Abstract
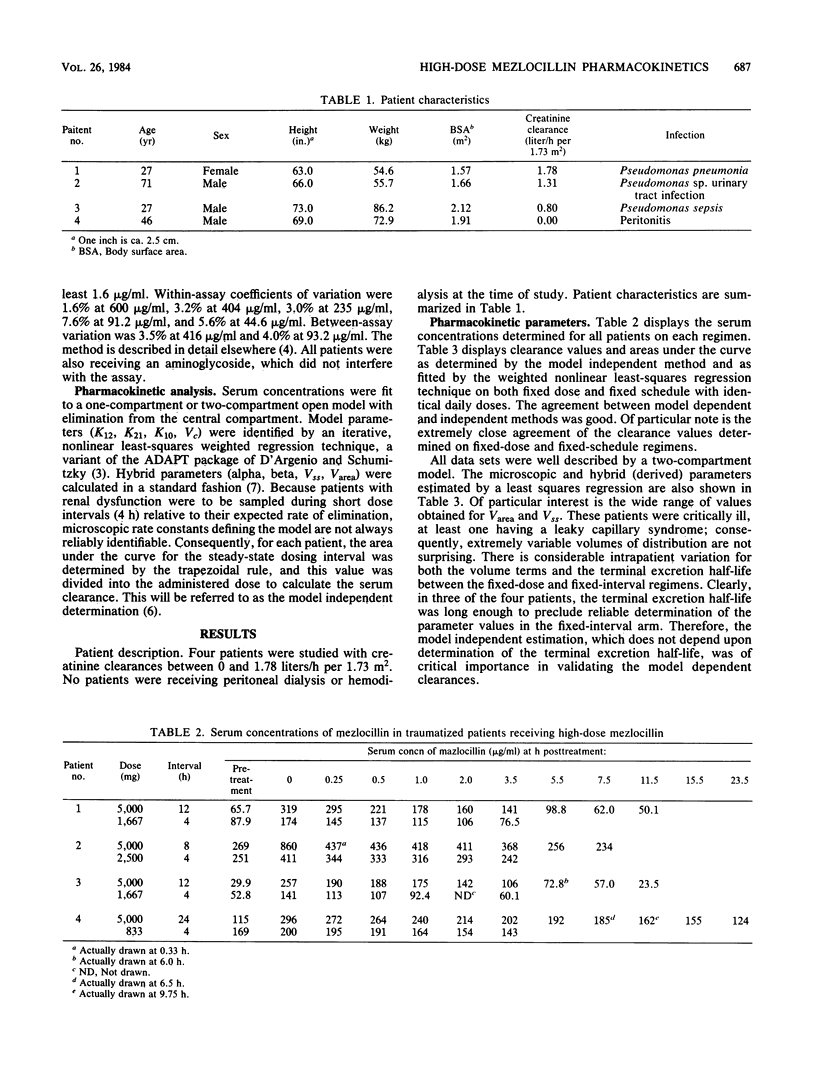
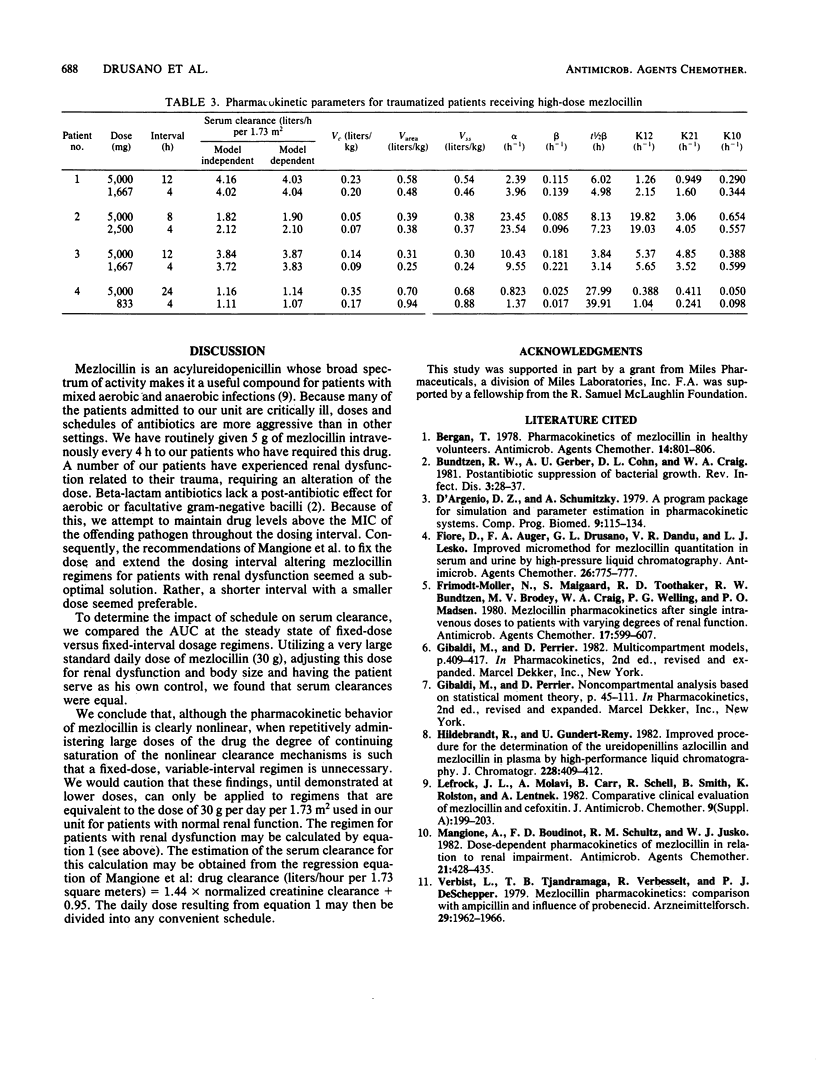
As mezlocillin has been shown to display nonlinear pharmacokinetics in single-dose evaluations, we evaluated a crossover trial in patients with renal dysfunction the impact on serum clearance of fixed-dose versus fixed-interval administration of identical daily doses of the drug. In four patients with creatinine clearances of 0.00 to 1.78 liters/h per 1.73 m2, equal serum clearances were observed when the calculated daily total dose of mezlocillin was given either as a fixed dose of 5,000 mg at various intervals or every 4 h at various doses. We found that repetitive large daily doses that are equivalent to 30 g/day in patients with normal renal function can be administered to patients with impaired renal function as a reduced dose every 4 h instead of prolonging the dosing interval, as suggested by Mangione et al. (Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 21:428-435, 1982). The observed serum clearances were equal for the two schedules, probably owing to the degree of continuing saturation of the nonlinear clearance mechanisms of mezlocillin.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergan T. Pharmacokinetics of mezlocillin in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):801–806. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundtzen R. W., Gerber A. U., Cohn D. L., Craig W. A. Postantibiotic suppression of bacterial growth. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):28–37. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Argenio D. Z., Schumitzky A. A program package for simulation and parameter estimation in pharmacokinetic systems. Comput Programs Biomed. 1979 Mar;9(2):115–134. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(79)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frimodt-Möller N., Maigaard S., Toothaker R. D., Bundtzen R. W., Brodey M. V., Craig W. A., Welling P. G., Madsen P. O. Mezlocillin pharmacokinetics after single intravenous doses to patients with varying degrees of renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):599–607. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt R., Gundert-Remy U. Improved procedure for the determination of the ureidopenicillins azlocillin and mezlocillin plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1982 Mar 12;228:409–412. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80464-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFrock J. L., Molavi A., Carr B., Schell R., Smith B., Rolston K., Lentnek A. Comparative clinical evaluation of mezlocillin and cefoxitin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jan;9 (Suppl A):199–203. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.suppl_a.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangione A., Boudinot F. D., Schultz R. M., Jusko W. J. Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics of mezlocillin in relation to renal impairment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):428–435. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Tjandramaga T. B., Verbesselt R., De Schepper P. J. Mezlocillin pharmacokinetics. Comparison with ampicillin and influence of probenecid. Arzneimittelforschung. 1979;29(12A):1962–1966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



