Abstract
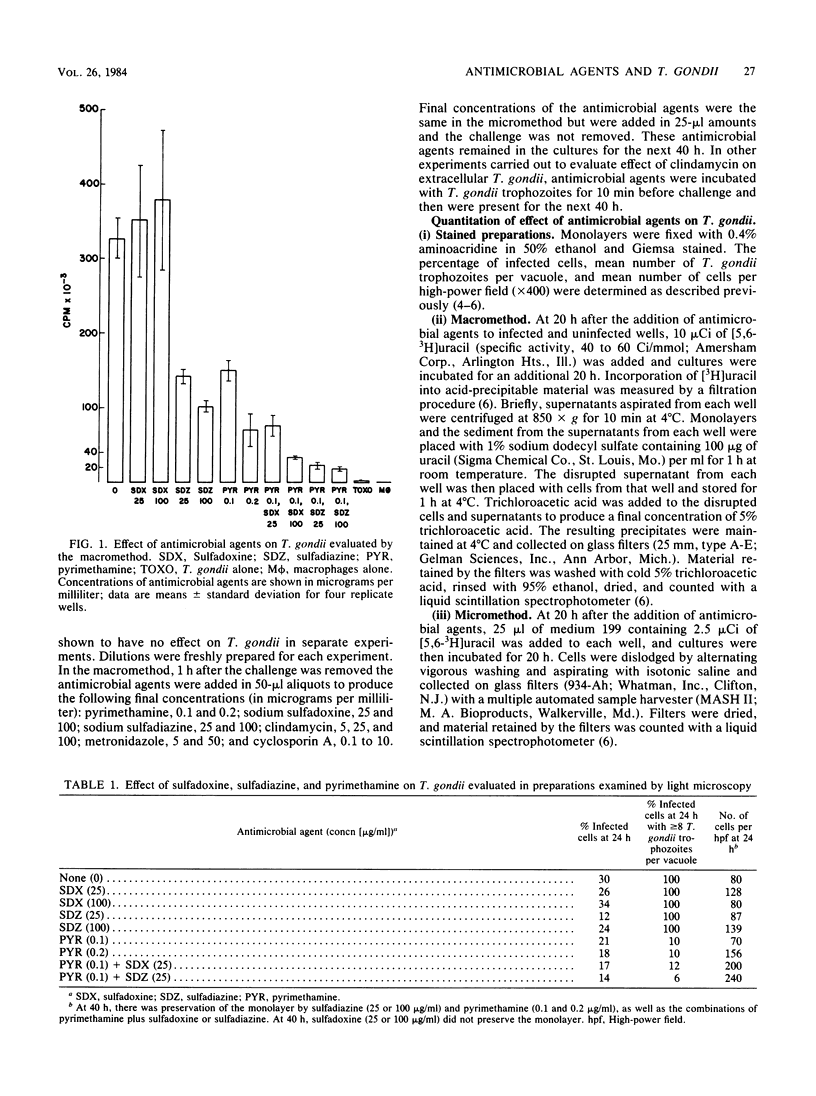
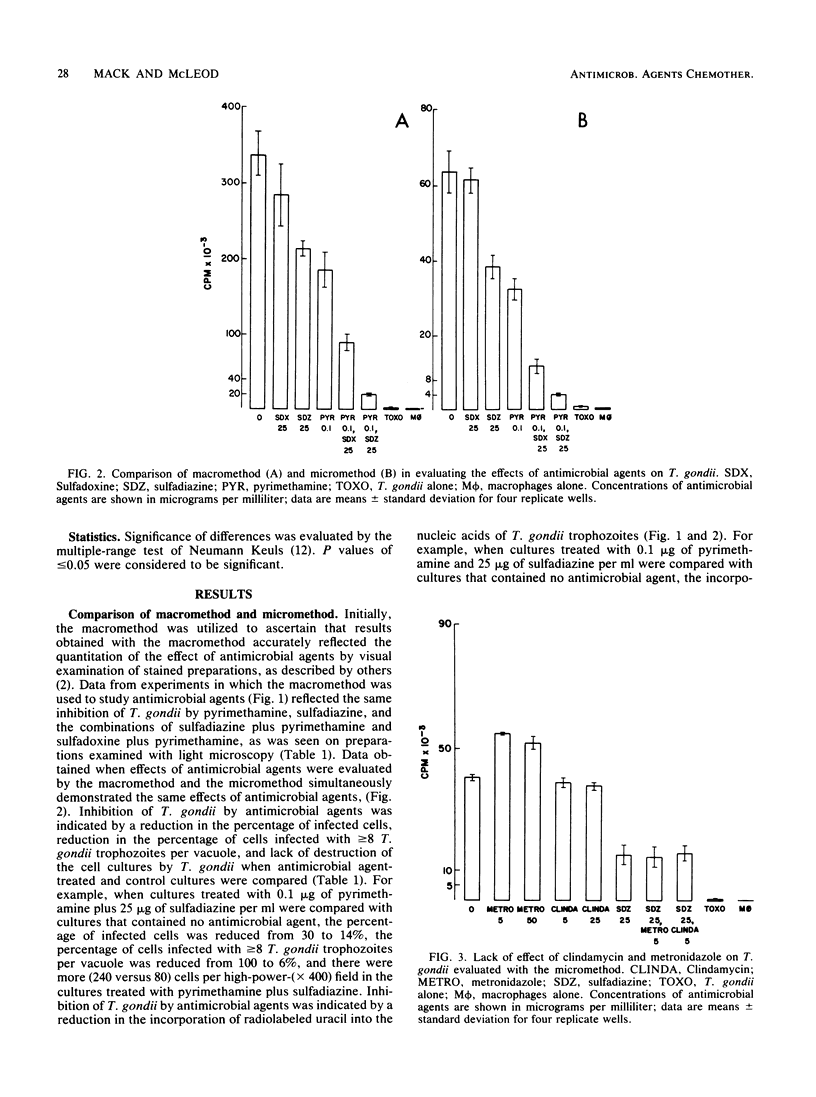
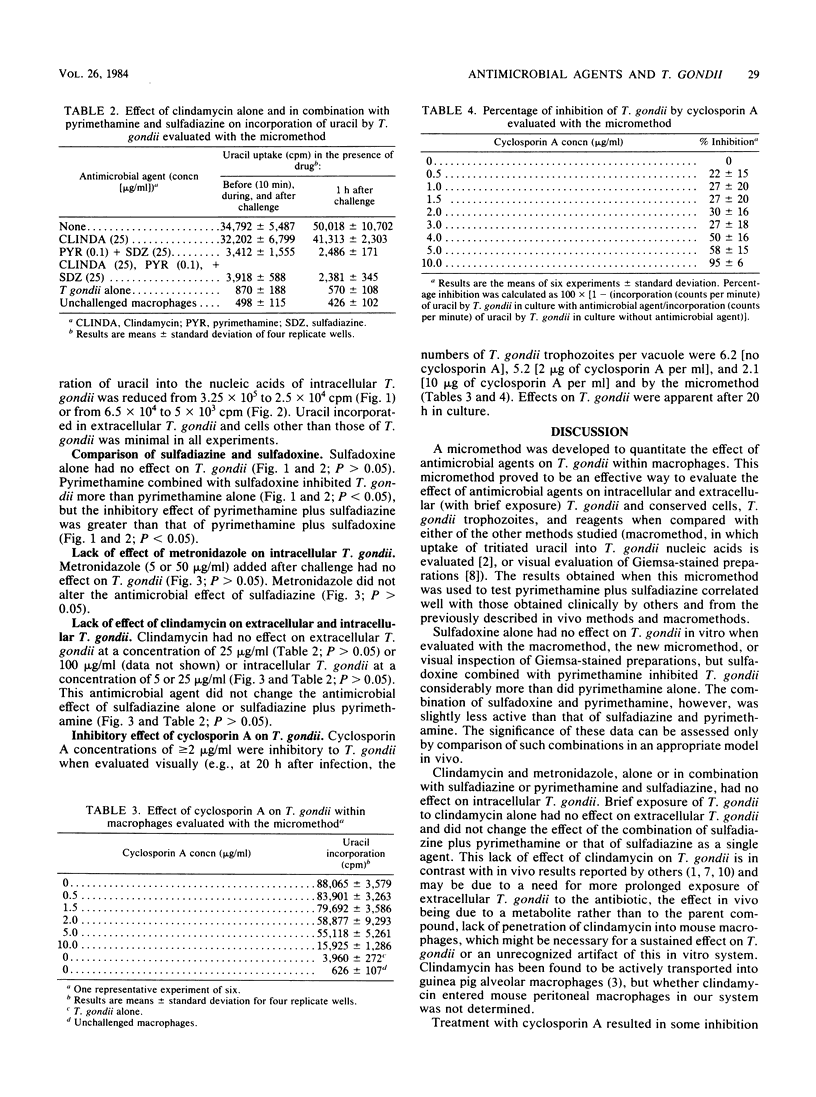
An in vitro method by which reagents, cells, and Toxoplasma gondii trophozoites are conserved (micromethod) was developed to quantitate the effect of antimicrobial agents on T. gondii. Sulfadoxine alone had no effect on T. gondii in vitro when evaluated with a macromethod, the new micromethod, or visual inspection of Giemsa-stained preparations. Sulfadoxine combined with pyrimethamine inhibited T. gondii more than did pyrimethamine alone, but the combination of sulfadoxine plus pyrimethamine was slightly less active than was the combination of sulfadiazine plus pyrimethamine. Neither clindamycin nor metronidazole, alone or in combination with sulfadiazine or pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine, had any effect on intracellular T. gondii. Brief exposure (10 min before and during challenge) to clindamycin had no effect on extracellular T. gondii when clindamycin was studied alone or with sulfadiazine or pyrimethamine plus sulfadiazine. Cyclosporin A inhibited T. gondii replication at concentrations of ca. greater than or equal to 2 micrograms/ml.