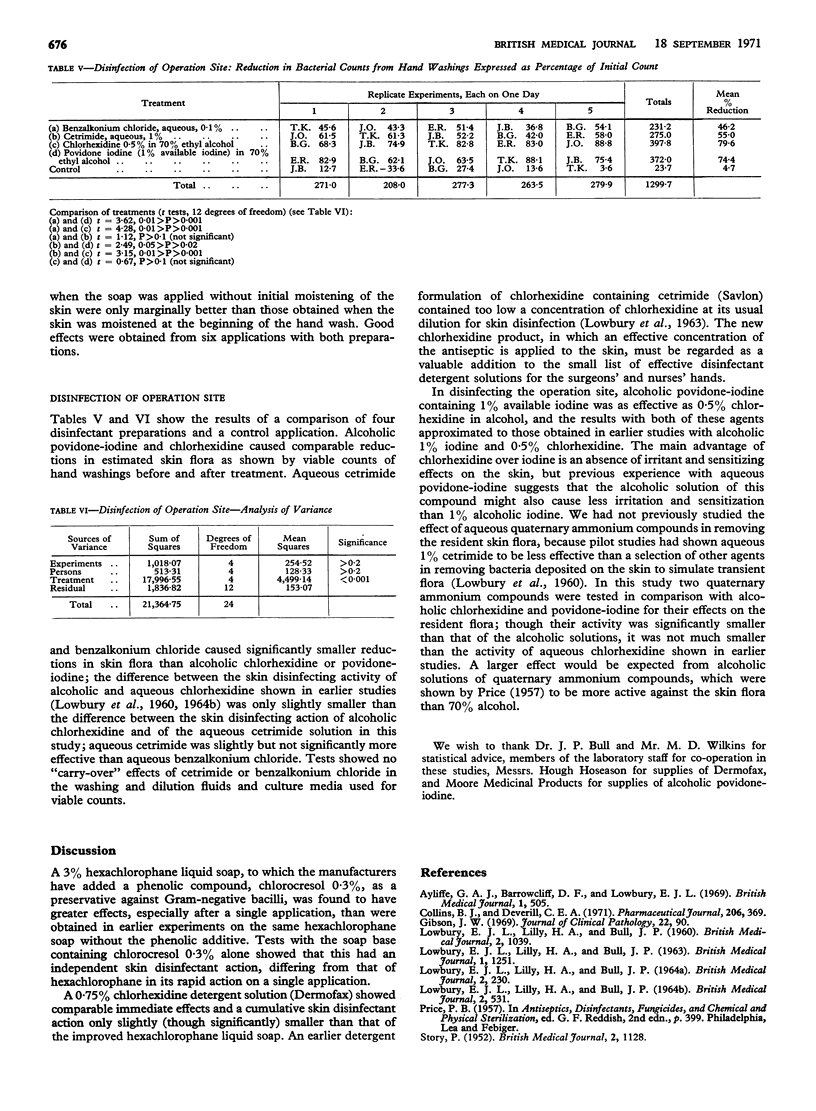
Disinfection of an operation site for two minutes with povidone-iodine containing 1% available iodine in 70% ethyl alcohol caused about as great a reduction in resident flora as a similar treatment with alcoholic 0·5% chlorhexidine. Both treatments were more effective than disinfection with aqueous 1% cetrimide or 0·1% benzalkonium chloride solutions.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gibson J. W. Comparative antibacterial activity of hexachlorophane in different formulations used for skin disinfection. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Jan;22(1):90–98. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A., BULL J. P. DISINFECTION OF HANDS: REMOVAL OF TRANSIENT ORGANISMS. Br Med J. 1964 Jul 25;2(5403):230–233. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5403.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A., BULL J. P. Disinfection of the skin of operation sites. Br Med J. 1960 Oct 8;2(5205):1039–1044. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5205.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A., BULL J. P. METHODS FOR DISINFECTION OF HANDS AND OPERATION SITES. Br Med J. 1964 Aug 29;2(5408):531–536. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5408.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STORY P. Testing of skin disinfectants. Br Med J. 1952 Nov 22;2(4794):1128–1130. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4794.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


