Abstract
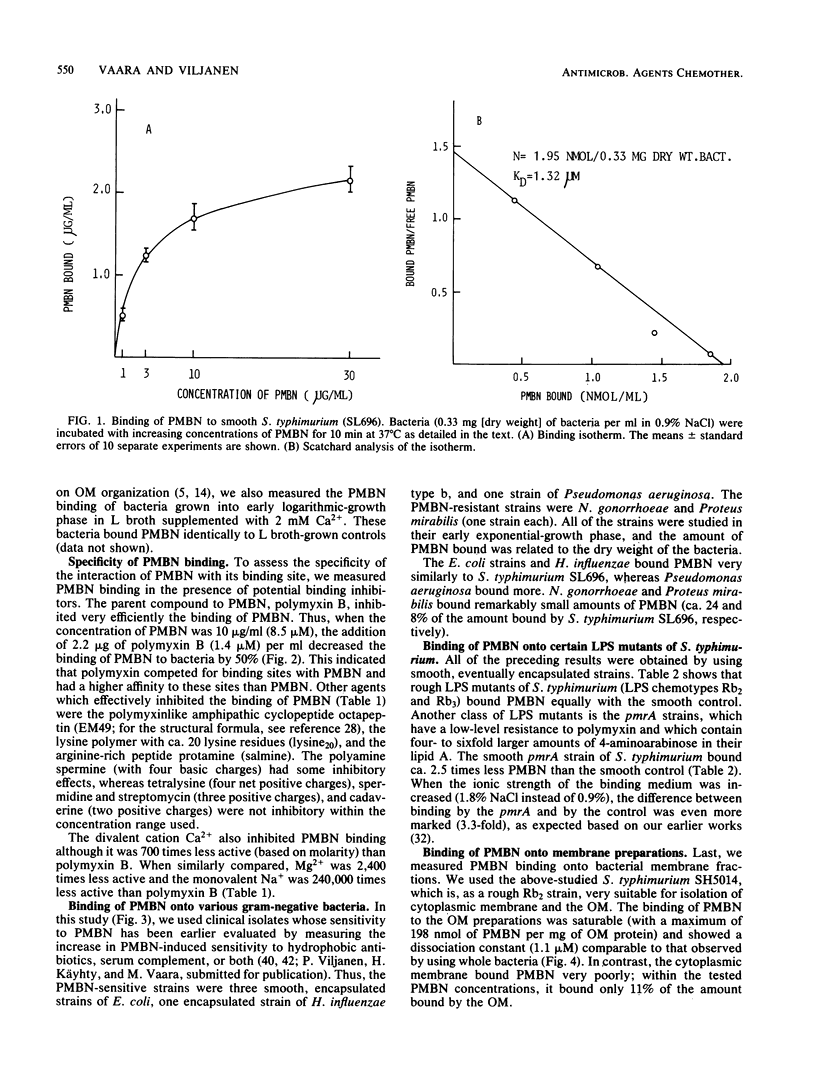
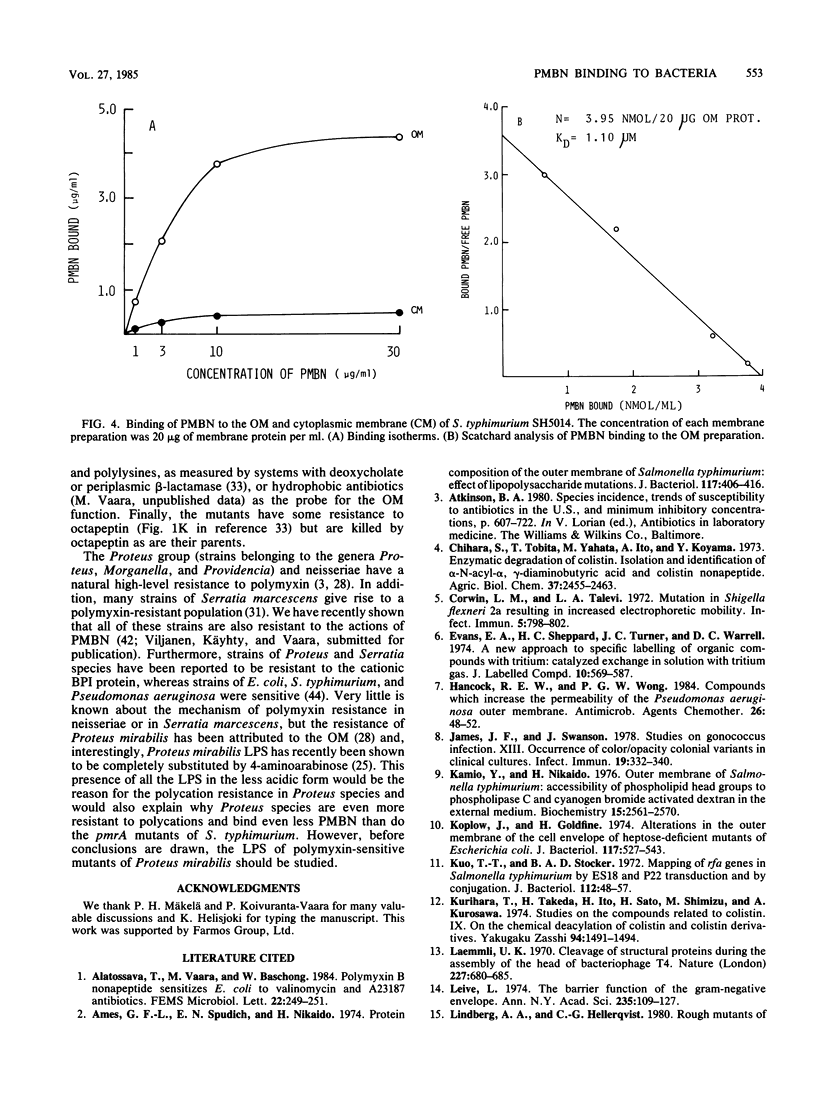
The binding of the outer membrane-disorganizing peptide polymyxin B nonapeptide (PMBN) to gram-negative bacteria was studied by using tritium-labeled PMBN. Smooth Salmonella typhimurium had a binding capacity of ca. 6 nmol of PMBN per mg (dry weight) of bacteria, which corresponds to ca. 1 X 10(6) to 2 X 10(6) molecules of PMBN per single cell. The binding was of relatively high affinity (Kd, 1.3 microM). The isolated outer membrane of S. typhimurium bound ca. 100 nmol of PMBN per mg of outer membrane protein (Kd, 1.1 microM), whereas the cytoplasmic membrane bound 9 to 10 times less. Other bacteria which are susceptible to the action of PMBN (Escherichia coli strains, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae) also bound large amounts of PMBN. The S. typhimurium pmrA mutant, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Proteus mirabilis (all known as resistant to polymyxin and PMBN) bound 3.3, 4, and 12 times less than S. typhimurium, respectively. The binding of PMBN to S. typhimurium was effectively inhibited by low concentrations of polymyxin B, compound EM49 (octapeptin), polylysine, and protamine. Spermine, Ca2+, and Mg2+ also inhibited the PMBN binding although they were ca. 160, 700, and 2,400 times less active (based on molarity) than polymyxin B, respectively. No binding inhibition was found at the tested concentrations of streptomycin, tetralysine, spermidine, or cadaverine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Spudich E. N., Nikaido H. Protein composition of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):406–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.406-416.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corwin L. M., Talevi L. A. Mutation in Shigella flexneri 2a resulting in increased electrophoretic mobility. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):798–802. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.798-802.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Wong P. G. Compounds which increase the permeability of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. F., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIII. Occurrence of color/opacity colonial variants in clinical cultures. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):332–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.332-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: accessibility of phospholipid head groups to phospholipase c and cyanogen bromide activated dextran in the external medium. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 15;15(12):2561–2570. doi: 10.1021/bi00657a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koplow J., Goldfine H. Alterations in the outer membrane of the cell envelope of heptose-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):527–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.527-543.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo T. T., Stocker B. A. Mapping of rfa Genes in Salmonella typhimurium by ES18 and P22 Transduction and by Conjugation. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):48–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.48-57.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara T., Takeda H., Ito H., Sato H., Shimizu M. [Studies on the compounds related to colistin. IX. On the chemical deacylation of colistin and colistin derivatives (author's transl)]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1974 Nov;94(11):1491–1494. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.94.11_1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K. Structure-activity relationship of colistins. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1967 Aug;15(8):1219–1224. doi: 10.1248/cpb.15.1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler M., Osborn M. J. Interaction of divalent cations and polymyxin B with lipopolysaccharide. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4425–4430. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Casey S. G., Spitznagel J. K. Lipid A and resistance of Salmonella typhimurium to antimicrobial granule proteins of human neutrophil granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):834–838. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.834-838.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Martin L. E., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic antimicrobial proteins isolated from human neutrophil granulocytes in the presence of diisopropyl fluorophosphate. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):29–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.29-35.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidorczyk Z., Zähringer U., Rietschel E. T. Chemical structure of the lipid A component of the lipopolysaccharide from a Proteus mirabilis Re-mutant. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 1;137(1-2):15–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm D. R., Rosenthal K. S., Swanson P. E. Polymyxin and related peptide antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:723–763. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M., Bader J. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes. Binding capacities for polymyxin B of inner and outer membranes isolated from Salmonella typhimurium G30. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Aug;109(1-2):51–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00425112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Polymyxin B-induced cocarde growth phenomenon of Serratia marcescens due to cationic detergent-like activity of polymyxin B. Chemotherapy. 1982;28(5):363–368. doi: 10.1159/000238124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M. Increased outer membrane resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate and cations in novel lipid A mutants. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):426–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.426-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Jensen M., Helander I., Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from the polymyxin-resistant pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations as outer membrane-disorganizing agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations sensitize enteric bacteria to antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Sarvas M. Decreased binding of polymyxin by polymyxin-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):664–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.664-667.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Sensitization of Gram-negative bacteria to antibiotics and complement by a nontoxic oligopeptide. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):526–528. doi: 10.1038/303526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Viljanen P., Vaara T., Mäkelä P. H. An outer membrane-disorganizing peptide PMBN sensitizes E. coli strains to serum bactericidal action. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2582–2589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljanen P., Vaara M. Susceptibility of gram-negative bacteria to polymyxin B nonapeptide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):701–705. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Elsbach P. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to purified bactericidal leukocyte proteins: relation to binding and bacterial lipopolysaccharide structure. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):619–628. doi: 10.1172/JCI109707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Victor M., Stendhal O., Elsbach P. Killing of gram-negative bacteria by polymorphonuclear leukocytes: role of an O2-independent bactericidal system. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):959–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI110535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