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Remington J. S. Effect of clindamycin on acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):647–651. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman P. L., Remington J. S. The effect of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole on Toxoplasma gondii in vitro and in vivo. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 May;28(3):445–455. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L. Membrane transport of clindamycin in alveolar macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):241–247. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod R., Remington J. S. A method to evaluate the capacity of monocytes and macrophages to inhibit multiplication of an intracellular pathogen. J Immunol Methods. 1979 May 10;27(1):19–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90235-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod R., Remington J. S. A new method for evaluation of intracellular inhibition of multiplication or killing by mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):1894–1897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod R., Remington J. S. Studies on the specificity of killing of intracellular pathogens by macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1977 Nov;34(1):156–174. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster P. R., Powers K. G., Finerty J. F., Lunde M. N. The effect of two chlorinated lincomycin analogues against acute toxoplasmosis in mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1973 Jan;22(1):14–17. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1973.22.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen B. T., Stadtsbaeder S. In vitro activity of cotrimoxazole on the intracellular multiplication of Toxoplasma gondii. Pathol Eur. 1975;10(4):307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Yagura T., Robinson W. S. The effect of rifampin on Toxoplasma gondii. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Oct;135(1):167–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabbara K. F., Nozik R. A., O'Connor G. R. Clindamycin effects on experimental ocular toxoplasmosis in the rabbit. Arch Ophthalmol. 1974 Sep;92(3):244–247. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1974.01010010252017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thommen-Scott K. Antimalarial activity of cyclosporin A. Agents Actions. 1981 Dec;11(6-7):770–773. doi: 10.1007/BF01978803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



