Abstract
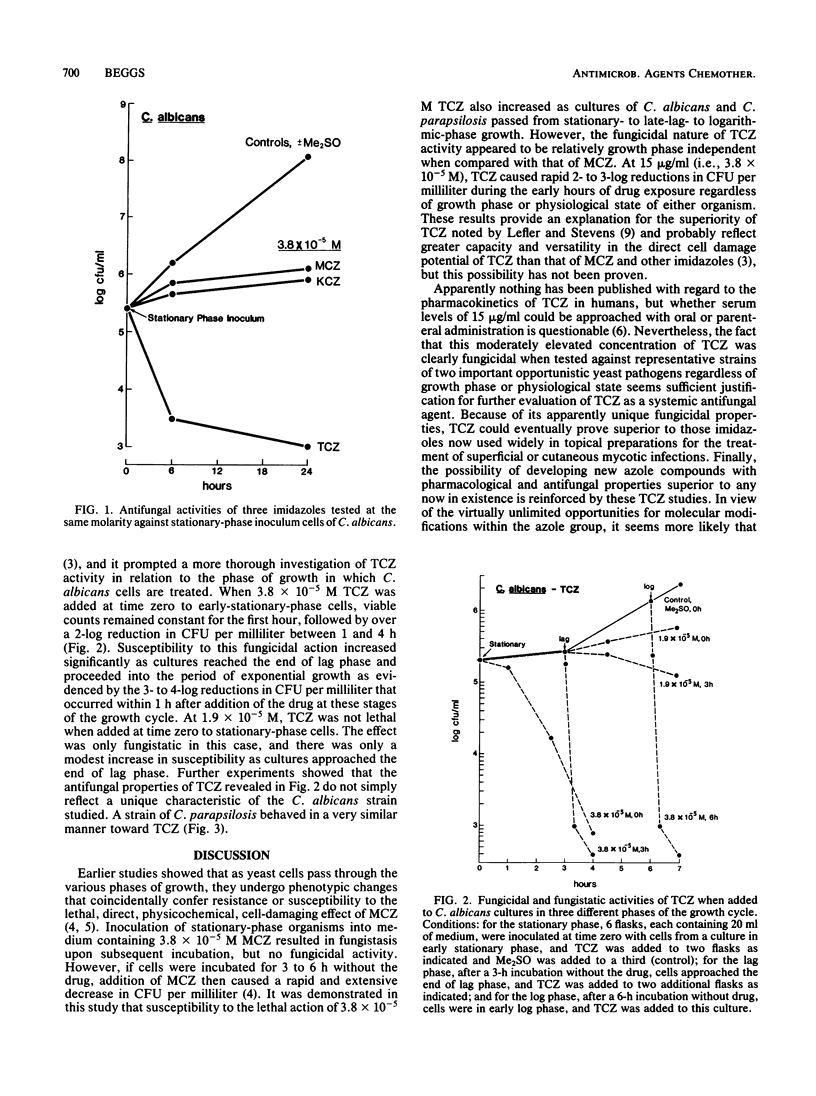
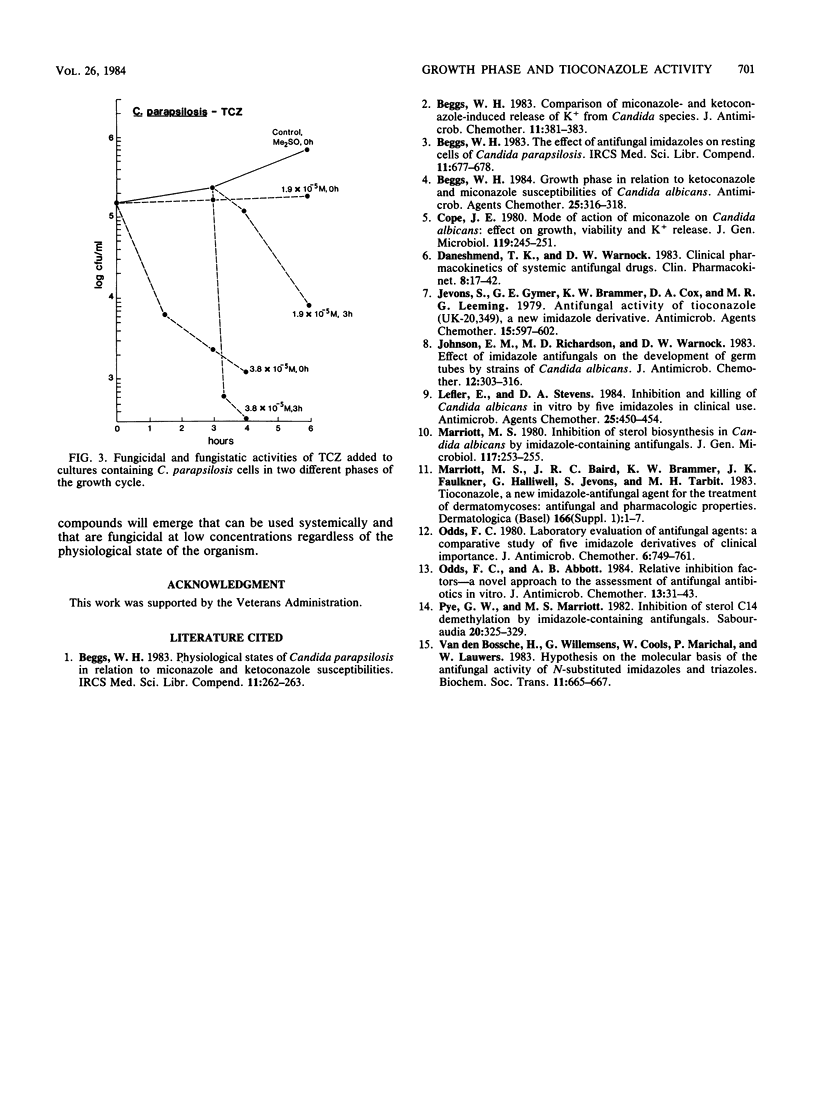
It was shown that tioconazole possesses an important property not shared by ketoconazole and miconazole, its well-known relatives in the imidazole group of antifungal drugs. At a concentration of 3.8 X 10(-5) M, tioconazole, like miconazole, caused rapid 2- to 3-log reductions in CFU per milliliter when added to late-logarithmic-phase Candida albicans or Candida parapsilosis cells. Only tioconazole, however, exerted similar reductions when added to diluted stationary-phase cultures. This growth-phase-independent lethal action has important clinical implications and may explain the superior performance of tioconazole, which was observed in earlier comparative drug studies.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beggs W. H. Comparison of miconazole- and ketoconazole-induced release of K+ from Candida species. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Apr;11(4):381–383. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.4.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs W. H. Growth phase in relation to ketoconazole and miconazole susceptibilities of Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):316–318. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope J. E. Mode of action of miconazole on Candida albicans: effect on growth, viability and K+ release. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jul;119(1):245–251. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-1-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneshmend T. K., Warnock D. W. Clinical pharmacokinetics of systemic antifungal drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1983 Jan-Feb;8(1):17–42. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198308010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jevons S., Gymer G. E., Brammer K. W., Cox D. A., Leeming M. R. Antifungal activity of tioconazole (UK-20,349), a new imidazole derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):597–602. