Abstract
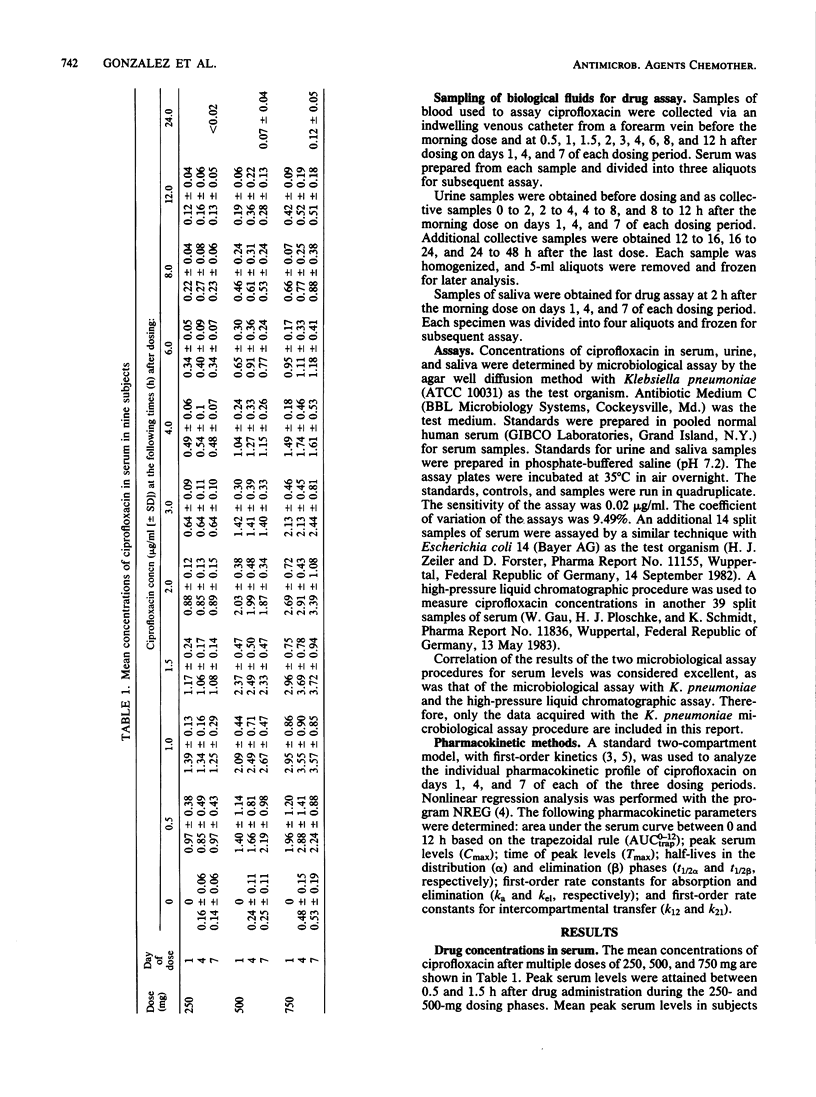
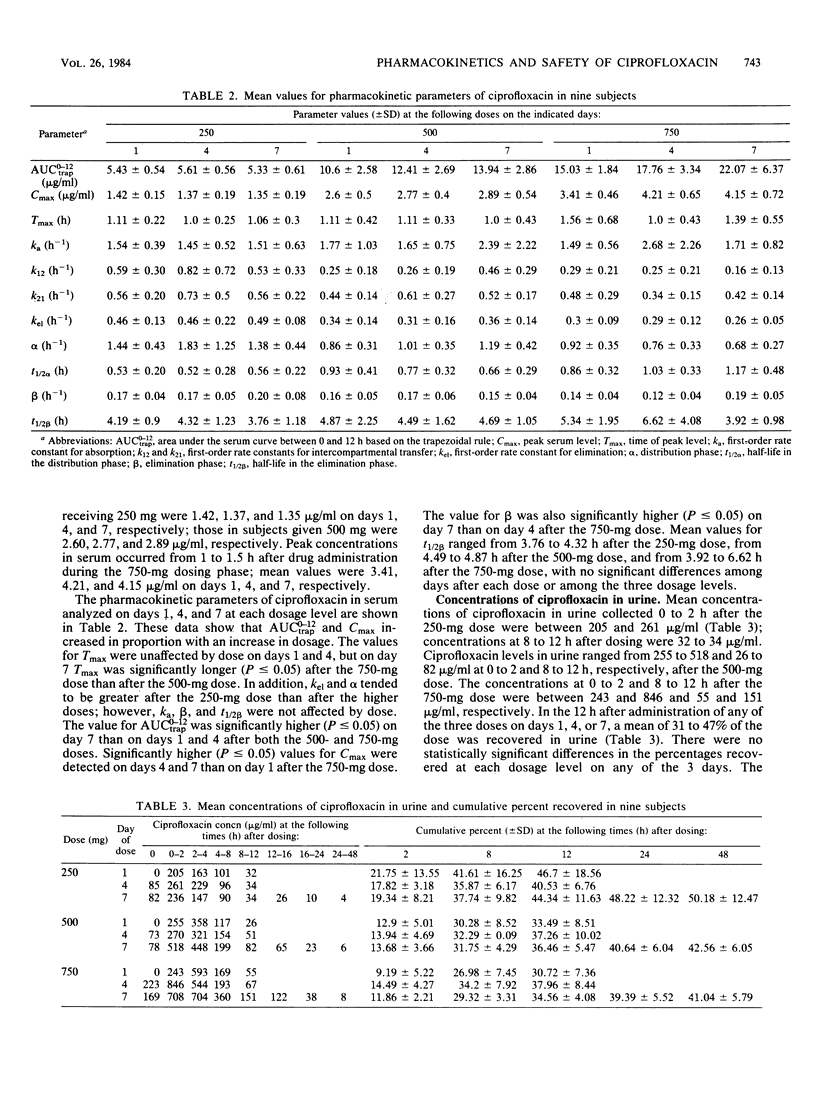
The multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and safety of ciprofloxacin, a new quinoline carboxylic acid derivative, were evaluated in normal volunteers. The drug was administered orally every 12 h during successive 7-day periods at doses of 250, 500, and 750 mg. Samples of serum, urine, and saliva obtained after the first dose on days 1, 4, and 7 of each dosing period were assayed by microbiological methods. Peak concentrations of ciprofloxacin in serum were achieved generally from 1 to 1.5 h after administration. Mean peak serum levels were 1.35 to 1.42 micrograms/ml after the 250-mg dose, 2.60 to 2.89 micrograms/ml after the 500-mg dose, and 3.41 to 4.21 micrograms/ml after the 750-mg dose. Terminal serum half-lives ranged from 3.8 to 4.3, 4.5 to 4.9, and 3.9 to 6.6 h after the 250-, 500-, and 750-mg doses, respectively. Mean concentrations of ciprofloxacin in urine samples collected 0 to 2 h after dosing were 205 to 261, 255 to 518, and 243 to 846 micrograms/ml after the 250-, 500-, and 750-mg doses, respectively. Between 30 and 45% of the dose was recovered in urine 0 to 12 h after drug administration. Mean concentrations of ciprofloxacin in saliva at 2 h after dosing were 0.43, 1.23, and 1.45 micrograms/ml after the 250-, 500-, and 750-mg doses, respectively. These levels were 30 to 45% of the peak levels in serum and between 40 and 65% of the levels in serum measured 2 h after dosing. Ciprofloxacin was well tolerated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02001575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump B., Wise R., Dent J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):784–786. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. New method for calculating the intrinsic absorption rate of drugs. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jun;57(6):918–928. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


