Abstract
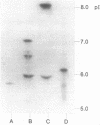
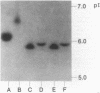
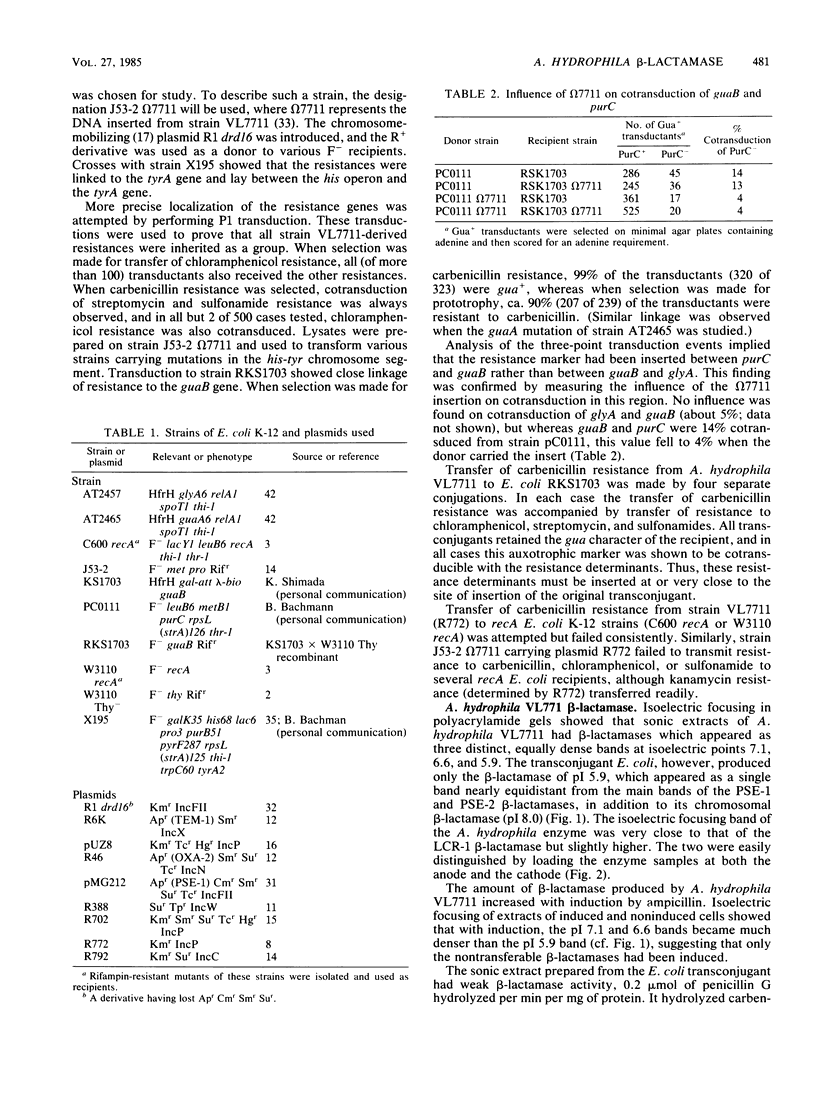
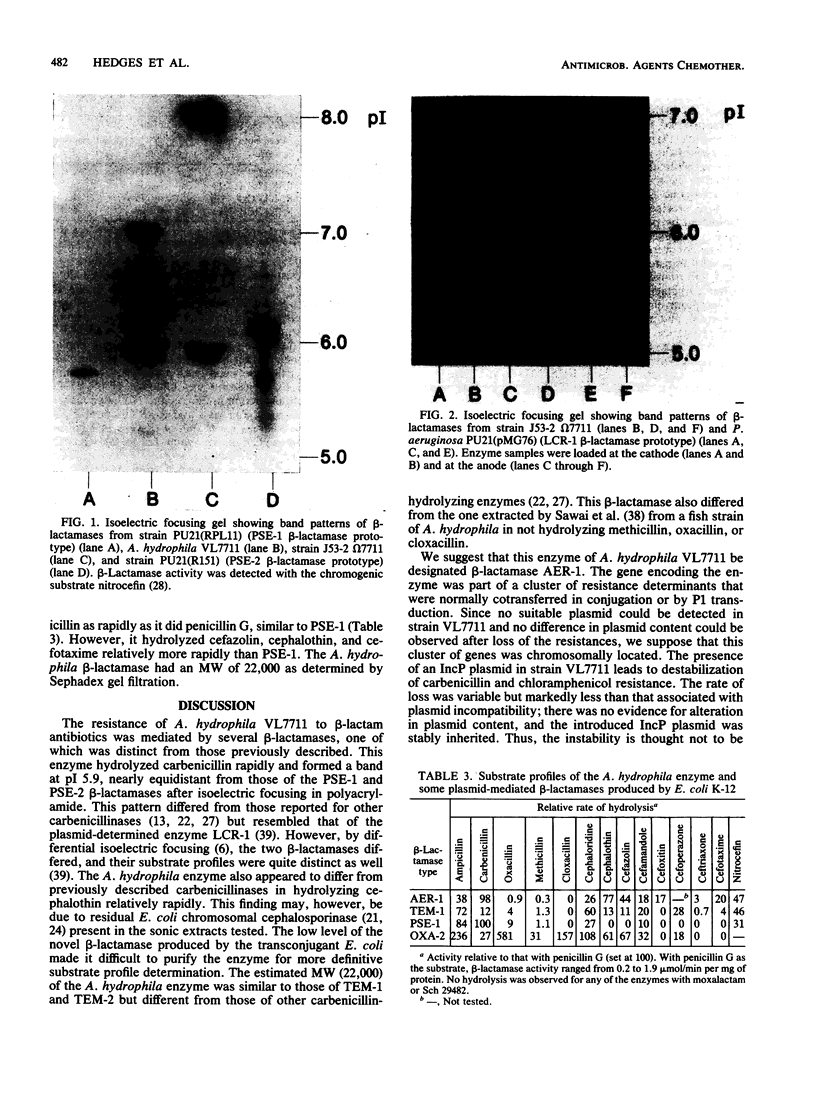
A novel carbenicillin-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase has been discovered in a blood isolate of Aeromonas hydrophila. The enzyme resembles plasmid-determined carbenicillinases in substrate profile but differs in isoelectric point (pI 5.9) and molecular weight (22,000) and has been termed AER-1. No evidence for a plasmid location could be obtained in A. hydrophila, but the AER-1 gene and resistance to chloramphenicol, streptomycin, and sulfonamide could be transferred by mobilization with IncP plasmids to Escherichia coli, where the gene cluster inserted at a unique chromosomal site. The linked resistances are similar to those found on multiresistance beta-lactamase transposons, but since insertion of the A. hydrophila gene cluster was site specific and recA+ dependent, the cluster is not a functional transposon.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. T., Datta N., Hedges R. W., Grinter N. J. Transposition of a deoxyribonucleic acid sequence encoding trimethoprim and streptomycin resistances from R483 to other replicons. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):800–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.800-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. T., Datta N. Two naturally occurring transposons indistinguishable from Tn7. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Sep;102(1):129–134. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-1-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. T., Grinter N. J. Map of plasmid RP4 derived by insertion of transposon C. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 5;113(3):455–474. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthelemy M., Guionie M., Labia R. Beta-lactamases: determination of their isoelectric points. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):695–698. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee J. N., Lecatsas G., Coetzee W. F., Hedges R. W. Properties of R plasmid R772 and the corresponding pilus-specific phage PR772. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):263–273. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W. Host ranges of R factors. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):453–460. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W. Trimethoprim resistance conferred by W plasmids in Enterobacteriaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):349–355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Kontomichalou P. Penicillinase synthesis controlled by infectious R factors in Enterobacteriaceae. Nature. 1965 Oct 16;208(5007):239–241. doi: 10.1038/208239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth A. J. Purification and properties of a constitutive beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain Dalgleish. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 19;377(2):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Jacob A. E. Transposition of ampicillin resistance from RP4 to other replicons. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;132(1):31–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00268228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Matthew M. Acquisition by Escherichia coli of plasmid-borne beta-lactamases normally confined to Pseudomonas spp. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W. R factors from Providence. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):171–181. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. Plasmids that mobilize bacterial chromosome. Plasmid. 1979 Jan;2(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Jacob A. E., Hedges R. W. Recombination between plasmids of incompatibility groups P-1 and P-2. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1278–1285. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1278-1285.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Sutton L., Knobel L., Mammen P. Properties of IncP-2 plasmids of Pseudomonas spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):168–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Andrillon J., Le Goffic F. Computerized microacidimetric determination of beta lactamase Michaelis-Menten constants. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 15;33(1):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Brunet G., Guionie M., Philippon A., Heitz M., Pitton J. S. Céphalosporinases constitutives de Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1976 Nov-Dec;127B(4):453–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Guionie M., Barthélémy M. Properties of three carbenicillin-hydrolysing beta-lactamases (CARB) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: identification of a new enzyme. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jan;7(1):49–56. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque R., Roy P. H., Letarte R., Pechère J. C. A plasmid-mediated cephalosporinase from Achromobacter species. J Infect Dis. 1982 May;145(5):753–761. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linström E. B., Boman H. G., Steele B. B. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. VI. Purification and characterization of the chromosomally mediated penicillinase present in ampA-containing strains. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):218–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.218-231.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marre R., Medeiros A. A., Pasculle A. W. Characterization of the beta-lactamases of six species of Legionella. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):216–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.216-221.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases of Gram-negative bacteria: properties and distribution. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Jul;5(4):349–358. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Sykes R. B. Properties of the beta-lactamase specified by the Pseudomonas plasmid RPL11. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):341–345. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.341-345.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., Hedges R. W., Jacoby G. A. Spread of a "Pseudomonas-specific" beta-lactamase to plasmids of enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):700–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.700-707.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F. Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B possessing a TEM-type beta-lactamase but little permeability barrier to ampicillin. Lancet. 1975 Mar 29;1(7909):716–719. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91630-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meynell E., Datta N. Mutant drug resistant factors of high transmissibility. Nature. 1967 May 27;214(5091):885–887. doi: 10.1038/214885a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Clowes R. C., Cohen S. N., Curtiss R., 3rd, Datta N., Falkow S. Uniform nomenclature for bacterial plasmids: a proposal. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):168–189. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.168-189.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce L. E., Meynell E. Specific chromosomal affinity of a resistant factor. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Jan;50(1):159–172. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A. M., Paul G. C., Jacoby G. A. Properties of PSE-2 beta-lactamase and genetic basis for its production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):362–369. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Morioka K., Ogawa M., Yamagishi S. Inducible oxacillin-hydrolyzing penicillinase in Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from fish. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):191–195. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair M. I., Holloway B. W. A chromosomally located transposon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):569–579. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.569-579.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A. The properties and host range of male-specific bacteriophages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):332–342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Revised linkage map of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):332–353. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.332-353.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Watanabe M., Matsumoto K., Sawai T. Tn2610, a transposon involved in the spread of the carbenicillin-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(2):282–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00337818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]