Abstract
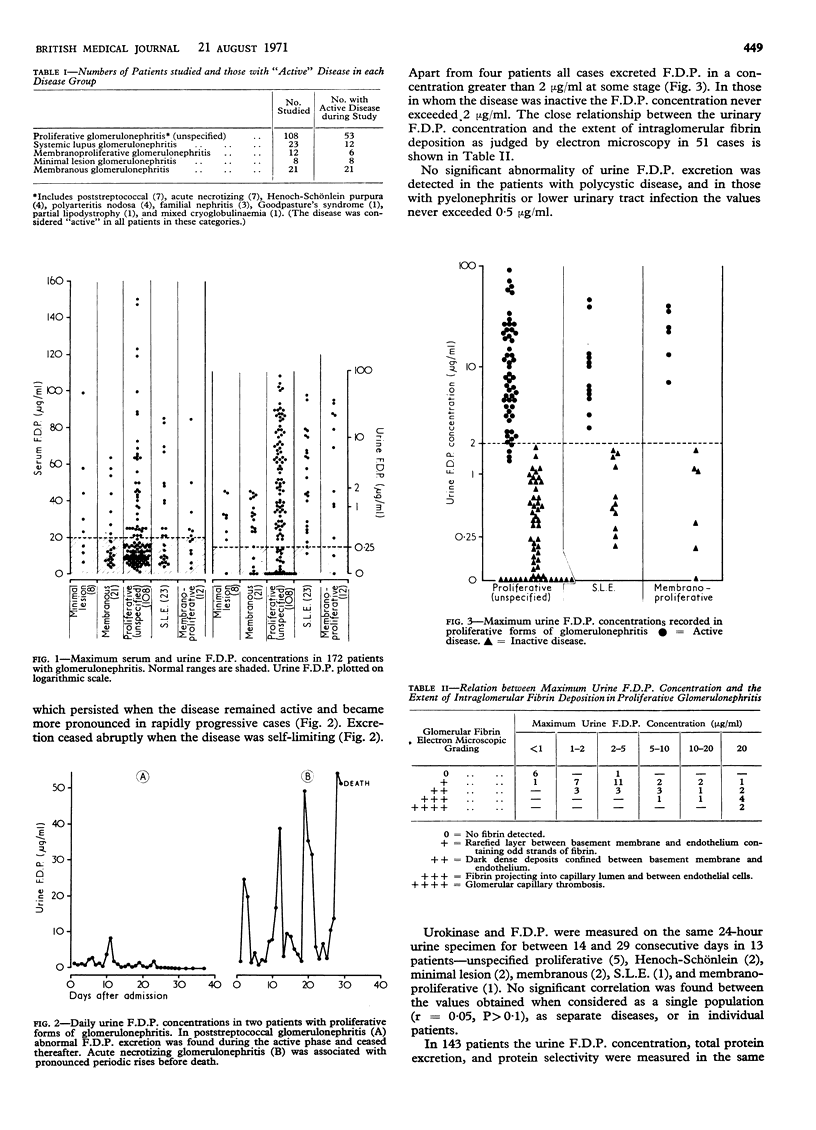
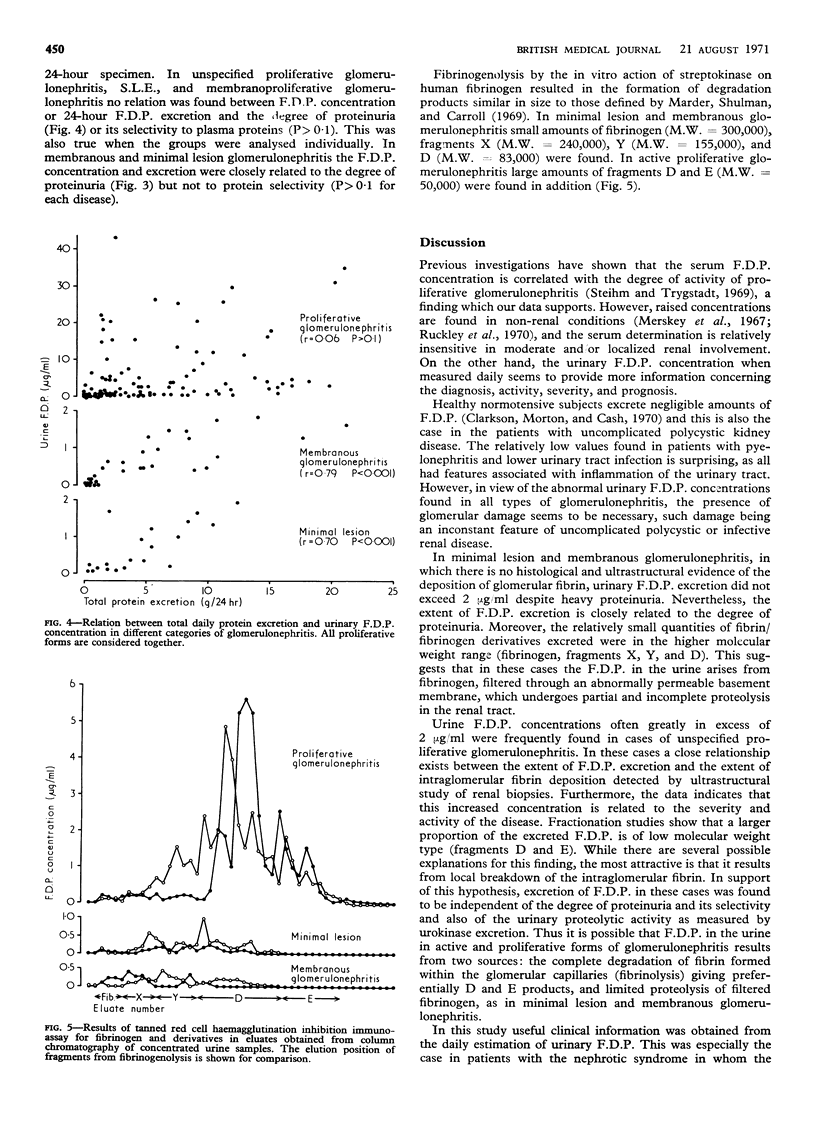
The serum and urine concentrations of fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products (F.D.P.) were estimated in 172 patients with glomerulonephritis. In each case the diagnosis was established on the basis of clinical, renal histological, and ultrastructural findings. Serum F.D.P. concentrations were often raised in all types of glomerulonephritis, though more consistently in active proliferative forms. The urinary concentration provided a reliable and sensitive index of activity, progression, and natural history in proliferative glomerulonephritis. In these forms the urinary F.D.P. content was thought to reflect predominantly lysis of intraglomerular fibrin deposits. In minimal lesion and membranous glomerulonephritis low but abnormal concentrations of urinary F.D.P. were consistently found. It is suggested that in these cases the products are derived from limited proteolysis of fibrinogen filtered through an abnormally permeable basement membrane.
