Abstract
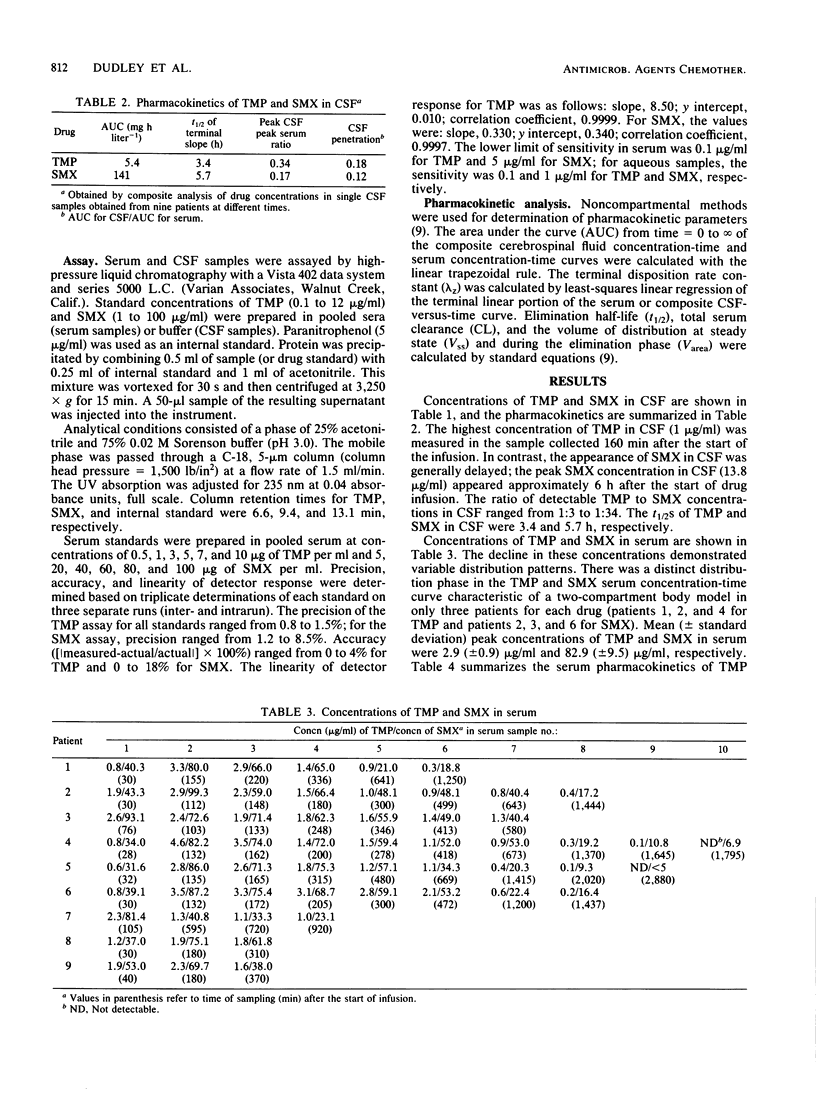
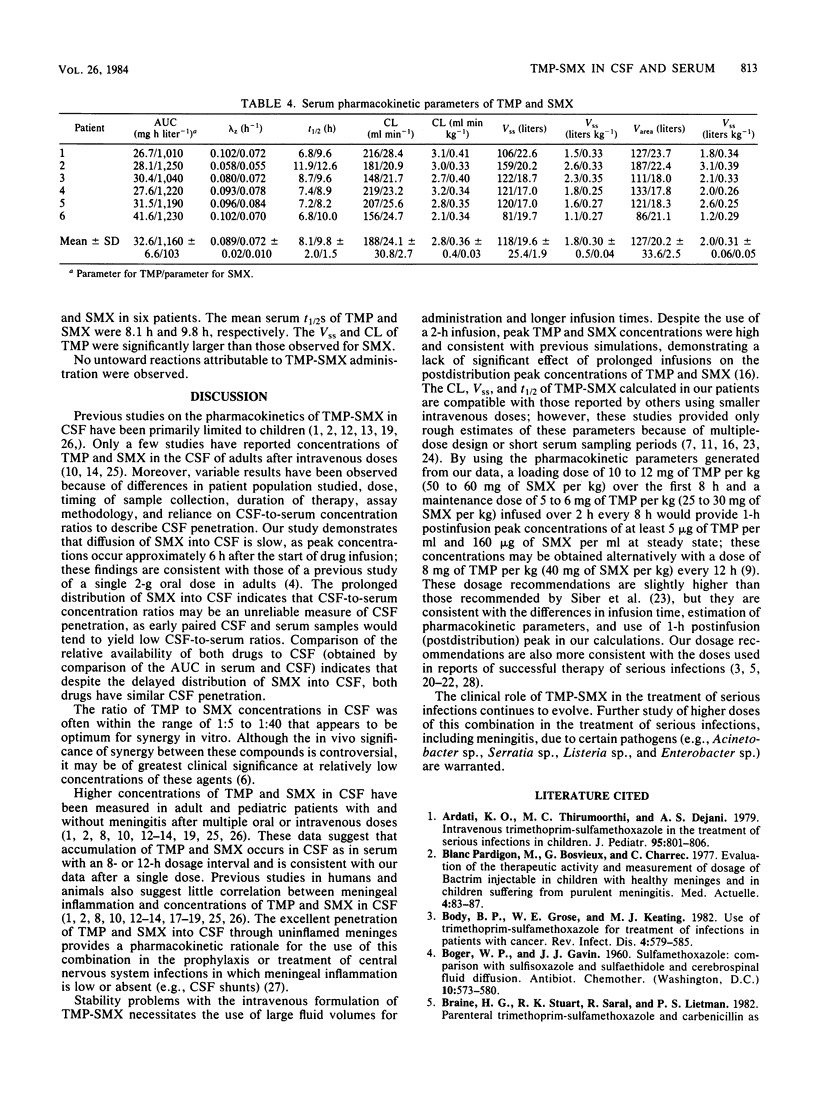
The pharmacokinetics of trimethoprim (TMP) and sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum after a single intravenous infusion of 5 mg of TMP and 25 mg of SMX per kg of body weight over approximately 120 min were studied i nine patients who had uninflamed meninges and were undergoing elective myelography. Peak concentrations of TMP and SMX in CSF were 1 microgram/ml and 13.8 micrograms/ml, respectively. The peak TMP concentration in CSF occurred significantly earlier than the peak SMX concentration (60 versus 480 min postinfusion). At 15 h, there was no detectable TMP in the CSF, and there was 4.7 micrograms of SMX per ml of CSF. In the postdistribution phase (in CSF), simultaneous CSF-to-serum concentration ratios ranged from 0.23 to 0.53 for TMP and from 0.20 to 0.36 for SMX. CSF penetration (measured by comparison of the area under the curve of the composite CSF and serum concentration-time curves) was 18% for TMP and 12% for SMX. A loading dose of TMP-SMX (bases on TMP) of 10 to 12 mg/kg and a maintenance dose of 6 mg/kg every 8 h or 8 mg/kg every 12 h (with a 2-h infusion) should yield steady-state peak concentrations of at least 5 micrograms of TMP per ml of serum and 160 micrograms of SMX per ml of serum. Further studies of TMP-SMX administered in these doses in the treatment of serious bacterial infection, including meningitis, are warranted.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardati K. O., Thirumoorthi M. C., Dajani A. S. Intravenous trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the treatment of serious infections in children. J Pediatr. 1979 Nov;95(5 Pt 1):801–806. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80740-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Grose W. E., Keating M. J. Use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for treatment of infections in patients with cancer. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):579–585. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushby S. R., Hitchings G. H. Trimethoprim, a sulphonamide potentiator. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 May;33(1):72–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries N., Keuth U., Braun J. S. Untersuchungen zur Liquorgängigkeit von Trimethoprim im Kindesalter. Fortschr Med. 1975 Sep 11;93(25):1178–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Bucens M. C., Davis R. E., Norcott T. C. High-dose co-trimoxazole and its penetration through uninflamed meninges. Med J Aust. 1981 Jul 11;2(1):24–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose W. E., Bodey G. P., Loo T. L. Clinical pharmacology of intravenously administered trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):447–451. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirwan W. O. Cerebrospinal fluid cotrimoxazole levels. J Ir Med Assoc. 1974 Feb 9;67(3):76–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz R. E., Dudley M. N., Quintiliani R., Mullany L. D., Nightingale C. H. Cerebrospinal fluid penetration of trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole in two patients with gram-negative bacillary meningitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Apr;13(4):400–401. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.4.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz R. E., Quintiliani R. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for bacterial meningitis. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jun;100(6):881–890. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-6-881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. J., Raymond K. Evaluation of slow infusions of co-trimoxazole by using predictive pharmacokinetics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):132–137. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylotte J. M., Bates T. R., Sergeant K. A., Matson R. E., Beam T. R., Jr Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole therapy of experimental Escherichia coli meningitis in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):81–87. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perfect J. R., Lang S. D., Durack D. T. Comparison of cotrimoxazole, ampicillin, and chloramphenicol in treatment of experimental Haemophilus influenzae type B meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jan;17(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabel K. G., Brandberg A. Treatment of meningitis and septicemia in infancy with a sulphamethoxazole/trimethorpim combination. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1975 Jan;64(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1975.tb04376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter A. J. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in treatment of severe infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):338–350. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler F. R., Remington J. S. Intravenous sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim for serious gram-negative bacillary infection. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Sep;143(9):1709–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt U., Sen P., Kapila R., Louria D. B. Clinical evaluation of intravenous trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for serious infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):332–337. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Gorham C. C., Ericson J. F., Smith A. L. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in children and adults with normal and impaired renal function. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):566–578. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicehandler J., Pollock A. A., Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J., Jr Intravenous pharmacokinetics and in vitro bactericidal activity of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):562–565. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedhem A., Iwarson S. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of trimethoprim during oral and parenteral treatment. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Nov;5(6):717–720. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.6.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. E., Prober C. G., Hendrick B. E., Hoffman H. J., Humphreys R. P. Prophylactic sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. JAMA. 1984 Mar 2;251(9):1174–1177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. E., Prober C. G. Ventricular cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Apr;11(4):385–389. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.4.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Lau W. K., Gale R. P., Young L. S. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jun;92(6):762–769. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-6-762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormser G. P., Keusch G. T. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):420–429. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


