Abstract
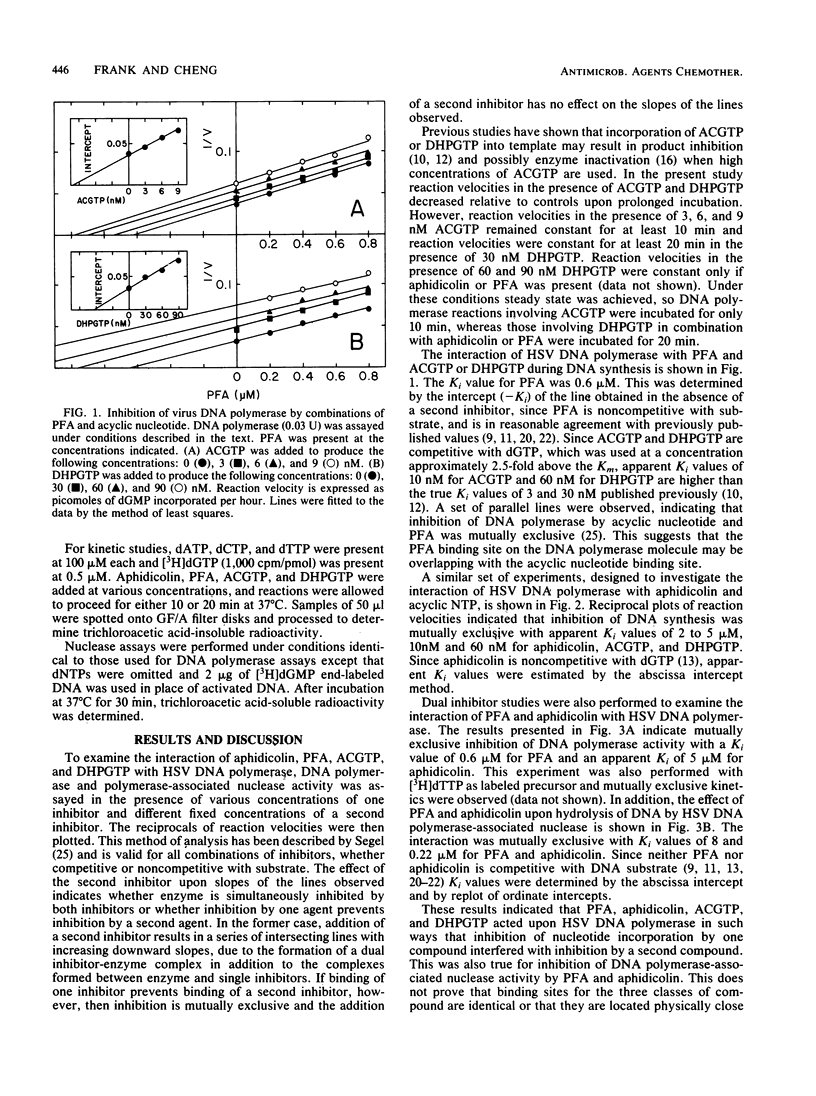
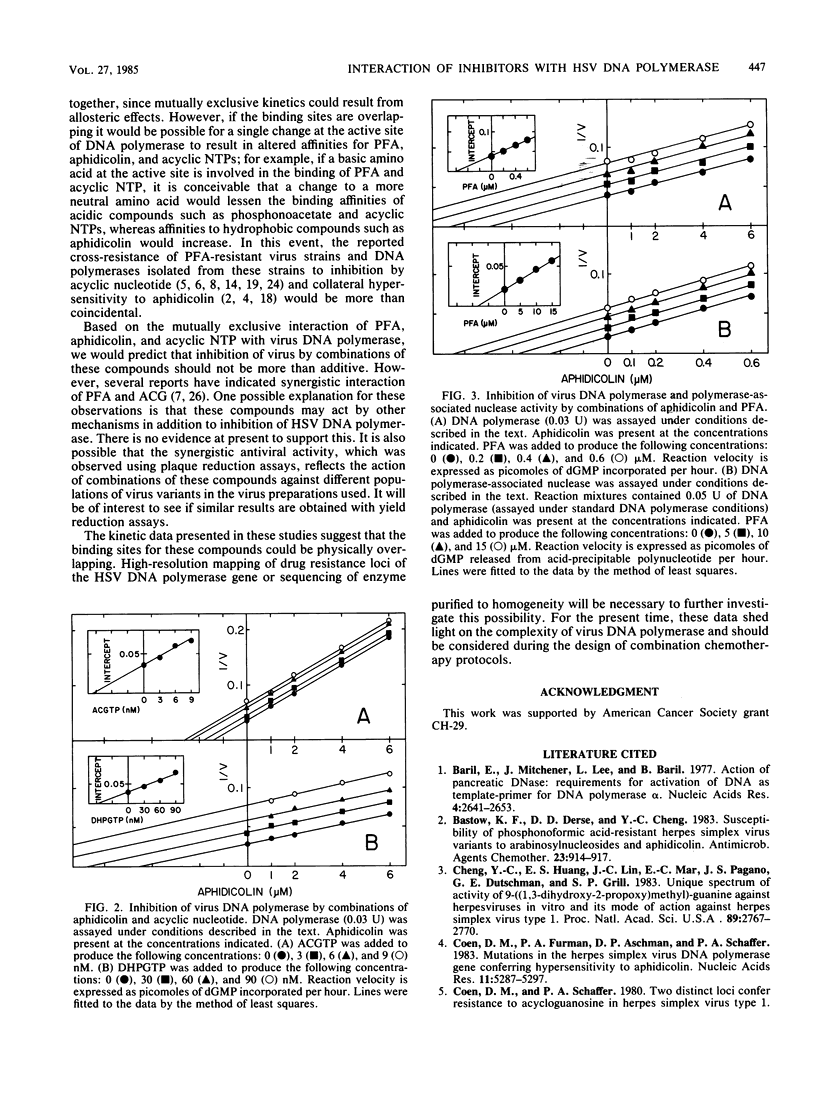
Dual inhibitor studies were performed to examine the interaction of aphidicolin, phosphonoformate, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine triphosphate, and 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine triphosphate with herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase. Kinetic data indicated that inhibition by one agent prevents simultaneous inhibition by a second agent, producing a mutually exclusive inhibition pattern. This suggested that binding sites on the DNA polymerase molecule for these compounds are kinetically overlapping. These findings should be taken into consideration for the design of future antiviral compounds and combination chemotherapy protocols.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baril E., Mitchener J., Lee L., Baril B. Action of pancreatic DNase: requirements for activation of DNA as a template-primer for DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2641–2653. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastow K. F., Derse D. D., Cheng Y. C. Susceptibility of phosphonoformic acid-resistant herpes simplex virus variants to arabinosylnucleosides and aphidicolin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):914–917. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Huang E. S., Lin J. C., Mar E. C., Pagano J. S., Dutschman G. E., Grill S. P. Unique spectrum of activity of 9-[(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]-guanine against herpesviruses in vitro and its mode of action against herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Furman P. A., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Mutations in the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene conferring hypersensitivity to aphidicolin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5287–5297. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumpacker C. S., Chartrand P., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Resistance of herpes simplex virus to acycloguanosine--genetic and physical analysis. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumpacker C. S., Kowalsky P. N., Oliver S. A., Schnipper L. E., Field A. K. Resistance of herpes simplex virus to 9-[[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl]guanine: physical mapping of drug synergism within the viral DNA polymerase locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1556–1560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Bastow K. F., Cheng Y. Characterization of the DNA polymerases induced by a group of herpes simplex virus type I variants selected for growth in the presence of phosphonoformic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10251–10260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Cheng Y. C., Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Elion G. B. Inhibition of purified human and herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerases by 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine triphosphate. Effects on primer-template function. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11447–11451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Cheng Y. C. Herpes simplex virus type I DNA polymerase. Kinetic properties of the associated 3'-5' exonuclease activity and its role in araAMP incorporation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8525–8530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B., Larsson A., Helgstrand E., Johansson N. G., Oberg B. Pyrophosphate analogues as inhibitors of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 28;607(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank K. B., Chiou J. F., Cheng Y. C. Interaction of herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase with 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1566–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank K. B., Derse D. D., Bastow K. F., Cheng Y. C. Novel interaction of aphidicolin with herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase and polymerase-associated exonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13282–13286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Coen D. M., St Clair M. H., Schaffer P. A. Acyclovir-resistant mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 express altered DNA polymerase or reduced acyclovir phosphorylating activities. