Abstract
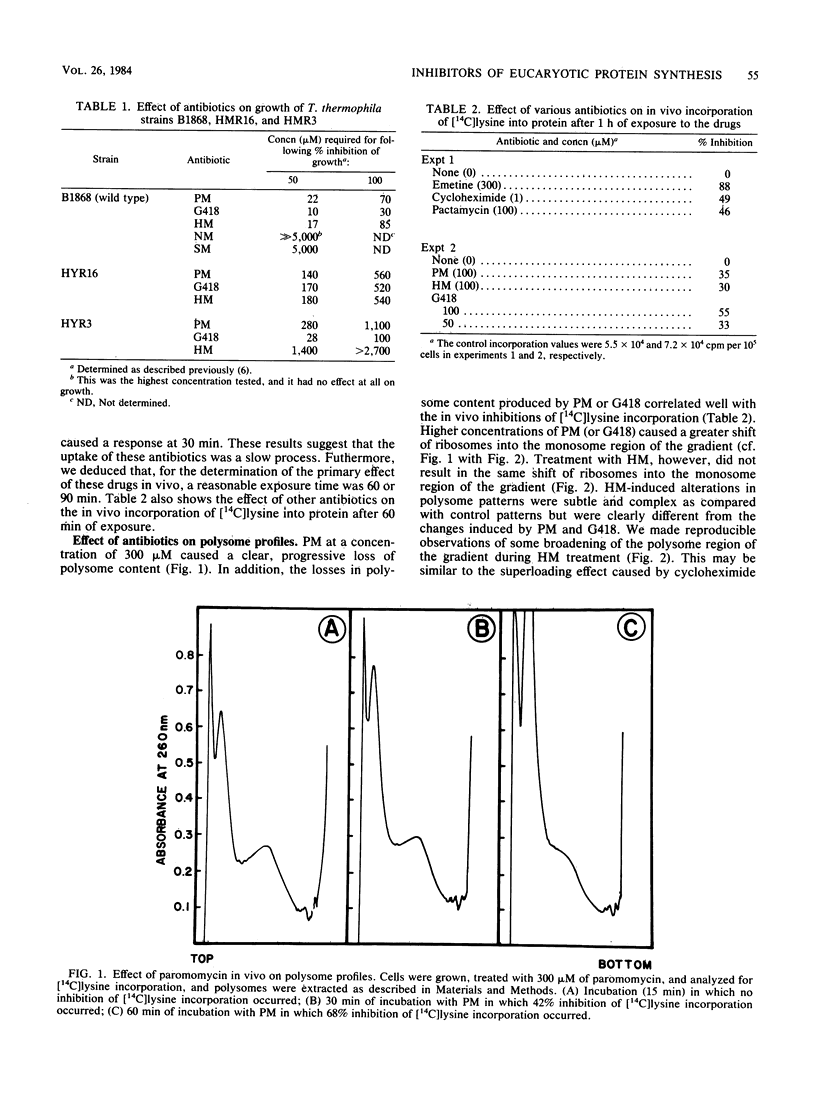
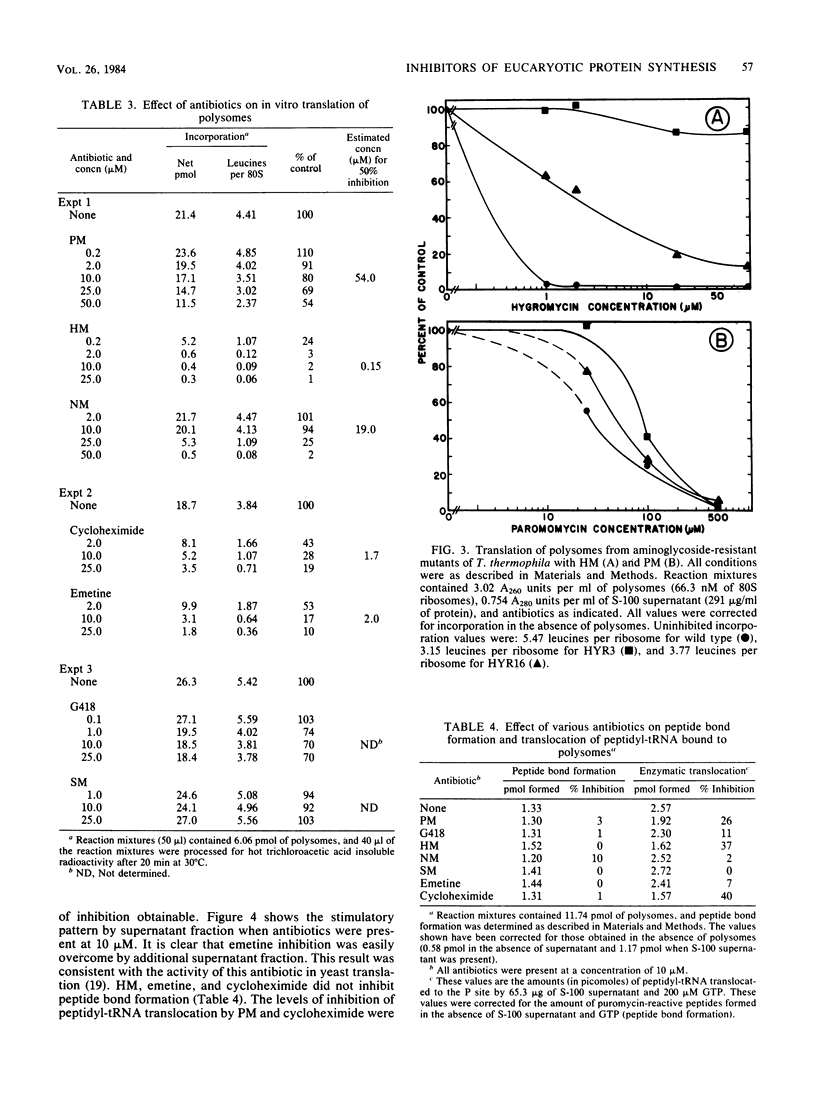
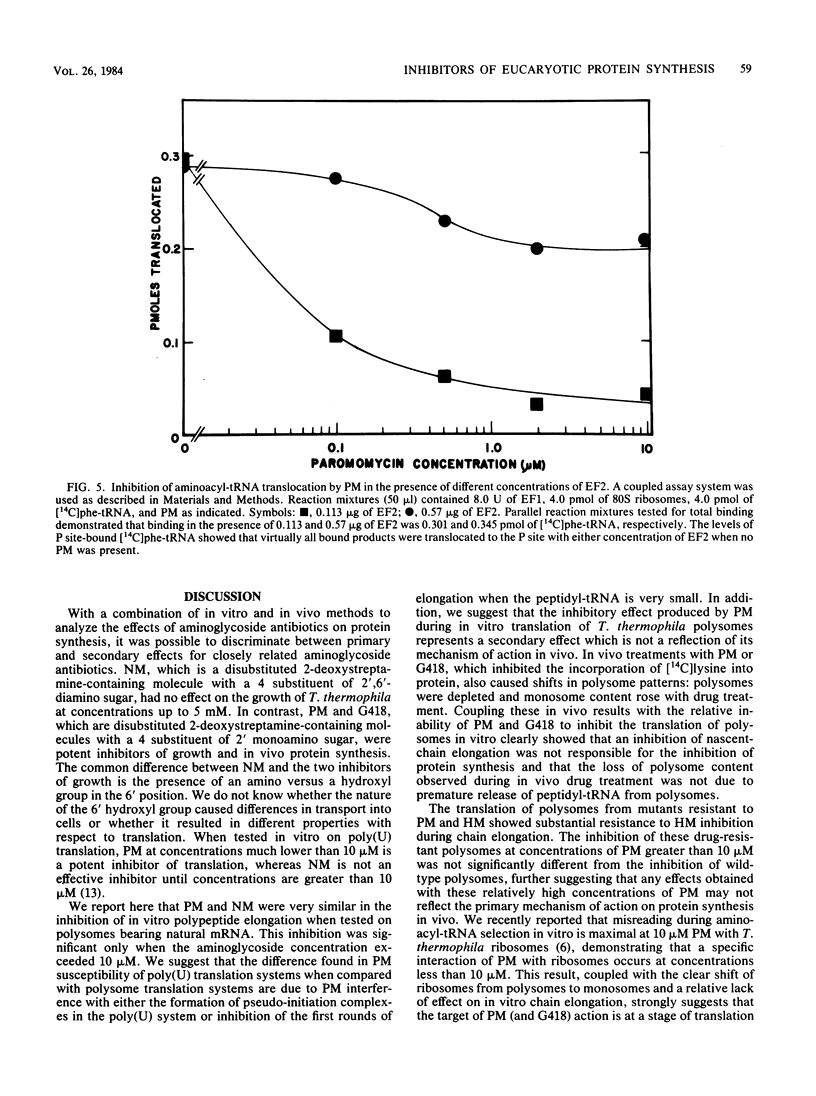
Tetrahymena thermophila is a eucaryotic organism that is highly susceptible to growth inhibition by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Concentrations of paromomycin, gentamicin G418, and hygromycin B at 22, 10, and 17 microM, respectively, inhibited growth by 50%. A combination of in vitro and in vivo methods was used to determine the mechanisms of action of these aminoglycoside antibiotics on protein synthesis in T. thermophila. Analysis of polysome profiles from paromomycin- and gentamicin G418-treated cells showed clear, progressive depletions of polysomes concomitant with an inhibition of in vivo [14C] lysine incorporation. In vitro, paromomycin and gentamicin G418, which are disubstituted 2-deoxystreptamine-containing molecules, were not very effective inhibitors of either the translocation of peptidyl-tRNA or the elongation of nascent polypeptide chains on polysomes. In contrast, we found that the translocation of phe-tRNA on polyuridylate programmed ribosomes was susceptible to inhibition by paromomycin. We conclude that the primary inhibitory action of paromomycin and gentamicin G418 was at (i) an early stage of elongation after initiation, (ii) the initiation stage of translation, or (iii) a stage of translation before initiation. Hygromycin B, which is a monosubstituted 2-deoxystreptamine-containing aminoglycoside, potently inhibited the elongation of nascent chains during the translation of polysomes. In addition, the in vitro translation of polysomes from two hygromycin B-resistant mutants was resistant to the inhibition of elongation caused by hygromycin B.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright E. B., Nowak T. S., Jr, Munro H. N. Assessment of counting efficiencies for labeled protein and other macromolecules in filter disk assays. Anal Biochem. 1978 Nov;91(1):258–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90839-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Fresno M., Vazquez D. Inhibitors of polypeptide elongation on yeast polysomes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975 Jun;28(6):453–462. