Abstract
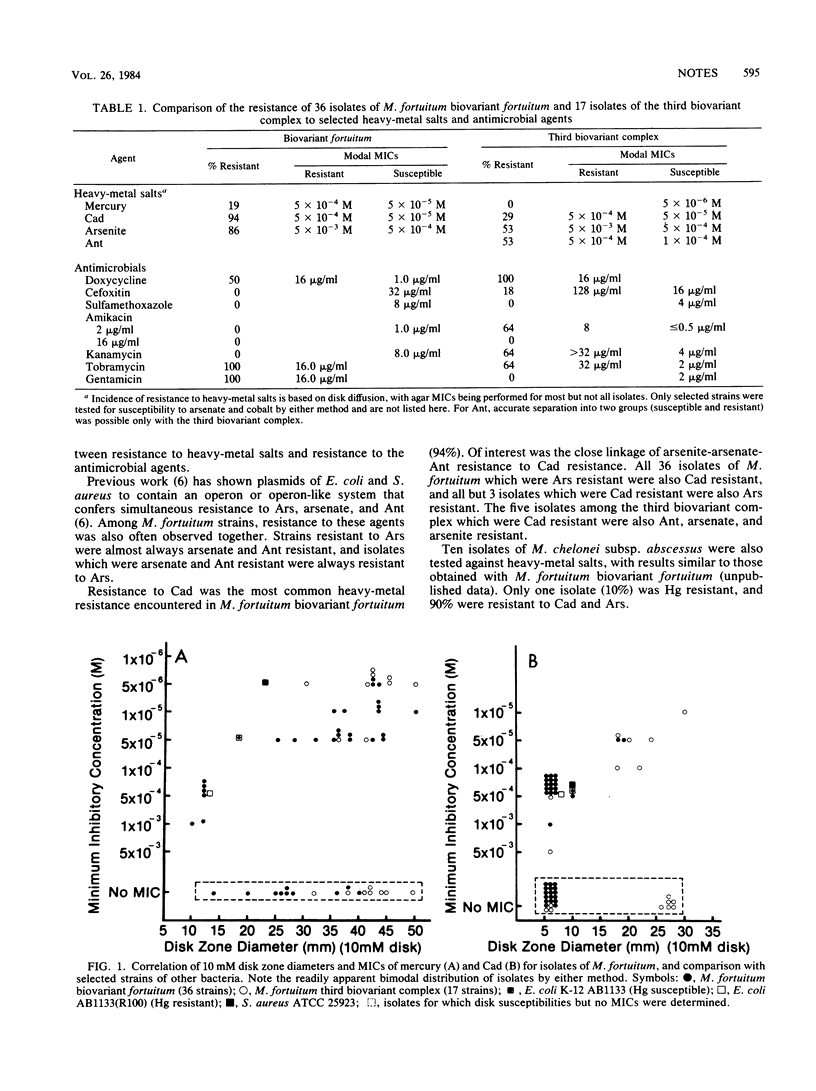
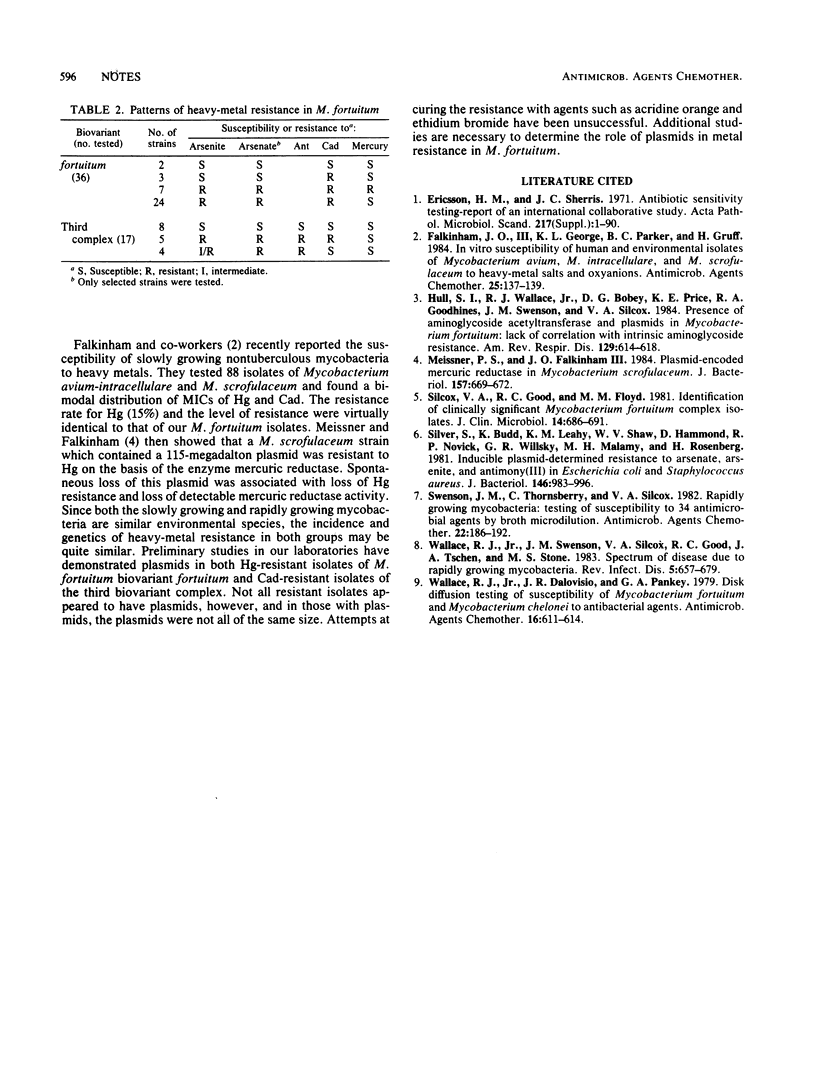
Fifty-three clinical isolates of Mycobacterium fortuitum were tested for susceptibility to heavy-metal salts and antimicrobial agents. The isolates exhibited a bimodal distribution for several heavy metals including mercury, whose resistance is often plasmid mediated. There was a biovariant difference in the incidence of resistance, and resistance to several metal ions was often observed together. There was no apparent relationship between resistance to heavy-metal salts and resistance to antimicrobial agents such as tetracycline.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Falkinham J. O., 3rd, George K. L., Parker B. C., Gruft H. In vitro susceptibility of human and environmental isolates of Mycobacterium avium, M. intracellulare, and M. scrofulaceum to heavy-metal salts and oxyanions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):137–139. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull S. I., Wallace R. J., Jr, Bobey D. G., Price K. E., Goodhines R. A., Swenson J. M., Silcox V. A. Presence of aminoglycoside acetyltransferase and plasmids in Mycobacterium fortuitum. Lack of correlation with intrinsic aminoglycoside resistance. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Apr;129(4):614–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner P. S., Falkinham J. O., 3rd Plasmid-encoded mercuric reductase in Mycobacterium scrofulaceum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):669–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.669-672.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silcox V. A., Good R. C., Floyd M. M. Identification of clinically significant Mycobacterium fortuitum complex isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):686–691. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.686-691.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Budd K., Leahy K. M., Shaw W. V., Hammond D., Novick R. P., Willsky G. R., Malamy M. H., Rosenberg H. Inducible plasmid-determined resistance to arsenate, arsenite, and antimony (III) in escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):983–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.983-996.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson J. M., Thornsberry C., Silcox V. A. Rapidly growing mycobacteria: testing of susceptibility to 34 antimicrobial agents by broth microdilution. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):186–192. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Dalovisio J. R., Pankey G. A. Disk diffusion testing of susceptibility of Mycobacterium fortuitum and Mycobacterium chelonei to antibacterial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):611–614. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Swenson J. M., Silcox V. A., Good R. C., Tschen J. A., Stone M. S. Spectrum of disease due to rapidly growing mycobacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):657–679. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