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):936–941. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.936-941.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Fyfe J. A., Rideout J. L., Keller P. M., Elion G. B. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase activity and viral DNA replication by 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine and its triphosphate. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.72-77.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Spector T. Acyclovir triphosphate is a suicide inactivator of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9575–9579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germershausen J., Bostedor R., Field A. K., Perry H., Liou R., Bull H., Tolman R. L., Karkas J. D. A comparison of the antiviral agents 2'-nor-2'-deoxyguanosine and acyclovir: uptake and phosphorylation in tissue culture and kinetics of in vitro inhibition of viral and cellular DNA polymerases by their respective triphosphates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):360–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Purifoy D. J., Young D., Gopal R., Cammack N., O'Hare P. Single mutations at many sites within the DNA polymerase locus of herpes simplex viruses can confer hypersensitivity to aphidicolin and resistance to phosphonoacetic acid. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf K. W., Kaufman E. R., Crumpacker C. Physical mapping of drug resistance mutations defines an active center of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase enzyme. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):746–757. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.746-757.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Reno J. M., Lee L. F., Isbell A. F., Boezi J. A. Mechanism of phosphonoacetate inhibition of herpesvirus-induced DNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):426–430. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrali-Noy G., Spadari S. Mechanism of inhibition of herpes simplex virus and vaccinia virus DNA polymerases by aphidicolin, a highly specific inhibitor of DNA replication in eucaryotes. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):457–464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.457-464.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reno J. M., Lee L. F., Boezi J. A. Inhibition of herpesvirus replication and herpesvirus-induced deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase by phosphonoformate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):188–192. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruth J. L., Cheng Y. C. Nucleoside analogues with clinical potential in antivirus chemotherapy. The effect of several thymidine and 2'-deoxycytidine analogue 5'-triphosphates on purified human (alpha, beta) and herpes simplex virus (types 1, 2) DNA polymerases. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;20(2):415–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnipper L. E., Crumpacker C. S. Resistance of herpes simplex virus to acycloguanosine: role of viral thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2270–2273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Galloway K. S., Ogilvie K. K., Cheriyan U. O. Synergism among BIOLF-62, phosphonoformate, and other antiherpetic compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):1026–1030. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


