Abstract
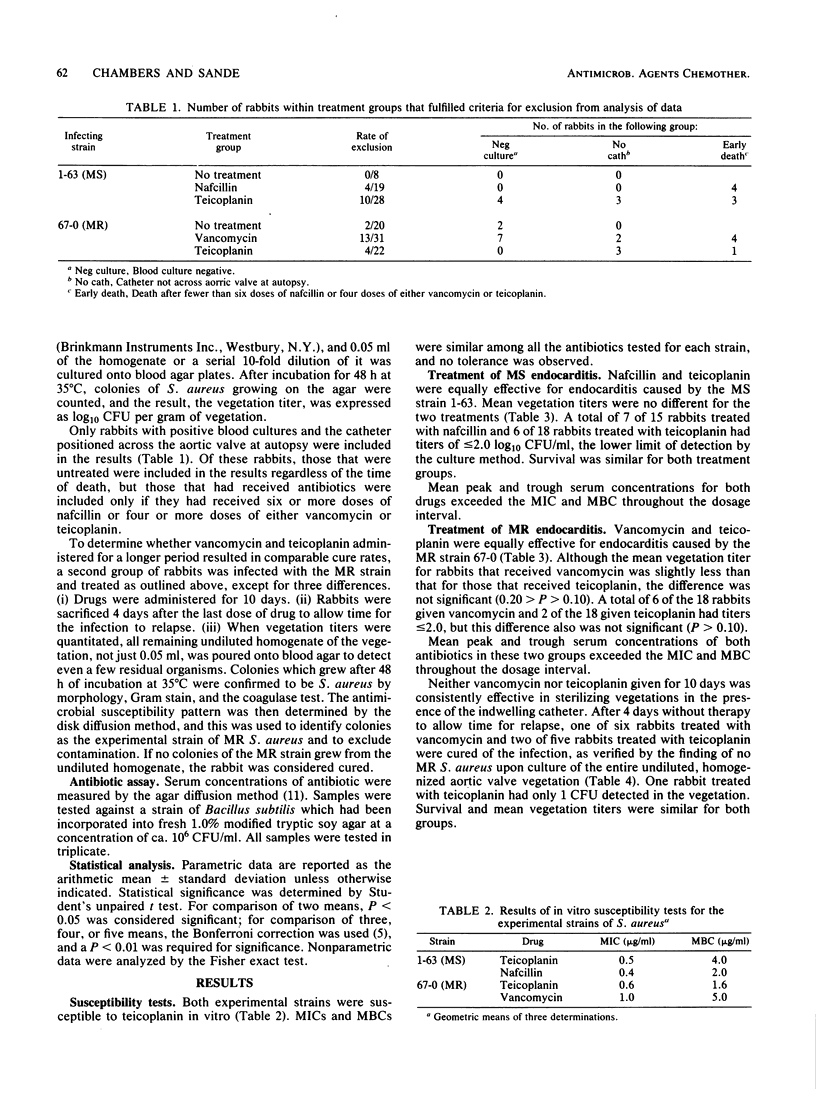
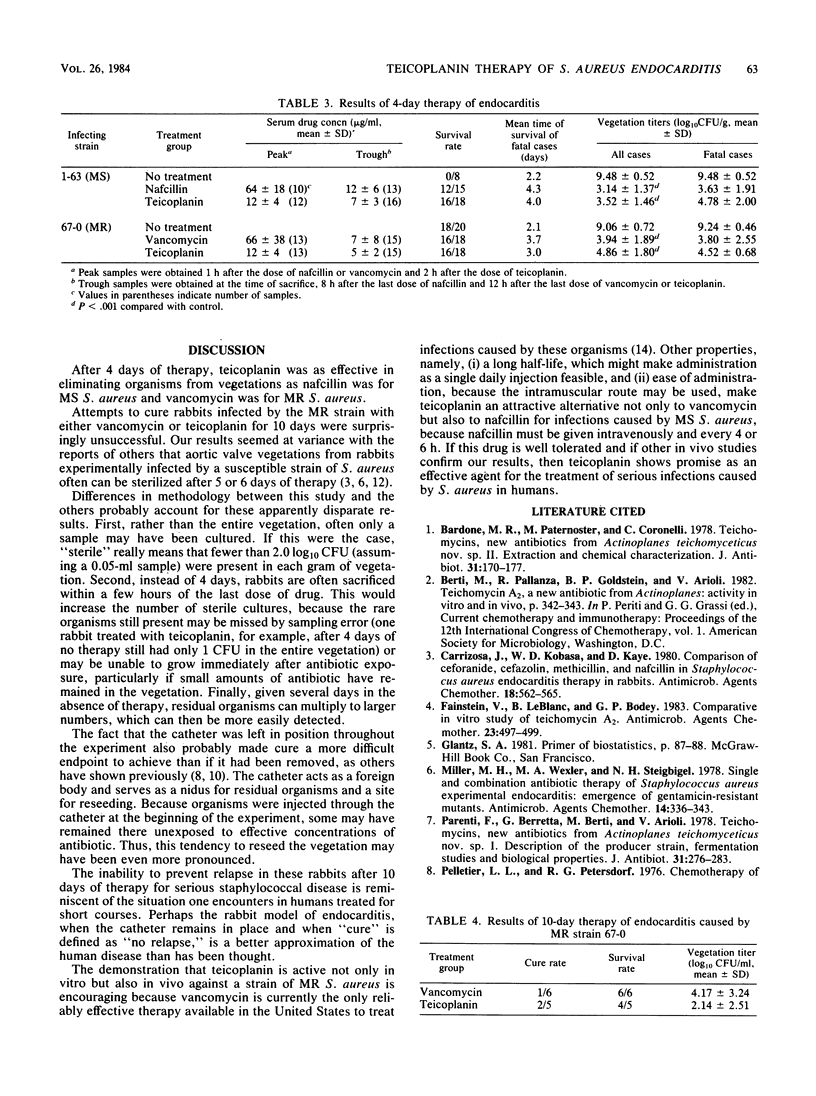
In rabbits with experimentally induced endocarditis, the efficacy of teicoplanin compared favorably both with that of nafcillin for infection by a methicillin-susceptible strain of Staphylococcus aureus and with that of vancomycin for infection by a methicillin-resistant strain of S. aureus. In a 4-day treatment regimen, teicoplanin was as effective as either nafcillin or vancomycin in eliminating organisms from aortic valve vegetations in the respective infection. In a 10-day regimen for methicillin-resistant S. aureus endocarditis, both teicoplanin and vancomycin sterilized the vegetations of some rabbits, but the relapse rate was high for both. These results justify further investigation into the role of teicoplanin for the treatment of serious infections caused by S. aureus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardone M. R., Paternoster M., Coronelli C. Teichomycins, new antibiotics from Actinoplanes teichomyceticus nov. sp. II. Extraction and chemical characterization. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Mar;31(3):170–177. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrizosa J., Kobasa W. D., Kaye D. Comparison of ceforanide, cefazolin, methicillin, and nafcillin in Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis therapy in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):562–565. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainstein V., LeBlanc B., Bodey G. P. Comparative in vitro study of teichomycin A2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Mar;23(3):497–499. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.3.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Wexler M. A., Steigbigel N. H. Single and combination antibiotic therapy of Staphylococcus aureus experimental endocarditis: emergence of gentamicin-resistant mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):336–343. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parenti F., Beretta G., Berti M., Arioli V. Teichomycins, new antibiotics from Actinoplanes teichomyceticus Nov. Sp. I. Description of the producer strain, fermentation studies and biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Apr;31(4):276–283. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman B. B., Freedman L. R. Experimental endocarditis. 3. Natural history of catheter induced staphylococcal endocarditis following catheter removal. Yale J Biol Med. 1971 Oct;44(2):214–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman B. B., Freedman L. R. Experimental endocarditis. II. Staphylococcal infection of the aortic valve following placement of a polyethylene catheter in the left side of the heart. Yale J Biol Med. 1971 Oct;44(2):206–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Johnson M. L. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):367–375. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C. Treatment of infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):376–378. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


