Abstract
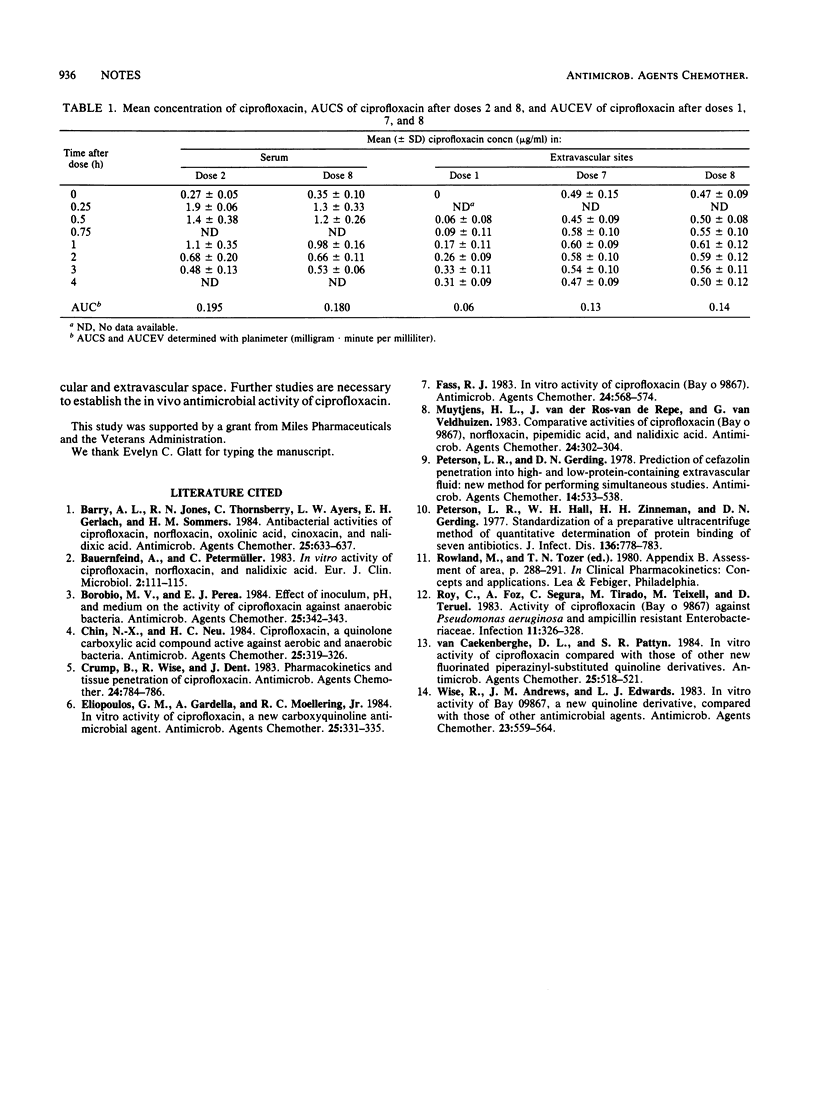
Ciprofloxacin penetration into extravascular spaces was studied in a rabbit Visking chamber model. The drug was administered (7 mg/kg) intramuscularly every 4 h for eight doses. Peak and trough drug levels by dose 8 were 1.3 and 0.35 micrograms/ml in serum and 0.61 and 0.50 micrograms/ml in extravascular sites. The ratio of extravascular site to serum free drug area under the drug curve by dose 8 was 91.1%. This potent, new antimicrobial agent appears to distribute freely to extravascular spaces in this animal model.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Ayers L. W., Gerlach E. H., Sommers H. M. Antibacterial activities of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, oxolinic acid, cinoxacin, and nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):633–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02001575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borobio M. V., Perea E. J. Effect of inoculum, pH, and medium on the activity of ciprofloxacin against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):342–343. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):319–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump B., Wise R., Dent J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):784–786. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Gardella A., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, a new carboxyquinoline antimicrobial agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):331–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin (Bay o 9867). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):568–574. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muytjens H. L., van der Ros-van de Repe J., van Veldhuizen G. Comparative activities of ciprofloxacin (Bay o 9867), norfloxacin, pipemidic acid, and nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):302–304. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Prediction of cefazolin penetration in high- and low-protein-containing extravascular fluid: new method for performing simultaneous studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):533–538. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Hall W. H., Zinneman H. H., Gerding D. N. Standardization of a preparative ultracentrifuge method for quantitative determination or protein binding of seven antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):778–783. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C., Foz A., Segura C., Tirado M., Teixell M., Teruel D. Activity of ciprofloxacin (BAYo 9867) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and ampicillin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Infection. 1983 Nov-Dec;11(6):326–328. doi: 10.1007/BF01641358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Caekenberghe D. L., Pattyn S. R. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin compared with those of other new fluorinated piperazinyl-substituted quinoline derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):518–521. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Edwards L. J. In vitro activity of Bay 09867, a new quinoline derivative, compared with those of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):559–564. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