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calzone F. J., Angerer R. C., Gorovsky M. A. Regulation of protein synthesis in Tetrahymena: isolation and characterization of polysomes by gel filtration and precipitation at pH 5.3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2145–2161. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras A., Vázquez D. Cooperative and antagonistic interactions of peptidyl-tRNA and antibiotics with bacterial ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 15;74(3):539–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eustice D. C., Kull F. J., Shrift A. Selenium toxicity: aminoacylation and Peptide bond formation with selenomethionine. Plant Physiol. 1981 May;67(5):1054–1058. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.5.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eustice D. C., Wilhelm J. M. Fidelity of the eukaryotic codon-anticodon interaction: interference by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 27;23(7):1462–1467. doi: 10.1021/bi00302a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando D., Cousin M. A., Ojasoo T., Raymond J. P. Paromomycin and dihydrostreptomycin binding to Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 15;66(3):597–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando D., Cousin M. A., Privat de Garilhe M. Misreading, a fundamental aspect of the mechanism of action of several aminoglycosides. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4528–4533. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughrea M. Speed-accuracy relationships during in vitro and in vivo protein biosynthesis. Biochimie. 1981 Mar;63(3):145–168. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelong J. C., Gros D., Cousin M. A., Grunberg-Manago M., Gros F. Streptomycin induced release of fMet-tRNA from the ribosomal initiation complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 5;42(3):530–537. