Abstract
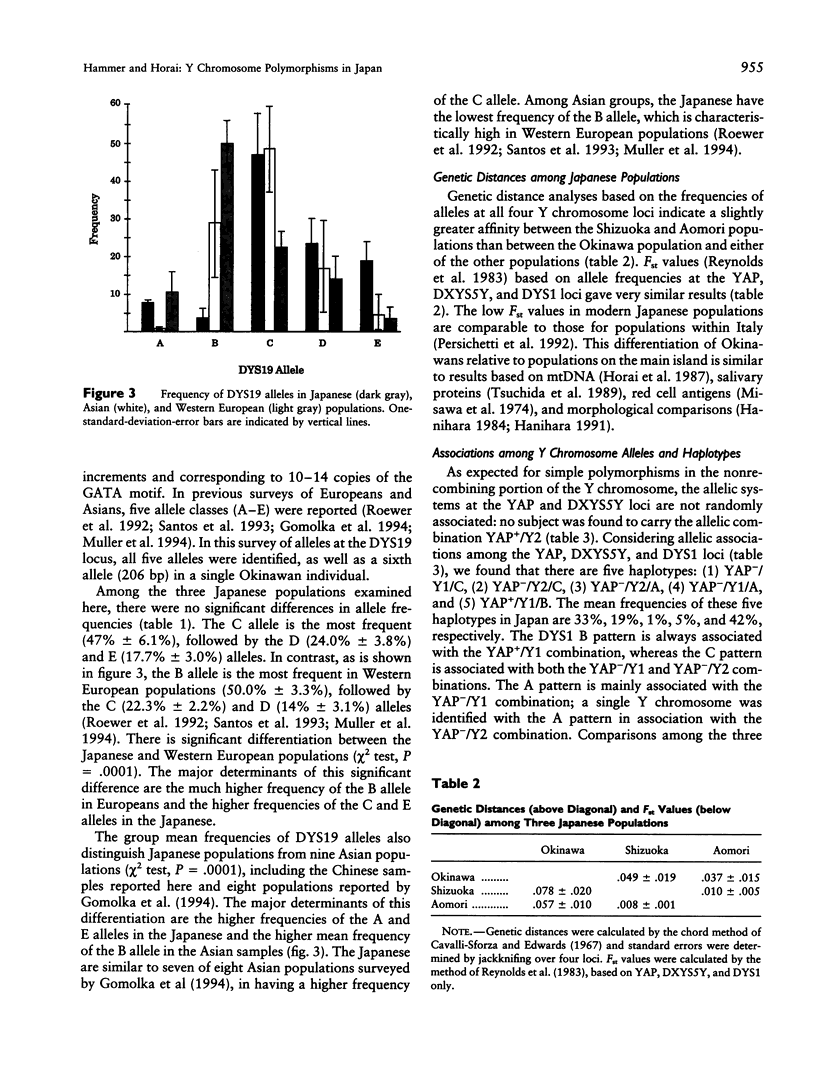
Four loci mapping to the nonrecombining portion of the Y chromosome were genotyped in Japanese populations from Okinawa, the southernmost island of Japan; Shizuoka and Aomori on the main island of Honshu; and a small sample of Taiwanese. The Y Alu polymorphic (YAP) element is present in 42% of the Japanese and absent in the Taiwanese, confirming the irregular distribution of this polymorphism in Asia. Data from the four loci were used to determine genetic distances among populations, construct Y chromosome haplotypes, and estimate the degree of genetic diversity in each population and on different Y chromosome haplotypes. Evolutionary analysis of Y haplotypes suggests that polymorphisms at the YAP (DYS287) and DXYS5Y loci originated a single time, whereas restriction patterns at the DYS1 locus and microsatellite alleles at the DYS19 locus arose more than once. Genetic distance analysis indicated that the Okinawans are differentiated from Japanese living on Honshu. The data support the hypotheses that modern Japanese populations have resulted from distinctive genetic contributions involving the ancient Jomon people and Yayoi immigrants from Korea or mainland China, with Okinawans experiencing the least amount of admixture with the Yayoi. It is suggested that YAP+ chromosomes migrated to Japan with the Jomon people > 10,000 years ago and that a large infusion of YAP- chromosomes entered Japan with the Yayoi migration starting 2,300 years ago. Different degrees of genetic diversity carried by these two ancient chromosomal lineages may be explained by the different life-styles (hunter-gatherer versus agriculturalist). of the migrant groups, the size of the founding populations, and the antiquities of the founding events.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop C. E., Guellaen G., Geldwerth D., Voss R., Fellous M., Weissenbach J. Single-copy DNA sequences specific for the human Y chromosome. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):831–832. doi: 10.1038/303831a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Kidd J. R., Mountain J. L., Hebert J. M., Carotenuto L., Kidd K. K., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Drift, admixture, and selection in human evolution: a study with DNA polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):839–843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann R. L., Stoneking M., Wilson A. C. Mitochondrial DNA and human evolution. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):31–36. doi: 10.1038/325031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Edwards A. W. Phylogenetic analysis. Models and estimation procedures. Am J Hum Genet. 1967 May;19(3 Pt 1):233–257. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomolka M., Hundrieser J., Nürnberg P., Roewer L., Epplen J. T., Epplen C. Selected di- and tetranucleotide microsatellites from chromosomes 7, 12, 14, and Y in various Eurasian populations. Hum Genet. 1994 May;93(5):592–596. doi: 10.1007/BF00202830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer M. F. A recent insertion of an alu element on the Y chromosome is a useful marker for human population studies. Mol Biol Evol. 1994 Sep;11(5):749–761. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer M. F., Silver L. M. Phylogenetic analysis of the alpha-globin pseudogene-4 (Hba-ps4) locus in the house mouse species complex reveals a stepwise evolution of t haplotypes. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Sep;10(5):971–1001. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanihara K. Origins and affinities of Japanese viewed from cranial measurements. Acta Anthropogenet. 