Abstract
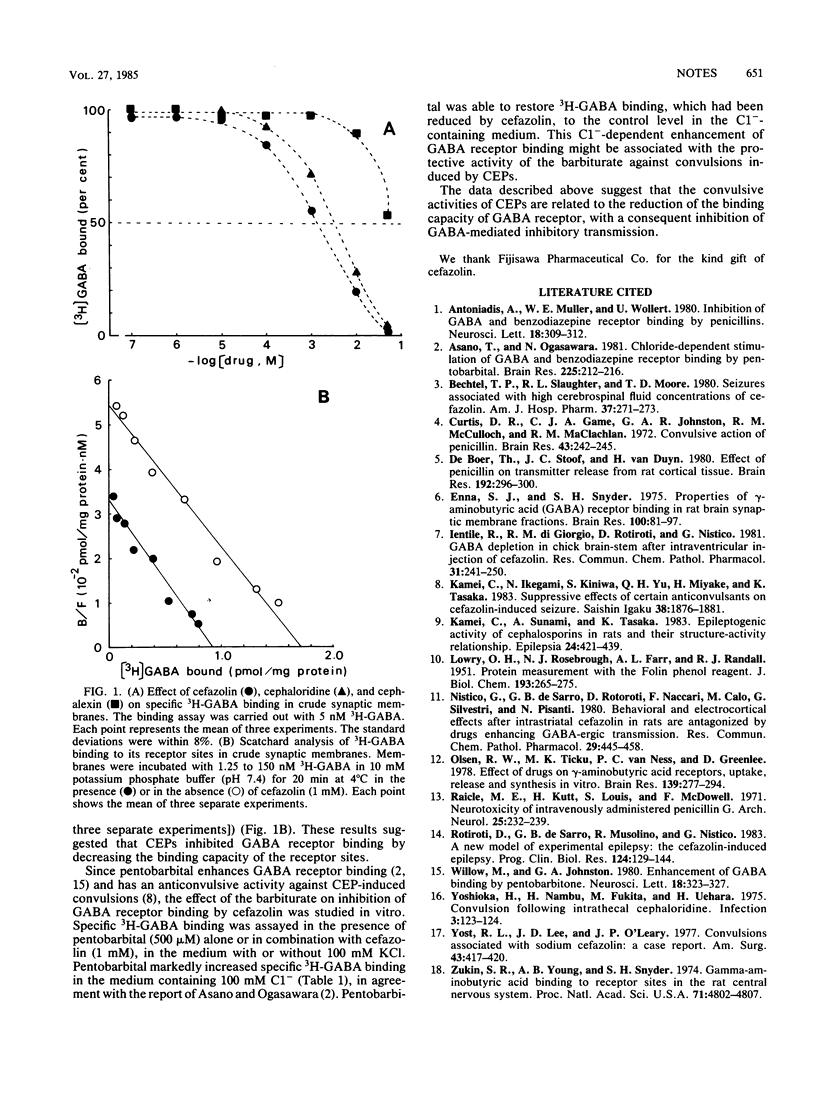
Cephalosporins inhibited gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor binding in a concentration-dependent manner in vitro. Scatchard analysis revealed that cefazolin decreased the binding capacity but did not change the affinity of the receptor. It is suggested that this inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor binding may be involved in the induction of convulsions by cephalosporins.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniadis A., Müller W. E., Wollert U. Inhibition of GABA and benzodiazepine receptor binding by penicillins. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Jul;18(3):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90302-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Ogasawara N. Chloride-dependent stimulation of GABA and benzodiazepine receptor binding by pentobarbital. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 23;225(1):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90333-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel T. P., Slaughter R. L., Moore T. D. Seizures associated with high cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of cefazolin. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1980 Feb;37(2):271–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Game C. J., Johnston G. A., McCulloch R. M., MacLachlan R. M. Convulsive action of penicillin. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 11;43(1):242–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding in rat brain synaptic membrane fractions. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 12;100(1):81–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ientile R., Di Giorgio R. M., Rotiroti D., Nistico' G. GABA depletion in chick brain-stem after intraventricular injection of cefazolin. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;31(2):241–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamei C., Sunami A., Tasaka K. Epileptogenic activity of cephalosporins in rats and their structure-activity relationship. Epilepsia. 1983 Aug;24(4):431–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1983.tb04913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistico G., De Sarro G. B., Rotiroti D., Naccari F., Calo M., Silvestri R., Pisanti N. Behavioral and electrocortical effects after intrastriatal cefazolin in rats are antagonized by drugs enhancing GABA-ergic transmission. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;29(3):445–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Ticku M. K., Van Ness P. C., Greenlee D. Effects of drugs on gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors, uptake, release and synthesis in vitro. Brain Res. 1978 Jan 13;139(2):277–294. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90929-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichle M. E., Kutt H., Louis S., McDowell F. Neurotoxicity of intravenously administered penicillin G. Arch Neurol. 1971 Sep;25(3):232–239. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00490030058006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotiroti D., de Sarro G. B., Musolino R., Nisticò G. A new model of experimental epilepsy: the cefazolin-induced epilepsy. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;124:129–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willow M., Johnston G. A. Enhancement of GABA binding by pentobarbitone. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Jul;18(3):323–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka H., Nambu H., Fujita M., Uehara H. Convulsion following intrathecal cephaloridine. Infection. 1975;3(2):123–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01641056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost R. L., Lee J. D., O'Leary J. P. Convulsions associated with sodium cefazolin: a case report. Am Surg. 1977 Jun;43(6):417–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer T., Stoof J. C., van Duyn H. Effect of penicillin on transmitter release from rat cortical tissue. Brain Res. 1980 Jun 16;192(1):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