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Richardson M. D., Warnock D. W. Effect of imidazole antifungals on the development of germ tubes by strains of Candida albicans. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Oct;12(4):303–316. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.4.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefler E., Stevens D. A. Inhibition and killing of Candida albicans in vitro by five imidazoles in clinical use. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):450–454. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott M. S., Baird J. R., Brammer K. W., Faulkner J. K., Halliwell G., Jevons S., Tarbit M. H. Tioconazole, a new imidazole-antifungal agent for the treatment of dermatomycoses. Antifungal and pharmacologic properties. Dermatologica. 1983;166 (Suppl 1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott M. S. Inhibition of sterol biosynthesis in Candida albicans by imidazole-containing antifungals. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Mar;117(1):253–255. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-1-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. Relative inhibition factors--a novel approach to the assessment of antifungal antibiotics in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jan;13(1):31–43. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Laboratory evaluation of antifungal agents: a comparative study of five imidazole derivatives of clinical importance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Nov;6(6):749–761. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.6.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pye G. W., Marriott M. S. Inhibition of sterol C14 demethylation by imidazole-containing antifungals. Sabouraudia. 1982 Dec;20(4):325–329. doi: 10.1080/00362178285380461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bossche H., Willemsens G., Cools W., Marichal P., Lauwers W. Hypothesis on the molecular basis of the antifungal activity of N-substituted imidazoles and triazoles. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Dec;11(6):665–667. doi: 10.1042/bst0110665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