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Davis B. D. Breakdown by streptomycin of initiation complexes formed on ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1148–1155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orias E., Bruns P. J. Induction and isolation of mutants in Tetrahymena. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:247–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E., Wilhelm J. M. Mistranslation in a eucaryotic organism. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E., Wilhelm J. M., Sherman F. Phenotypic suppression of nonsense mutants in yeast by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):148–150. doi: 10.1038/277148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. XIX. Effect of antibiotics on peptidyl puromycin synthesis on polyribosoms from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4669–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogerson L. Separation and characterization of yeast elongation factors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:676–685. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton C. A., Ares M., Jr, Hallberg R. L. Cycloheximide resistance can be mediated through either ribosomal subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3158–3162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm J. M., Jessop J. J., Pettitt S. E. Aminoglycoside antibiotics and eukaryotic protein synthesis: stimulation of errors in the translation of natural messengers in extracts of cultured human cells. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1149–1153. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm J. M., Pettitt S. E., Jessop J. J. Aminoglycoside antibiotics and eukaryotic protein synthesis: structure--function relationships in the stimulation of misreading with a wheat embryo system. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1143–1149. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurmbach P., Nierhaus K. H. The inhibition pattern of antibiotics on the extent and accuracy of tRNA binding to the ribosome, and their effect on the subsequent steps in chain elongation. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):9–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