1984;8(1-2):149–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harihara S., Hirai M., Suutou Y., Shimizu K., Omoto K. Frequency of a 9-bp deletion in the mitochondrial DNA among Asian populations. Hum Biol. 1992 Apr;64(2):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai S., Kondo R., Murayama K., Hayashi S., Koike H., Nakai N. Phylogenetic affiliation of ancient and contemporary humans inferred from mitochondrial DNA. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1991 Sep 30;333(1268):409–417. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1991.0091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai S., Matsunaga E. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in Japanese. II. Analysis with restriction enzymes of four or five base pair recognition. Hum Genet. 1986 Feb;72(2):105–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00283927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubiczka S., Arnemann J., Cooke H. J., Krawczak M., Schmidtke J. A search for restriction fragment length polymorphism on the human Y chromosome. Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;84(1):86–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00210680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H. Distribution of nucleotide differences between two randomly chosen cistrons in a finite population. Genetics. 1977 Feb;85(2):331–337. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. J., Tanaka K., Leonard W., Gerelsaikhan T., Dashnyam B., Nyamkhishig S., Hida A., Nakahori Y., Omoto K., Crawford M. H. A Y-associated allele is shared among a few ethnic groups of Asia. Jpn J Hum Genet. 1994 Sep;39(3):299–304. doi: 10.1007/BF01874048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucotte G., Sriniva K. R., Loirat F., Hazout S., Ruffié J. The p49/TaqI Y-specific polymorphisms in three groups of Indians. Gene Geogr. 1990 Apr;4(1):21–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaspina P., Persichetti F., Novelletto A., Iodice C., Terrenato L., Wolfe J., Ferraro M., Prantera G. The human Y chromosome shows a low level of DNA polymorphism. Ann Hum Genet. 1990 Oct;54(Pt 4):297–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1990.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias N., Bayés M., Tyler-Smith C. Highly informative compound haplotypes for the human Y chromosome. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):115–123. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountain J. L., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Inference of human evolution through cladistic analysis of nuclear DNA restriction polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6515–6519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller S., Gomolka M., Walter H. The Y-specific SSLP of the locus DYS19 in four different European samples. Hum Hered. 1994 Sep-Oct;44(5):298–300. doi: 10.1159/000154233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagome Y., Young S. R., Akane A., Numabe H., Jin D. K., Yamori Y., Seki S., Tamura T., Nagafuchi S., Shiono H. A Y-associated allele may be characteristic of certain ethnic groups in Asia. Ann Hum Genet. 1992 Oct;56(Pt 4):311–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1992.tb01158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahori Y., Tamura T., Yamada M., Nakagome Y. Two 47z [DXYS5] RFLPs on the X and the Y chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2152–2152. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanaga M., Yasuda T., Tenjo E., Nadano D., Fujiki N., Kishi K. Transferrin polymorphisms in Japanese populations: north-south cline in the distribution of the TF*C2 allele. Hum Biol. 1991 Apr;63(2):186–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics. 1978 Jul;89(3):583–590. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Roychoudhury A. K. Evolutionary relationships of human populations on a global scale. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Sep;10(5):927–943. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngo K. Y., Vergnaud G., Johnsson C., Lucotte G., Weissenbach J. A DNA probe detecting multiple haplotypes of the human Y chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Apr;38(4):407–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persichetti F., Blasi P., Hammer M., Malaspina P., Jodice C., Terrenato L., Novelletto A. Disequilibrium of multiple DNA markers on the human Y chromosome. Ann Hum Genet. 1992 Oct;56(Pt 4):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1992.tb01157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed T. E. Caucasian genes in American Negroes. Science. 1969 Aug 22;165(3895):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3895.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J., Weir B. S., Cockerham C. C. Estimation of the coancestry coefficient: basis for a short-term genetic distance. Genetics. 1983 Nov;105(3):767–779. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards B., Skoletsky J., Shuber A. P., Balfour R., Stern R. C., Dorkin H. L., Parad R. B., Witt D., Klinger K. W. Multiplex PCR amplification from the CFTR gene using DNA prepared from buccal brushes/swabs. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):159–163. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roewer L., Arnemann J., Spurr N. K., Grzeschik K. H., Epplen J. T. Simple repeat sequences on the human Y chromosome are equally polymorphic as their autosomal counterparts. Hum Genet. 1992 Jun;89(4):389–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00194309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. R., Jorde L. B. Genetic evidence on modern human origins. Hum Biol. 1995 Feb;67(1):1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos F. R., Pena S. D., Epplen J. T. Genetic and population study of a Y-linked tetranucleotide repeat DNA polymorphism with a simple non-isotopic technique. Hum Genet. 1993 Feb;90(6):655–656. doi: 10.1007/BF00202486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurdle A. B., Woodfield D. G., Hammer M. F., Jenkins T. The genetic affinity of Polynesians: evidence from Y chromosome polymorphisms. Ann Hum Genet. 1994 Jul;58(Pt 3):251–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1994.tb01889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurdle A., Jenkins T. Y chromosome probe p49a detects complex PvuII haplotypes and many new TaqI haplotypes in southern African populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;50(1):107–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torroni A., Semino O., Scozzari R., Sirugo G., Spedini G., Abbas N., Fellous M., Santachiara Benerecetti A. S. Y chromosome DNA polymorphisms in human populations: differences between Caucasoids and Africans detected by 49a and 49f probes. Ann Hum Genet. 1990 Oct;54(Pt 4):287–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1990.tb00384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida S., Ikemoto S. Further studies of salivary polymorphisms in the Japanese population. Hum Hered. 1989;39(2):61–66. doi: 10.1159/000153836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuner C. G., 2nd Dental evidence on the origins of the Ainu and Japanese. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):911–913. doi: 10.1126/science.781841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainscoat J. S., Hill A. V., Boyce A. L., Flint J., Hernandez M., Thein S. L., Old J. M., Lynch J. R., Falusi A. G., Weatherall D. J. Evolutionary relationships of human populations from an analysis of nuclear DNA polymorphisms. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):491–493. doi: 10.1038/319491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]