Abstract
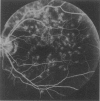
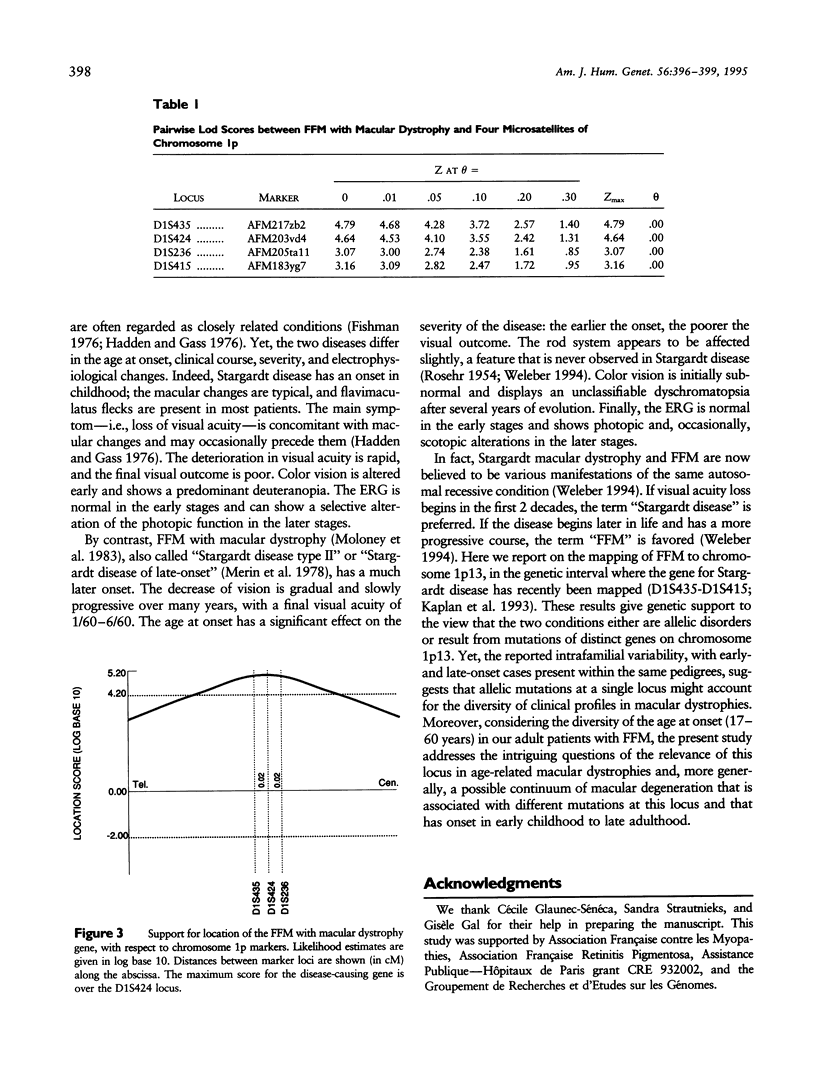
Fundus flavimaculatus with macular dystrophy is an autosomal recessive disease responsible for a progressive loss of visual acuity in adulthood, with pigmentary changes of the macula, perimacular flecks, and atrophy of the retinal pigmentary epithelium. Since this condition shares several clinical features with Stargardt disease, which has been mapped to chromosome 1p21-p13, we tested the disease for linkage to chromosome 1p. We report here the mapping of the disease locus to chromosome 1p13-p21, in the genetic interval defined by loci D1S435 and D1S415, in four multiplex families (maximum lod score 4.79 at recombination fraction 0 for probe AFM217zb2 at locus D1S435). Thus, despite differences in the age at onset, clinical course, and severity, fundus flavimaculatus with macular dystrophy and Stargardt disease are probably allelic disorders. This result supports the view that allelic mutations produce a continuum of macular dystrophies, with onset in early childhood to late adulthood.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fishman G. A. Fundus flavimaculatus. A clinical classification. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976 Dec;94(12):2061–2067. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1976.03910040721003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschetti A., François J. Fundus flavimaculatus. Arch Ophtalmol Rev Gen Ophtalmol. 1965 Sep;25(6):505–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden O. B., Gass J. D. Fundus flavimaculatus and Stargardt's disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976 Oct;82(4):527–539. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(76)90539-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Gerber S., Larget-Piet D., Rozet J. M., Dollfus H., Dufier J. L., Odent S., Postel-Vinay A., Janin N., Briard M. L. A gene for Stargardt's disease (fundus flavimaculatus) maps to the short arm of chromosome 1. Nat Genet. 1993 Nov;5(3):308–311. doi: 10.1038/ng1193-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar-Singh R., Jordan S. A., Farrar G. J., Humphries P. Poly (T/A) polymorphism at the human retinal degeneration slow (RDS) locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5800–5800. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moloney J. B., Mooney D. J., O'Connor M. A. Retinal function in Stargardt's disease and fundus flavimaculatus. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 Jul;96(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(83)90455-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone E. M., Nichols B. E., Kimura A. E., Weingeist T. A., Drack A., Sheffield V. C. Clinical features of a Stargardt-like dominant progressive macular dystrophy with genetic linkage to chromosome 6q. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994 Jun;112(6):765–772. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1994.01090180063036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weleber R. G. Stargardt's macular dystrophy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994 Jun;112(6):752–754. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1994.01090180050033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., Bither P. P., Park R., Donoso L. A., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. A dominant Stargardt's macular dystrophy locus maps to chromosome 13q34. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994 Jun;112(6):759–764. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1994.01090180057035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]