Daily measurement of urinary F.D.P. concentration is of potential value in the differential diagnosis of patients with glomerulonephritis and at the same time provides a sensitive assessment of the activity and natural history of proliferative disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin D. S., Lowenstein J., Rothfield N. F., Gallo G., McCluskey R. T. The clinical course of the proliferative and membranous forms of lupus nephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Dec;73(6):929–942. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-6-929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. S., Glasgow E. F., Ogg C. S., White R. H. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis and persistent hypocomplementaemia. Br Med J. 1970 Oct 3;4(5726):7–14. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5726.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson A. R., MacDonald M. K., Fuster V., Cash J. D., Robson J. S. Glomerular coagulation in acute ischaemic renal failure. Q J Med. 1970 Oct;39(156):585–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson A. R., Morton J. B., Cash J. D. Urinary fibrin-fibrinogen degradation poducts after renal homotransplantation. Lancet. 1970 Dec 12;2(7685):1220–1223. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Braun W. E., Busch G. J., Dammin G. J., Merrill J. P. Coagulation studies in the hyperacute and other forms of renal-allograft rejection. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 25;281(13):685–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909252811301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das P. C. Investigations and preparation of fibrinogencoated tan A/Das PC: Investigations and preparation of fibrinogen-coated tanned sheep red cells. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Mar;23(2):149–155. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.2.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDWICKE J., SQUIRE J. R. The relationship between plasma albumin concentration and protein excretion in patients with proteinuria. Clin Sci. 1955 Aug;14(3):509–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humair L., Kwaan H. C., Potter E. V. The role of fibrinogen in renal disease. II. Effect of anticoagulants and urokinase on experimental lesions in mice. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jul;74(1):72–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humair L., Potter E. V., Kwaan H. C. The role of fibrinogen in renal disease. I. Production of experimental lesions in mice. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jul;74(1):60–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid-Smith P., Laver M. C., Fairley K. F. Dipyridamole and anticoagulants in renal disease due to glomerular and vascular lesions. A new approach to therapy. Med J Aust. 1970 Jan 24;1(4):145–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid-Smith P., Saker B. M., Fairley K. F. Anticoagulants in "irreversible" acute renal failure. Lancet. 1968 Dec 28;2(7583):1360–1363. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92671-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD M. K., LAMBIE A. T., ROBSON J. S. Resolution of glomerular lesions in the nephrotic syndrome treated with cortisone: electron microscopic studies in an adult case. Scott Med J. 1959 Sep;4:415–421. doi: 10.1177/003693305900400902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUEHRCKE R. C., KARK R. M., PIRANI C. L., POLLAK V. E. Lupus nephritis: a clinical and pathologic study based on renal biopsies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1957 Feb;36(1):1–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean P. R., Robson J. S. A simple method for determining selectivity of proteinuria. Lancet. 1967 Mar 11;1(7489):539–542. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R., Carroll W. R. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. I. Physicochemical and immunological characterization. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2111–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Johnson A. J., Kleiner G. J., Wohl H. The defibrination syndrome: clinical features and laboratory diagnosis. Br J Haematol. 1967 Jul;13(4):528–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb00762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Kleiner G. J., Johnson A. J. Quantitative estimation of split products of fibrinogen in human serum, relation to diagnosis and treatment. Blood. 1966 Jul;28(1):1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollak V. E., Rosen S., Pirani C. L., Muehrcke R. C., Kark R. M. Natural history of lipoid nephrosis and of membranous glomerulonephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Dec;69(6):1171–1196. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-6-1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruckley C. V., Das P. C., Leitch A. G., Donaldson A. A., Copland W. A., Redpath A. T., Scott P., Cash J. D. Serum fibrin-fibrinogen degradation products associated with postoperative pulmonary embolus and venous thrombosis. Br Med J. 1970 Nov 14;4(5732):395–398. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5732.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Trygstad C. W. Split products of fibrin in human renal disease. Am J Med. 1969 May;46(5):774–786. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSALLI P., MCCLUSKEY R. T. THE COAGULATION PROCESS AND GLOMERULAR DISEASE. Am J Med. 1965 Aug;39:179–183. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSALLI P., SIMON G., ROUILLER C. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF GLOMERULAR LESIONS RESULTING FROM INTRAVASCULAR FIBRIN FORMATION. Am J Pathol. 1963 Oct;43:579–617. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermylen J., Dotremont G., de Gaetano G., Donati M. B., Michielsen P. Indomethacin and urinary excretion of fibrinogen-like material in proliferative glomerulonephritis. Rev Eur Etud Clin Biol. 1970 Nov;15(9):979–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N., Taylor G. Fibrin breakdown products and fibrinolysis in renal disease. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Mar;21(2):140–146. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.2.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


